 W
WThe Arikara War was an armed conflict between the United States, their allies from the Sioux tribe and Arikara Native Americans that took place in the summer of 1823, along the Missouri River in present-day South Dakota. It was the first Indian war west of the Missouri fought by the U.S. Army and its only conflict ever with the Arikara. The war came as a response to an Arikara attack on trappers, called "the worst disaster in the history of the Western fur trade".
 W
WThe Battle of Slim Buttes was fought on September 9–10, 1876, in the Great Sioux Reservation between the United States Army and Miniconjou Sioux during the Great Sioux War of 1876. It marked the first significant victory for the army since the stunning defeat of General George Custer at the Battle of Little Bighorn in June.
 W
WThe Crow Creek massacre occurred around the mid 1300s CE between Native American groups at a site along the Missouri River in the South Dakota area; it is now within the Crow Creek Indian Reservation. Crow Creek Site, the site of the massacre near Chamberlain, is an archaeological site and a U.S. National Historic Landmark, located at coordinates 43°58′48″N 99°19′54″W. An excavation of part of the site was done in the 1950s, with additional excavations in 1978 and later.
 W
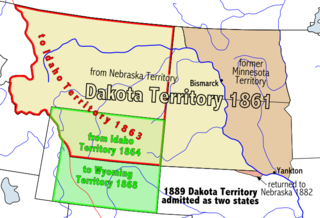
WThe Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North Dakota and South Dakota.
 W
WThe Enabling Act of 1889 is a United States statute that permitted the entrance of Montana and Washington into the United States of America, as well as the splitting of Territory of Dakota into two states: North Dakota and South Dakota. The Territory of Dakota was to be split on the "seventh standard parallel produced due west to the western boundary". The initial convention centers chosen for North Dakota and South Dakota were Bismarck and Sioux Falls respectively, but the latter was later changed to the city of Pierre.
 W
WFort Bennett was originally called the Post at Cheyenne River Agency and was established during the Indian wars in the Department of Dakota by the U.S. Army to control the Sioux.
 W
WFort Meade was established in 1878 to protect the new settlements in the northern Black Hills, especially the nearby gold mining area around Deadwood. Several stage and freighting routes passed through Fort Meade en route to Deadwood.
 W
WThe Fort Randall Military Post was established in 1856 to help keep peace on the frontier. It was located on the south side of the Missouri River in South Dakota, just below the present site of the Fort Randall Dam.
 W
WFort Sisseton near Britton, South Dakota was established in 1864. As Fort Sisseton Historic State Park, it was designated as a State Historical Park in 1959. Fort Sisseton is listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WThe Great Sioux Reservation was the original area encompassing what are today the various Sioux Indian reservations in South Dakota and Nebraska.
 W
WThe Territory of Iowa was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1838, until December 28, 1846, when the southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Iowa. The remainder of the territory would have no organized territorial government until the Minnesota Territory was organized on March 3, 1849.
 W
WSpanish Louisiana was a governorate and administrative district of the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1762 to 1801 that consisted of a vast territory in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlled by France, which had named it La Louisiane in honor of King Louis XIV in 1682. Spain secretly acquired the territory from France near the end of the Seven Years' War by the terms of the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762). The actual transfer of authority was a slow process, and after Spain finally attempted to fully replace French authorities in New Orleans in 1767, French residents staged an uprising which the new Spanish colonial governor did not suppress until 1769. Spain also took possession of the trading post of St. Louis and all of Upper Louisiana in the late 1760s, though there was little Spanish presence in the wide expanses of the "Illinois Country".
 W
WThe Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from France in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi. However, France only controlled a small fraction of this area, with most of it inhabited by American Indians; for the majority of the area, what the United States bought was the "preemptive" right to obtain Indian lands by treaty or by conquest, to the exclusion of other colonial powers. The total cost of all subsequent treaties and financial settlements over the land has been estimated to be around 2.6 billion dollars.
 W
WThe Territory of Louisiana or Louisiana Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1805, until June 4, 1812, when it was renamed the Missouri Territory. The territory was formed out of the District of Louisiana, which consisted of the portion of the Louisiana Purchase north of the 33rd parallel.
 W
WThe Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit was the territorial capital.
 W
WThe Territory of Missouri was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 4, 1812 until August 10, 1821. In 1819, the Territory of Arkansas was created from a portion of its southern area. In 1821, a southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Missouri, and the rest became unorganized territory for several years.
 W
WThe Territory of Nebraska was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until March 1, 1867, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Nebraska. The Nebraska Territory was created by the Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854. The territorial capital was Omaha. The territory encompassed areas of what is today Nebraska, Wyoming, South Dakota, North Dakota, Colorado, and Montana.
 W
WThe following outline traces the territorial evolution of the U.S. State of South Dakota.
 W
WThe Pembina Region, also referred to as the Pembina District and Pembina Department, is the historic name of an unorganized territory of land that was ceded to the United States. The area included parts of what became North Dakota and a portion of central eastern to northeastern South Dakota. The eastern boundary was the Red River and included the Pembina River area. The region was formerly part of British Rupert's Land and the Red River Colony, that encompassed an area then known as the Assiniboia District, from 1763 to the signing of the Treaty of 1818. The treaty transferred the region that was south of the 49th parallel from the British to the United States.
 W
WThe Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin. Belmont was initially chosen as the capital of the territory. In 1837, the territorial legislature met in Burlington, just north of the Skunk River on the Mississippi, which became part of the Iowa Territory in 1838. In that year, 1838, the territorial capital of Wisconsin was moved to Madison.
 W
WThe Yankton Treaty was a treaty signed in 1858 between the United States government and the Yankton Sioux (Nakota) Native American tribe, ceding most of eastern South Dakota to the United States government. The treaty was signed in April 1858, and ratified by the United States Congress on February 16, 1859. The agreement immediately opened this territory up for settlement by whites, resulting in the establishment of an unofficial local government not recognized by Washington. The treaty also created the 400,000 acre Yankton Sioux Reservation, located in present-day Charles Mix County in South Dakota.