 W
WThe Italian Social Republic, popularly and historically known as the Republic of Salò, was a German puppet state with limited recognition that was created during the later part of World War II, existing from the beginning of German occupation of Italy in September 1943 until the surrender of German troops in Italy in May 1945.
 W
WThe participation of Italy in the Second World War was characterized by a complex framework of ideology, politics, and diplomacy, while its military actions were often heavily influenced by external factors. Italy joined the war as one of the Axis Powers in 1940, as the French Third Republic surrendered, with a plan to concentrate Italian forces on a major offensive against the British Empire in Africa and the Middle East, known as the "parallel war", while expecting the collapse of British forces in the European theatre. The Italians bombed Mandatory Palestine, invaded Egypt and occupied British Somaliland with initial success. However, German and Japanese actions in 1941 led to the entry of the Soviet Union and United States, respectively, into the war, thus ruining the Italian plan of forcing Britain to agree to a negotiated peace settlement.
 W
WThe Republic of Alba was a short-lived state that existed from 10 October to 2 November 1944 in Alba, northern Italy, as a local resistance against Italian fascism during World War II, and which was part of the so-called Italian Partisan Republics, the first of which was the Republic of Corniolo. It was named after the Napoleonic Republic of Alba that existed in 1796 in Piedmont.
 W
WThe Battle of Ancona was a battle involving forces from Poland serving as part of the British Army and German forces that took place from 16 June–18 July 1944 during the Italian campaign in World War II. The battle was the result of an Allied plan to capture the city of Ancona in Italy in order to gain possession of a seaport closer to the fighting so that they could shorten their lines of communication. The Polish 2nd Corps was tasked with capture of the city on 16 June 1944, accomplishing the task a month later on 18 July 1944.
 W
WThe Ardeatine massacre, or Fosse Ardeatine massacre, was a mass killing of 335 civilians and political prisoners carried out in Rome on 24 March 1944 by German occupation troops during the Second World War as a reprisal for the Via Rasella attack in central Rome against the SS Police Regiment Bozen the previous day.
 W
WThe Balvano train disaster was the deadliest railway accident in Italian history and one of the worst railway disasters ever. It occurred on the night between 2-3 March 1944 in Balvano, Basilicata. Over 500 people in a steam-hauled, coal-burning freight train died of carbon monoxide poisoning during a protracted stall in a tunnel.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that took place from January 22, 1944 to June 5, 1944. The operation was opposed by German forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno.
 W
WThe Battle of Gemmano took place during World War II, between the dates of September 4th, and September 15th of 1944. The battle occurred in the area of the Gothic Line, near the Apennine Mountains in northern Italy, which would soon turn out to be the last line of defense for the Axis Powers in Italy. The village of Gemmano was eventually captured on September 9th, 1944 by the invading Eighth Army, but two more subsequent attacks were needed to secure the area surrounding the village of Gemmano. Fighting was so fierce, similar to that of the famous battle of Monte Cassino, that the battle was sometimes referred to as, “ The Cassino of the Adriatic”.
 W
WThe Bernhardt Line was a German defensive line in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. Having reached the Bernhardt Line at the start of December 1943, it took until mid-January 1944 for the U.S. Fifth Army to fight their way to the next line of defences, the Gustav Line. The line was defended by XIV Panzer Corps, part of the German Tenth Army.
 W
WBolzano was a transit camp operated by Nazi Germany in Bolzano from 1944 to 3 May 1945 during World War II. It was one of the largest Nazi Lager on Italian soil, along with those of Fossoli, Borgo San Dalmazzo and Trieste.
 W
WDuring World War II the Italian city of Bologna, the regional capital and largest city of Emilia-Romagna, suffered nearly a hundred air raids by the Royal Air Force and the USAAF, mostly aimed at disabling its strategically important marshalling yards, used for the movements of German troops and supplies between Northeastern Italy and central Italy. These raids destroyed or damaged almost half of the city, and caused nearly 2,500 victims among its population.
