 W
WNew France, also sometimes known as the French North American Empire or Royal New France, was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spain in 1763 under the Treaty of Paris (1763).
 W
WThe Beaver Wars, also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars, encompass a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America. They were battles for economic welfare throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the lower Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the northern Algonquians and the Algonquians' French allies. From medieval times, Europeans had obtained furs from Russia and Scandinavia. American pelts came on the European market during the 16th century, decades before the French, English, and Dutch established permanent settlements and trading posts on the continent. Basque fishermen chasing cod off Newfoundland's Grand Banks bartered with local Indigenous peoples for beaver robes to help fend off the Atlantic chill. By virtue of their location, the tribes wielded considerable influence in European–Indian relations from the early seventeenth century onwards.
 W
WSamuel de Champlain was a French colonist, navigator, cartographer, draftsman, soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He made between 21 and 29 trips across the Atlantic Ocean, and founded Quebec, and New France, on 3 July 1608. An important figure in Canadian history, Champlain created the first accurate coastal map during his explorations, and founded various colonial settlements.
 W
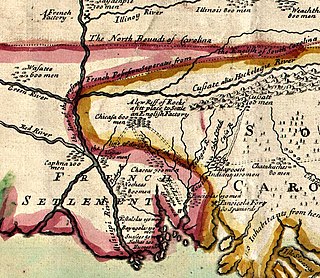
WThe Chickasaw Wars were fought in the 18th century between the Chickasaw allied with the British against the French and their allies the Choctaws and Illinois Confederation. The Province of Louisiana extended from Illinois to New Orleans, and the French fought to secure their communications along the Mississippi River. The Chickasaw, dwelling in northern Mississippi and western Tennessee, lay across the French path. Much to the eventual advantage of the British and the later United States, the Chickasaw successfully held their ground. The wars came to an end only with the French cession of New France to the British in 1763 according to terms of the Treaty of Paris.
 W
WColonial American military history is the military record of the Thirteen Colonies from their founding to the American Revolution in 1775.
 W
WThe Dummer's War was a series of battles between New England and the Wabanaki Confederacy who were allied with New France. The eastern theater of the war was fought primarily along the border between New England and Acadia in Maine, as well as in Nova Scotia; the western theater was fought in northern Massachusetts and Vermont at the border between Canada and New England. During this time, Maine and Vermont were part of Massachusetts.
 W
WFort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on June 22, 1564, as a new territorial claim in French Florida and a safe haven for Huguenots, who were being persecuted in France because they were Protestant, rather than Catholic. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine in September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on September 20. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.
 W
WThe French colonization of Texas began with the establishment of a fort in present-day southeastern Texas. It was established in 1685 near Arenosa Creek and Matagorda Bay by explorer Robert Cavelier de La Salle. He intended to found the colony at the mouth of the Mississippi River, but inaccurate maps and navigational errors caused his ships to anchor instead 400 miles (640 km) to the west, off the coast of Texas. The colony survived until 1688. The present-day town of Inez is near the fort's site. The colony faced numerous difficulties during its brief existence, including Native American raids, epidemics, and harsh conditions. From that base, La Salle led several expeditions to find the Mississippi River. These did not succeed, but La Salle did explore much of the Rio Grande and parts of east Texas.
 W
WFrench Florida was a colonial territory established by French Huguenot colonists in what is now Florida between 1562 and 1565.
 W
WThe Spanish assault on French Florida began as part of imperial Spain's geopolitical strategy of developing colonies in the New World to protect its claimed territories against incursions by other European powers. From the early 16th century, the French had historic claims to some of the lands in the New World that the Spanish called La Florida. The French crown and the Huguenots led by Admiral Gaspard de Coligny believed that planting French settlers in Florida would help defuse religious conflicts in France and strengthen its own claim to a part of North America. The Crown wanted to discover and exploit valuable commodities, especially silver and gold, as the Spanish had done with the mines of Mexico and Central and South America. The political and religious enmities that existed between the Catholics and Huguenots of France resulted in the attempt by Jean Ribault in February 1562 to settle a colony at Charlesfort on Port Royal Sound, and the subsequent arrival of René Goulaine de Laudonnière at Fort Caroline, on the St. Johns River in June 1564.
 W
WThe western theatre of Dummer's War in the 1720s in northern New England was referred to as "Grey Lock's War". Grey Lock distinguished himself by conducting guerrilla raids into Vermont and western Massachusetts. He consistently eluded his pursuers, and acquired the name Wawanolet, meaning "he who fools the others, or puts someone off the track."
 W
WThe Huguenot Church, also called the French Huguenot Church or the French Protestant Church, is a Gothic Revival church located at 136 Church Street in Charleston, South Carolina. Built in 1844 and designed by architect Edward Brickell White, it is the oldest Gothic Revival church in South Carolina, and has been designated a National Historic Landmark and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The congregation it serves traces its origins to the 1680s, and is the only independent Huguenot church in the United States.
 W
WKing George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in the British provinces of New York, Massachusetts Bay, New Hampshire, and Nova Scotia. Its most significant action was an expedition organized by Massachusetts Governor William Shirley that besieged and ultimately captured the French fortress of Louisbourg, on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, in 1745. In French, it is known as the Troisième Guerre Intercoloniale or Third Intercolonial War.
 W
WKing William's War was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg. It was the first of six colonial wars fought between New France and New England along with their respective Native allies before France ceded its remaining mainland territories in North America east of the Mississippi River in 1763.
 W
WRene Goulaine de Laudonnière was a French Huguenot explorer and the founder of the French colony of Fort Caroline in what is now Jacksonville, Florida. Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, a Huguenot, sent Jean Ribault and Laudonnière to explore potential sites in Florida suitable for settlement by the French Protestants.
 W
WLouisiana or French Louisiana was an administrative district of New France. Under French control 1682 to 1769 and 1801 (nominally) to 1803, the area was named in honor of King Louis XIV, by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle. It originally covered an expansive territory that included most of the drainage basin of the Mississippi River and stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico and from the Appalachian Mountains to the Rocky Mountains.
 W
WThe Pays d'en Haut was a territory of New France covering the regions of North America located west of Montreal. The vast territory included most of the Great Lakes region, expanding west and south over time into the North American continent as the French had explored. The Pays d'en Haut was established in 1610 and dependent upon the colony of Canada until 1763, when the Treaty of Paris ended New France, and both were ceded to the British as the Province of Quebec.
 W
WRedwood is an unincorporated community located southeast of Twin Lake in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. The town is located near the junction of U.S. Route 61 and Mississippi Highway 3, approximately 10 miles north of Vicksburg. Its zip code is 39156.
 W
WJean Ribault was a French naval officer, navigator, and a colonizer of what would become the southeastern United States. He was a major figure in the French attempts to colonize Florida. A Huguenot and officer under Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, Ribault led an expedition to the New World in 1562 that founded the outpost of Charlesfort on Parris Island in present-day South Carolina.
 W
WThe Third Treaty of San Ildefonso was a secret agreement signed on 1 October 1800 between the Spanish Empire and the French Republic by which Spain agreed in principle to exchange its North American colony of Louisiana for territories in Tuscany. The terms were later confirmed by the March 1801 Treaty of Aranjuez.