 W
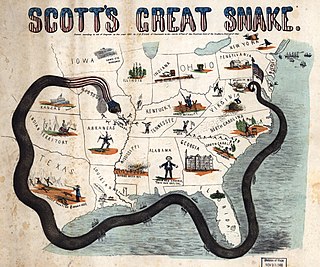
WThe Anaconda Plan is the name applied to a Union Army outline strategy for suppressing the Confederacy at the beginning of the American Civil War. Proposed by Union General-in-Chief Winfield Scott, the plan emphasized a Union blockade of the Southern ports and called for an advance down the Mississippi River to cut the South in two. Because the blockade would be rather passive, it was widely derided by a vociferous faction of Union generals who wanted a more vigorous prosecution of the war and likened it to the coils of an anaconda suffocating its victim. The snake image caught on, giving the proposal its popular name.
 W
WThe American Civil War saw cavalry tactics move largely away from the offensive towards the defensive, with the emphasis on screening, reconnaissance, raiding and harassment. Development of the rifled musket had also rendered the cavalry charge impractical.
 W
WPatrick Ronayne Cleburne was an Irish-born American soldier, best known for his service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War, where he rose to the rank of major general.
 W
WThe court-martial of Fitz John Porter was a major event of the American Civil War. Major General Fitz John Porter was found guilty of disobeying a lawful order, and misconduct in front of the enemy and removed from command based on internal political machinations of the Union Army. The court-martial was later found to be unjust and overturned, and Porter was reinstated in the United States Army.
 W
WRichard Stoddert Ewell was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He achieved fame as a senior commander under Stonewall Jackson and Robert E. Lee and fought effectively through much of the war, but his legacy has been clouded by controversies over his actions at the Battle of Gettysburg and at the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House.
 W
WThe Floating Battery of Charleston Harbor was an ironclad vessel that was constructed by the Confederacy in early 1861, a few months before the American Civil War ignited. Apart from being a marvel to contemporary Charlestonians, it was a strategic naval artillery platform that took part in the bombardment of Fort Sumter on April 12 and April 13, 1861, making it the first floating battery to engage in hostilities during the Civil War.
 W
WForeign enlistment in the American Civil War largely favored the Union, which was far more successful in attracting international volunteers. Nonetheless, thousands of immigrants and mercenaries served with the Confederacy.
 W
WErasmus Corwin Gilbreath was a major in the United States Army who began his 37-year career as a first lieutenant in the 20th Indiana Volunteer Regiment. Gilbreath was involved in numerous battles during the American Civil War, such as Gettysburg and bearing witness to the battle between the CSS Virginia and the USS Monitor, the American Indian Wars, in which he helped establish Fort Custer, and the Spanish–American War. Gilbreath is buried in Arlington National Cemetery with his wife, Susan, and daughter, Etta.
 W
WUlysses S. Grant was the most acclaimed Union general during the American Civil War and was twice elected President. Grant began his military career as a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point in 1839. After graduation he went on to serve with distinction as a lieutenant in the Mexican–American War. Grant was a keen observer of the war and learned battle strategies serving under Generals Zachary Taylor and Winfield Scott. After the war Grant served at various posts especially in the Pacific Northwest; he was forced to retire from the service in 1854 due to accusations of drunkenness. He was unable to make a success of farming and on the onset of the Civil War in April 1861, Grant was working as a clerk in his father's leather goods store in Galena, Illinois. When the war began his military experience was needed, and Congressman Elihu B. Washburne became his patron in political affairs and promotions in Illinois and nationwide.
 W
WDaniel Harvey Hill was a Confederate general during the American Civil War and a Southern scholar. He is usually referred to as D. H. Hill, in part to distinguish him from unrelated Confederate general A. P. Hill, who served with him in the Army of Northern Virginia.
 W
WThomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson served as a Confederate general (1861–1863) during the American Civil War, and became one of the best-known Confederate commanders after General Robert E. Lee. Jackson played a prominent role in nearly all military engagements in the Eastern Theater of the war until his death, and had a key part in winning many significant battles.
 W
WJewish Americans have served in the United States armed forces dating back to before the colonial era, when Jews had served in militias of the Thirteen Colonies. Jewish military personnel have served in all branches of the armed forces and in every major armed conflict to which the United States has been involved. According to the U.S. Department of Defense, as of 2006 there were currently 3,973 known Jewish servicemen and servicewomen on active duty.
