 W
WWilliam III, also widely known as William of Orange, was sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s and King of England, Ireland and Scotland from 1689 until his death. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is commemorated by unionists, who display orange colours in his honour. Popular histories usually refer to his joint reign with his wife, Queen Mary II, as that of William and Mary.
 W
WThe Absence of King William Act 1689 was an Act of the Parliament of England which stated that Queen Mary II was to govern England whenever her husband, King William III, was absent from England.
 W
WThe Act of Seclusion was an Act of the States of Holland, required by a secret annex in the Treaty of Westminster (1654) between the United Provinces and the Commonwealth of England in which William III, Prince of Orange, was excluded from the office of Stadtholder. The First Stadtholderless Period had been heralded in January 1651 by States Party Regenten, among whom the republican-minded brothers Cornelis and Andries de Graeff and their cousins Andries and Cornelis Bicker, during the Grote Vergadering in The Hague, a meeting of representatives of the States of each of the United Provinces. This meeting was convened after the death of stadtholder William II on November 6, 1650, when the States of Holland decided to leave the office of Stadtholder vacant in their province.
 W
WThe Bill of Rights 1689, also known as the Bill of Rights 1688, is a landmark Act in the constitutional law of England that sets out certain basic civil rights and clarifies who would be next to inherit the Crown. It received the Royal Assent on 16 December 1689 and is a restatement in statutory form of the Declaration of Right presented by the Convention Parliament to William III and Mary II in February 1689, inviting them to become joint sovereigns of England. The Bill of Rights lays down limits on the powers of the monarch and sets out the rights of Parliament, including the requirement for regular parliaments, free elections, and freedom of speech in Parliament. It sets out certain rights of individuals including the prohibition of cruel and unusual punishment and reestablished the right of Protestants to have arms for their defence within the rule of law. It also includes no right of taxation without Parliament’s agreement. Furthermore, the Bill of Rights described and condemned several misdeeds of James II of England.
 W
WThe Battle of the Boyne was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, versus those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II, had acceded to the Crowns of England and Scotland in 1689. The battle took place across the River Boyne close to the town of Drogheda in the Kingdom of Ireland, modern-day Republic of Ireland, and resulted in a victory for William. This turned the tide in James's failed attempt to regain the British crown and ultimately aided in ensuring the continued Protestant ascendancy in Ireland.
 W
WThe Boyne Obelisk, also known as King William's Obelisk, was an obelisk located in Oldbridge, near Drogheda, County Louth, Ireland.
 W
WThe College of William & Mary is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William III and Queen Mary II, it is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States, after Harvard University.
 W
WThe Flag of the Orange Order, also known as the Boyne Standard or the Orange Standard, is the flag used by the Northern Irish Protestant fraternal organisation, the Orange Order. The flag consists of an orange background with a purple star and a Cross of Saint George in canton.
 W
WThe Glorious Revolution of November 1688, or Revolution of 1688, covers events leading to the deposition of James II and VII, and replacement by his daughter Mary II, and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange. While the Revolution was quick and relatively bloodless, establishing the new regime took much longer and led to significant casualties. The term was first used by John Hampden in late 1689.
 W
WThe Grand Alliance is the anti-French coalition formed on 20 December 1689 between England, the Dutch Republic and the Archduchy of Austria. It was signed by the two leading opponents of France; William III, King of England and Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, and Emperor Leopold, on behalf of the Archduchy of Austria.
 W
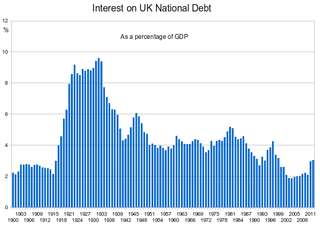
WThe history of the British national debt can be traced back to the reign of William III, who engaged a syndicate of City traders and merchants to offer for sale an issue of government debt, which evolved into the Bank of England. In 1815, at the end of the Napoleonic Wars, British government debt reached a peak of £1 billion.
 W
WKensington Palace is a royal residence set in Kensington Gardens, in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London, England. It has been a residence of the British Royal Family since the 17th century, and is currently the official London residence of the Duke and Duchess of Cambridge, Princess Eugenie and her husband Jack Brooksbank, the Duke and Duchess of Gloucester, the Duke and Duchess of Kent, and Prince and Princess Michael of Kent.
 W
WKing William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.
 W
WMary, Princess Royal, was an English princess, member of the House of Stuart, and by marriage Princess consort of Orange and Countess consort of Nassau; she also acted as Regent for her minor son from 1651 to 1660. She also was the first holder of the title Princess Royal.
 W
WThe Meeting of Parliament Act 1694, also known as the Triennial Act 1694, is an Act of the Parliament of England. This Act is Chapter II Rot. Parl. pt. 1. nu. 2.
 W
WNassau County is located in the U.S. state of New York. At the time of the 2010 census, the county's population was 1,339,532, estimated to have increased to 1,356,924 in 2019. The county seat is Mineola and the largest town is Hempstead.
 W
WNassau Street is a street in the Financial District, within the borough of Manhattan in New York City. Its southern end is at the intersection with Broad Street and Wall Street, and its northern end is at Spruce Street, at Pace University near the foot of the Brooklyn Bridge. For its entire route, Nassau Street runs one block east of Broadway and Park Row.
 W
WThe Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy and Portugal. It was fought in Europe and the surrounding seas, in North America, and in India. It is sometimes considered the first global war. The conflict encompassed the Williamite war in Ireland and Jacobite risings in Scotland, where William III and James II struggled for control of England and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Indigenous allies, today called King William's War by Americans.
 W
WOrange County is a county located in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 372,813. The county seat is Goshen. This county was first created in 1683 and reorganized with its present boundaries in 1798.
 W
WThe Loyal Orange Institution, commonly known as the Orange Order, is an international Protestant fraternal order based in Northern Ireland. It also has lodges in England, Scotland and the Republic of Ireland, as well as throughout the British Commonwealth and the United States. The Orange Order was founded in County Armagh in 1795, during a period of Protestant–Catholic sectarian conflict, as a Masonic-style fraternity sworn to maintain the Protestant Ascendancy. It is headed by the Grand Orange Lodge of Ireland, which was established in 1798. Its name is a tribute to the Dutch-born Protestant king William of Orange, who defeated the army of Catholic king James II in the Williamite–Jacobite War (1688–1691). The order is best known for its yearly marches, the biggest of which is held on or around 12 July.
 W
WElizabeth Hamilton, Countess of Orkney was an English courtier from the Villiers family and the reputed mistress of William III & II, King of England and Scotland, from 1680 until 1695. She was a lady-in-waiting to his wife and co-monarch, Queen Mary II.
 W
WRoyal Succession Bills and Acts are pieces of (proposed) legislation to determine the legal line of succession to the Monarchy of the United Kingdom.
 W
WWilliam II was sovereign Prince of Orange and Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, Overijssel and Groningen in the United Provinces of the Netherlands from 14 March 1647 until his death three years later. His only child, William III, reigned as King of England, Ireland, and Scotland.
 W
WA Williamite was a follower of King William III of England who deposed King James II and VII in the Glorious Revolution. William, the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, replaced James with the support of English Whigs.
 W
WThe Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called the Jacobite War in Ireland or the Williamite–Jacobite War in Ireland.
 W
WWilliamsburg is a city in the U.S. state of Virginia. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, the population was 14,068. In 2019, the population was estimated to be 14,954. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is bordered by James City County and York County.