 W
WThe bombing of Ferrara was a series of attacks by the United States Army Air Force and the Royal Air Force on the Italian city of Ferrara, Emilia-Romagna, during the final two years of World War II. The purpose of these raids was to disable the city's marshalling yard, but they also resulted in considerable collateral damage to the city itself, and over a thousand deaths among the population.
 W
WOwing to the importance of its port and industries, the Italian port city of Genoa, the regional capital and largest city of Liguria, was heavily bombarded by both Allied air and naval forces during Second World War, suffering heavy damage.
 W
WDuring World War II, Tuscany, the Italian port city of Livorno was repeatedly bombed by the Allied air forces, suffering about a hundred raids altogether, which resulted in it being among the most war-damaged cities in Italy.
 W
WThe bombing of Padua was a series of attacks by the United States Army Air Force and the Royal Air Force on the Italian city of Padua, Veneto, during World War II. These raids were aimed at disabling Padua's marshalling yard, but also resulted in heavy damage to the city and civilian casualties.
 W
WThe bombing of Rome in World War II took place on several occasions in 1943 and 1944, primarily by Allied and to a smaller degree by Axis aircraft, before the city was invaded by the Allies on June 4, 1944. Pope Pius XII was initially unsuccessful in attempting to have Rome declared an open city, through negotiations with President Roosevelt via Archbishop Francis Spellman. Rome was eventually declared an open city on August 14, 1943 by the defending forces.
 W
WOwing to its importance as an industrial center, home to Fiat and several other industries engaged in war production, Turin, the regional capital of Piedmont, suffered over a hundred raids by the Allied air forces during World War II; the Piedmontese capital was thus among the most bombed cities in Northern Italy, suffering damage to about 40% of its housing stock, and over 2,000 victims among its population.
 W
WThe bombing of Vicenza was a series of attacks by the United States Army Air Force and the Royal Air Force on the Italian city of Vicenza, Veneto, during World War II. The purpose of these raids was to disable the city's marshalling yard and airport, but the bombing also caused considerable collateral damage to the city itself.
 W
WThe Capistrello massacre was a mass killing carried out in Capistrello, a small town in Abruzzo, Italy, on 4 June 1944 by Nazist and Fascist occupation troops during World War II. A first tragical episode occurred a few months earlier on 20 March, when a local youth was barbarically tortured and then shot. The following roundup made by Nazists and Fascists on the slopes of Mount Salviano led to the capture and torture of 33 shepherds and breeders. The shooting occurred near Capistrello railway station.
 W
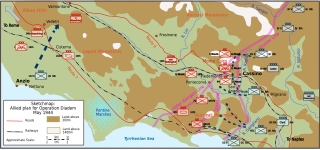
WOperation Diadem, also referred to as the Fourth Battle of Monte Cassino or, in Canada, the Battle of the Liri Valley, was an offensive operation undertaken by the Allies of World War II in May 1944, as part of the Italian Campaign of World War II. Diadem was supported by air attacks called Operation Strangle. The opposing force was the German 10th Army.
 W
WThe Battle of Garfagnana, known to the Germans as Operation Winter Storm and nicknamed the "Christmas Offensive", was a successful Axis offensive against American forces on the western sector of the Gothic Line during World War II. It took place in December 1944 in the north Tuscan Apennines, near Massa and Lucca.
 W
WOperation Hasty was a mission behind German lines in Italy, during the Second World War. The operation was carried out in June 1944, by a small force of 60 men drawn from the 2nd Independent Parachute Brigade.
 W
WThe Marzabotto massacre, or more correctly, the massacre of Monte Sole, was a World War II war crime consisting of the mass murder of at least 770 civilians by Nazi troops, which took place in the territory around the small village of Marzabotto, in the mountainous area south of Bologna. It was the largest massacre of civilians committed by the Waffen SS in Western Europe during the war. It is also the deadliest mass shooting in the history of Italy.
 W
WThe Battle of Monte Castello was an engagement that took place from 25 November 1944 to 21 February 1945 during the Italian campaign of World War II. It was fought between the Allied forces advancing into northern Italy and the dug-in German defenders. The battle marked the Brazilian Expeditionary Force's entry into the land war in Europe. Starting in November 1944, fierce combat dragged on for three months, ending on 21 February 1945. Six Allied attacks were mounted against the German forces, four of which were tactical failures.
