 W
WEvents in the year 1918 in British-administered Palestine.
 W
WThe Battle of Abu Tellul was fought on 14 July 1918 during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I after German and Ottoman Empire forces attacked the British Empire garrison in the Jordan Valley. The valley had been occupied by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) from February 1918 when Jericho was captured. Following two raids east of the River Jordan by the EEF the first in March and second in April the defence of the valley became the responsibility of the Desert Mounted Corps.
 W
WThe occupation of the Jordan Valley by the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) began in February 1918 during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. After the Capture of Jericho in February the Auckland Mounted Rifle Regiment began patrolling an area of the Jordan Valley near Jericho at the base of the road from Jerusalem. Towards the end of March the First Transjordan attack on Amman and the First Battle of Amman were launched from the Jordan Valley followed a few weeks later by the equally unsuccessful Second Transjordan attack on Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt at the end of April. During this time the occupation of the Jordan was fully established and continued through the summer of 1918. The occupation ended in September with the Battle of Megiddo which consisted of the Battle of Sharon and the Battle of Nablus. The Third Transjordan attack and Second Battle of Amman were fought as part of the Battle of Nablus.
 W
WThe Battle of Haifa was fought on 23 September 1918 towards the end of the Battle of Sharon which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September during the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the Battle of Haifa, the Indian 15th Cavalry Brigade, 5th Cavalry Division and part of the Desert Mounted Corps attacked rearguard forces of the Ottoman Empire that resulted in the capture of the towns of Haifa and Acre. This attack took place at the north western edge of the Esdraelon Plain 40–50 miles (64–80 km) behind the front line in the Judean Hills after the Desert Mounted Corps had occupied the plain, during the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon.
 W
WThe Hogarth Message was a January 1918 message from Commander David Hogarth, head of the Arab Bureau in Cairo, to Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, following Hussein's request for an explanation of the Balfour Declaration.
 W
WThe Charge at Irbid occurred on 26 September 1918 as a consequence of the victory at the Battle of Megiddo during the subsequent inland pursuit by Desert Mounted Corps to capture Damascus in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. The charge occurred when the 2nd Lancers of the 10th Cavalry Brigade, 4th Cavalry Division, attacked the Ottoman Army garrison defending the town of Irbid.
 W
WThe Capture of Jenin occurred on 20 September 1918, during the Battle of Sharon which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September during the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon carried out by the Desert Mounted Corps, the 3rd Light Horse Brigade, Australian Mounted Division attacked and captured the town of Jenin located on the southern edge of the Esdraelon Plain 40–50 miles (64–80 km) behind the front line in the Judean Hills. The Australian light horse captured about 2,000 prisoners, the main supply base and the ordnance depot of the Seventh and the Eighth Armies in and near the town. They also cut the main road from Nablus and a further 6,000 Ottoman Empire and German Empire prisoners, were subsequently captured as they attempted to retreat away from the Judean Hills.
 W
WThe Capture of Jisr ed Damieh took place on 22 September 1918 during the Third Transjordan attack of the Battle of Nablus which, along with the main Battle of Sharon formed the Battle of Megiddo fought during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. Units of Chaytor's Force under the commanded by Brigadier-General William Meldrum, and known as "Meldrum's Force", attacked and captured the bridge. This successful attack cut the most direct line of retreat from the Judean Hills for the Seventh and remnants of the Eighth Armies, while units from these two armies were moving towards, and crossing the Jisr ed Damieh bridge over the Jordan River. This victory by Meldrum's Force opened the way for Chaytor's Force to advance along the main Nablus to Es Salt road to capture Es Salt and to continue on to the victory at the Second Battle of Amman.
 W
WThe Battle of Nablus took place, together with the Battle of Sharon during the set piece Battle of Megiddo between 19 and 25 September 1918 in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. Fighting took place in the Judean Hills where the British Empire's XX Corps attacked the Ottoman Empire's Yildirim Army Group's Seventh Army defending their line in front of Nablus. This battle was also fought on the right flank in the Jordan Valley, where Chaytor's Force attacked and captured the Jordan River crossings, before attacking the Fourth Army at Es Salt and Amman capturing many thousands of prisoners and extensive territory. The Battle of Nablus began half a day after the main Battle of Sharon, which was fought on the Mediterranean section of the front line where the XXI Corps attacked the Eighth Army defending the line in front of Tulkarm and Tabsor and the Desert Mounted Corps which rode north to capture the Esdrealon Plain. Together these two battles, known as the Battle of Megiddo, began the Final Offensive of the war in the Sinai and Palestine campaign.
 W
WThe Battle of Nazareth began on 20 September 1918, during the Battle of Sharon, which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought during the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon the Desert Mounted Corps rode to the Esdraelon Plain 40 and 50 miles behind the front line in the Judean Hills. At Nazareth on the plain, the 13th Cavalry Brigade of the 5th Cavalry Division attempted to capture the town and the headquarters of the Yildirim Army Group which was eventually captured the following day after the garrison had withdrawn.
 W
WThe Battle of Samakh was fought on 25 September 1918, during the Battle of Sharon which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought from 19 to 25 September 1918, in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon the Desert Mounted Corps commanded by the Australian Lieutenant General Harry Chauvel, captured the Esdraelon Plain 40–50 miles (64–80 km) behind the front line in the Judean Hills on 20 September, when the 3rd Light Horse Brigade captured Jenin. The 4th Light Horse Brigade, Australian Mounted Division was deployed guarding supply columns, and prisoners, before being ordered to attack and capture Samakh on the shore of the Sea of Gallilee. Here the Ottoman and German garrison had been ordered by the commander of the Yildirim Army Group to fight to the last man.