 W
WJoseph Eggleston Johnston was an American career army officer, serving with distinction in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848), and Seminole Wars. After Virginia seceded from the Union, he entered the Confederate States Army as one of its most senior general officers.
 W
WRobert Edward Lee was an American Confederate general best known as a commander of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He commanded the Army of Northern Virginia from 1862 until its surrender in 1865 and earned a reputation as a skilled tactician.
 W
WJames Longstreet was one of the foremost Confederate generals of the American Civil War and the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his "Old War Horse". He served under Lee as a corps commander for most of the famous battles fought by the Army of Northern Virginia in the Eastern Theater, and briefly with Braxton Bragg in the Army of Tennessee in the Western Theater.
 W
WDuring the American Civil War, a parole camp was a place where Union or Confederate soldiers on parole could be kept by their own side, in a non-combat role. They could be restored to a combat role if some prisoners of war were traded to the other side. This would enable them to be returned to a combat role as an exchange for the newly freed prisoners of war. Conditions in the camps were unpleasant; the parolees refused to do guard duty or routine work, claiming that would violate their parole. Many escaped to go home.
 W
WJohn Clifford Pemberton, was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He resigned his commission to serve as a Confederate Lieutenant-general during the American Civil War. He led the Army of Mississippi from December 1862 to July 1863 and was the commanding officer during the Confederate surrender at the Siege of Vicksburg.
 W
WWilliam Nelson Pendleton was an American teacher, Episcopal priest, and soldier. He served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, noted for his position as Gen. Robert E. Lee's chief of artillery for most of the conflict. After the war, Pendleton returned to his priestly duties and also wrote religious materials. Camp Pendleton in Virginia Beach, Virginia, is named in his honor.
 W
WLeonidas Polk was a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Church of the United States of America. He was a slaveholding planter in Maury County, Tennessee, and a second cousin of President James K. Polk. He resigned his ecclesiastical position to become a major general in the Confederate army, when he was called "Sewanee's Fighting Bishop". His official portrait at the University of the South depicts him dressed as a bishop with his army uniform hanging nearby.
 W
WThe Rock City Guards were a militia battalion raised in Nashville, Tennessee in 1860 in anticipation of the American Civil War. 327 men joined the organization; among them were George Maney, who served as captain; lawyer Thomas H. Malone, who served as lieutenant; and Charles Todd Quintard, who served as chaplain. In May 1861 the unit, now consisting of three companies, was mustered into Confederate service as part of the 1st Tennessee Infantry Regiment; George Maney becoming Colonel. The regiment served during the whole American Civil War.
 W
WSlavery played the central role during the American Civil War. The primary catalyst for secession was slavery, especially Southern political leaders' resistance to attempts by Northern antislavery political forces to block the expansion of slavery into the western territories. Slave life went through great changes, as the South saw Union Armies take control of broad areas of land. During and before the war, enslaved people played an active role in their own emancipation, and thousands of enslaved people escaped from bondage during the war. On January 1, 1863, President Abraham Lincoln announced the Emancipation Proclamation, making 3 million blacks legally free. During the war, both sides used African Americans for military purposes; in the South as enslaved labor and in the north as wage labor and military volunteers. Over 100,000 formerly enslaved people fought for the Union and over 500,000 fled their plantations for Union lines. Religiosity and cultural expression also developed greatly during the civil war.
 W
WThe United States Colored Troops Memorial Statue is a memorial to the more than 700 African-American soldiers and sailors from St. Mary's County, Maryland who served in the Union forces during the American Civil War.
 W
WWilliam Orton Williams, called Orton Williams until he changed his name to Lawrence Williams Orton, was a Confederate officer who, after having been caught behind Union lines in a U.S. Army uniform, was executed as a spy.
 W
WPierce Manning Butler Young was a Major General in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War and a post-war politician, diplomat, and four-term United States Congressman from Georgia.
 W
WJohn Celivergos Zachos was a physician, literary scholar, elocutionist, author, lecturer, inventor, and educational pioneer. He was an early proponent of equal education rights for African Americans and women. He advocated and expanded the Oratory systems of François Delsarte and James Rush.