 W
WThe National Liberation Committee was a political umbrella organization and the main representative of the Italian resistance movement fighting against the German occupation of Italy in the aftermath of the armistice of Cassibile. It was a multi-party entity, whose members were united by their anti-fascism. The CLN coordinated and directed the Italian resistance and was subdivided into the Central Committee for National Liberation (CCLN) based in Rome and the later National Liberation Committee for Northern Italy (CLNAI) based in Milan.
 W
WThe Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills was a Nazi German occupation zone in the sub-Alpine area in Italy during World War II.
 W
WOperation Partridge was a British Commando raid during the Second World War. It was carried out during the Italian Campaign by No. 9 Commando as a diversionary raid behind the German lines, to cover the withdrawal of the X Corps in preparation for its proposed assault across the Garigliano river.
 W
WThe Piazza Tasso massacre was a massacre that occurred on July 17, 1944, at Piazza Tasso in Florence, Tuscany, Italy.
 W
WThe Battle of Rapido River was fought from 20 to 22 January 1944 during one of the Allies' many attempts to breach the Winter Line in the Italian Campaign during World War II. Despite its name, the battle occurred on the Gari River.
 W
WThe Sant'Anna di Stazzema massacre was a Nazi German war crime committed in the hill village of Sant'Anna di Stazzema in Tuscany, Italy, in the course of an operation against the Italian resistance movement during the Italian Campaign of World War II. On 12 August 1944 the Waffen-SS, with the help of the Brigate Nere, murdered about 560 local villagers and refugees, including more than a hundred children, and burned their bodies. These crimes have been defined as voluntary and organized acts of terrorism by the Military Tribunal of La Spezia and the highest Italian court of appeal.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that took place from January 22, 1944 to June 5, 1944. The operation was opposed by German forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno.
 W
WThe Verona Trial was a show trial held in January 1944 in the Italian Social Republic (ISR) to punish—by five almost-immediately executed death sentences and one 30-year imprisonment—the members of the Grand Council of Fascism who had committed the offence of voting for Benito Mussolini's removal from power in the Kingdom of Italy and had later been arrested by Mussolini's forces.
 W
WThe Via Rasella attack was an action taken by the Italian resistance movement against the Nazi German occupation forces in Rome, Italy on 23 March 1944.
 W
WThe bombing of Treviso, a town in Northeastern Italy, took place on 7 April 1944, during World War II. Aimed at disabling the town's marshalling yard, it resulted in the destruction of most of the town.
 W
WThe Western Front was a military theatre of World War II encompassing Denmark, Norway, Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Germany. World War II military engagements in Southern Europe and elsewhere are generally considered as separate theatres. The Western Front was marked by two phases of large-scale combat operations. The first phase saw the capitulation of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France during May and June 1940 after their defeat in the Low Countries and the northern half of France, and continued into an air war between Germany and Britain that climaxed with the Battle of Britain. The second phase consisted of large-scale ground combat, which began in June 1944 with the Allied landings in Normandy and continued until the defeat of Germany in May 1945.
 W
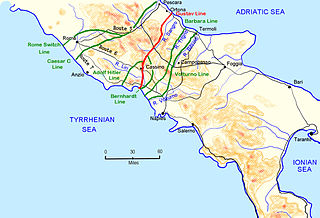
WThe Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section of Italy, focused around the town of Monte Cassino, through which ran the important Highway 6 which led uninterrupted to Rome. The primary Gustav Line ran across Italy from just north of where the Garigliano River flows into the Tyrrhenian Sea in the west, through the Apennine Mountains to the mouth of the Sangro River on the Adriatic coast in the east. The two subsidiary lines, the Bernhardt Line and the Hitler Line ran much shorter distances from the Tyrrehnian sea to just North East of Cassino where they would merge into the Gustav Line. Relative to the Gustav Line, the Hitler Line stood to the North-West and the Bernhardt Line to the South-East of the primary defenses.