 W
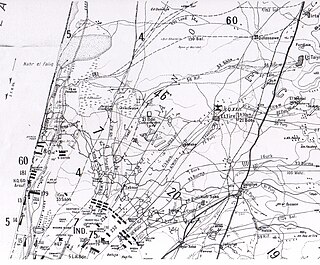
WThe Battle of Sharon fought between 19 and 25 September 1918, began the set piece Battle of Megiddo half a day before the Battle of Nablus, in which large formations engaged and responded to movements by the opposition, according to pre-existing plans, in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. The fighting took place over a wide area from the Mediterranean Sea east to the Rafat salient in the Judean Hills. Here the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) XXI Corps with the French brigade sized Détachement Français de Palestine et de Syrie attacked the Yildirim Army Group Eighth Army's XXII Corps and German Asia Corps. The Battle of Sharon extended well behind the Ottoman front lines when the Desert Mounted Corps rode through a gap in the front line across the Plain of Sharon to occupy the Esdraelon Plain. Meanwhile, during the Battle of Nablus the XX Corps attacked Nablus while Chaytor's Force held the right flank in the Jordan Valley before advancing to secure bridges and fords across the Jordan River, to continue the encirclement the defenders in the Judean Hills. Subsequently, Chaytor's Force advanced against the Fourth Army to capture Es Salt and Amman after the Second Battle of Amman.
 W
WThe Sinai and Palestine campaign of the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I was fought by the Arab Revolt and the British Empire, against the Ottoman Empire and its Imperial German allies. It started with an Ottoman attempt at raiding the Suez Canal in 1915, and ended with the Armistice of Mudros in 1918, leading to the cession of Ottoman Syria.
 W
WThe Battle of Tabsor was fought on 19–20 September 1918 beginning the Battle of Sharon, which along with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the infantry phase of the Battle of Sharon the British Empire 60th Division, XXI Corps attacked and captured the section of the front line nearest the Mediterranean coast under cover of an intense artillery barrage including a creeping barrage and naval gunfire. This Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) victory over the entrenched Ottoman Eighth Army, composed of German and Ottoman soldiers, began the Final Offensive, ultimately resulting in the destruction of the equivalent of one Ottoman army, the retreat of what remained of two others, and the capture of many thousands of prisoners and many miles of territory from the Judean Hills to the border of modern-day Turkey. After the end of the battle of Megiddo, the Desert Mounted Corps pursued the retreating soldiers to Damascus, six days later. By the time the Armistice of Mudros was signed between the Allies and the Ottoman Empire five weeks later, Aleppo had been captured.
 W
WThe Battle of Tell 'Asur, known as the Action of Tell 'Asur also known as the Battle of Turmus 'Aya, took place between 8 and 12 March 1918, after the decisive victory at the Battle of Jerusalem and the Capture of Jericho during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I. Fighting took place over an area which extended from the Mediterranean to Abu Tellul and Mussalabeh on the edge of the Jordan Valley.
 W
WThe Capture of Tiberias took place on 25 September 1918 during the Battle of Sharon which together with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the cavalry phase of the Battle of Sharon the Desert Mounted Corps occupied the Esdraelon Plain 40–50 miles (64–80 km) behind the front line in the Judean Hills. One squadron from each of the 3rd and 4th Light Horse Brigades Australian Mounted Division attacked and captured Tiberias, along with the Yildirim Army Group's Ottoman and German garrison.
 W
WThe Second Transjordan attack on Shunet Nimrin and Es Salt, officially known by the British as the Second action of Es Salt and by others as the Second Battle of the Jordan, was fought east of the Jordan River between 30 April and 4 May 1918, during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. The battle followed the failure of the First Transjordan attack on Amman fought at the beginning April. During this second attack across the Jordan River, fighting occurred in three main areas. The first area in the Jordan Valley between Jisr ed Damieh and Umm esh Shert the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) defended their advanced position against an attack by units of the Seventh Army based in the Nablus region of the Judean Hills. The second area on the eastern edge of the Jordan Valley where the Ottoman Army garrisons at Shunet Nimrin and El Haud, on the main road from Ghoraniyeh to Amman were attacked by the 60th (London) Division many of whom had participated in the First Transjordan attack. The third area of fighting occurred after Es Salt was captured by the light horse brigades to the east of the valley in the hills of Moab, when they were strongly counterattacked by Ottoman forces converging on the town from both Amman and Nablus. The strength of these Ottoman counterattacks forced the EEF mounted and infantry forces to withdraw back to the Jordan Valley where they continued the Occupation of the Jordan Valley during the summer until mid September when the Battle of Megiddo began.
 W
WThe Battle of Tulkarm took place on 19 September 1918, beginning of the Battle of Sharon, which along with the Battle of Nablus formed the set piece Battle of Megiddo fought between 19 and 25 September in the last months of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of the First World War. During the infantry phase of the Battle of Sharon the British Empire 60th Division, XXI Corps attacked and captured the section of the front line nearest the Mediterranean coast under cover of an intense artillery barrage including a creeping barrage and naval gunfire. This Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) victory over the entrenched Ottoman Eighth Army, composed of German and Ottoman soldiers, began the Final Offensive, ultimately resulting in the destruction of the equivalent of one Ottoman army, the retreat of what remained of two others, and the capture of many thousands of prisoners and many miles of territory from the Judean Hills to the border of modern-day Turkey. After the end of the battle of Megiddo, the Desert Mounted Corps pursued the retreating soldiers to Damascus, six days later. By the time an Armistice of Mudros was signed between the Allies and the Ottoman Empire five weeks later, Aleppo had been captured.