 W
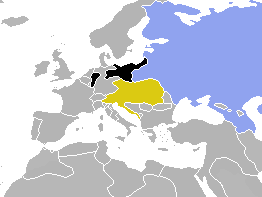
WThe Austrian Empire was a Central European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, it was the third most populous empire after the Russian Empire and the United Kingdom in Europe. Along with Prussia, it was one of the two major powers of the German Confederation. Geographically, it was the third largest empire in Europe after the Russian Empire and the First French Empire. Proclaimed in response to the First French Empire, it partially overlapped with the Holy Roman Empire until the latter's dissolution in 1806.
 W
WAustria and Prussia were the most powerful principalities in the Holy Roman Empire by the 18th and 19th centuries and had engaged in a struggle for supremacy in Central Europe. Locally known as Deutscher Dualismus, 'German dualism', the rivalry was characterized by major territorial conflicts, economic, cultural and political contention for sovereign leadership among the German-speaking peoples.
 W
WThis article is about the Austrian post offices in Liechtenstein.
 W
WDuring the course of his lifetime, Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827) enjoyed relationships with many of his musical contemporaries. Beethoven was famously difficult to get along with, and the history of his relationships with contemporaries is littered with arguments, misunderstandings, and reconciliations. Beethoven had well-known fallings out with his one-time teacher, Joseph Haydn, with the piano virtuoso and composer Johann Nepomuk Hummel, the German composer Carl Maria von Weber and the Italian violinist Niccolò Paganini. Conversely, he regarded Franz Schubert positively, praising the latter's compositions on his deathbed.
 W
WThe Czech lands or the Bohemian lands are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic since 1 January 1969 and the Czech Republic since 1 January 1993.
 W
WFort Bourguignon is one of many fortresses in Pula, Croatia that were built by the Austrian Empire in the second half of the 19th century.
 W
WGalicia or Halychyna is a historical and geographic region between Central and Eastern Europe. It was once the small Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia and later a crown land of Austria-Hungary, the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, which straddled the modern-day border between Poland and Ukraine. The area, named after the medieval city of Halych, was first mentioned in Hungarian historical chronicles in the year 1206 as Galiciæ. In 1253 Prince Daniel of Galicia was crowned the King of Rus or King of Ruthenia following the Mongol invasion in Ruthenia. In 1352 the Kingdom of Poland annexed the Kingdom of Galicia and Volhynia as the Ruthenian Voivodeship.
 W
WThe Holy Alliance was a coalition linking the monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia. It was created after the final defeat of Napoleon at the behest of Emperor (Tsar) Alexander I of Russia and signed in Paris on 26 September 1815. The alliance aimed to restrain liberalism and secularism in Europe in the wake of the devastating French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars, and it nominally succeeded in this until the Crimean War. Otto von Bismarck managed to reunite the Holy Alliance following the unification of Germany in 1871, but the alliance again faltered by the 1880s over Austrian and Russian conflicts of interest over the dissolution of the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WThe House of Deputies was, from 1861, the lower house of the bicameral Imperial Council parliament of the Austrian Empire and, from 1867 to 1918, of the Cisleithanian lands within Austria-Hungary. The upper chamber was the House of Lords.
 W
WThe House of Lords was the upper house of the Imperial Council, the bicameral legislature of the Austrian Empire from 1861 and of the Cisleithanian (Austrian) half of Austria-Hungary upon the Compromise of 1867. Created by the February Patent issued by Emperor Franz Joseph I on 26 February 1861, it existed until the end of World War I and the dissolution of the Dual Monarchy, when on 12 November 1918 the transitional National Assembly of German-Austria declared it abolished. It was superseded by the Federal Council of the Austrian Parliament implemented by the 1920 Federal Constitutional Law.
 W
WThe Illyrian Provinces were an autonomous province of France during the First French Empire that existed under Napoleonic Rule from 1809 to 1814. The province encompassed modern-day Croatia, Slovenia, Gorizia, and parts of Austria. Its capital was Ljubljana in Slovenia. It encompassed six départements, making it a relatively large portion of territorial France at the time. Parts of Croatia were split up into Civil Croatia and Military Croatia, the former served as a residential space for French immigrants and Croatian inhabitants and the latter as a military base to check the Ottoman Empire.
 W
WLodomeria is a derivative name (Latinized) of Vladimir which was a name of a Ruthenian duchy, the Principality of Volhynia a western Kievan Rus' principality founded by the Rurik dynasty in 987 and centered in the region of Volhynia, straddling the borders of modern-day Poland, Ukraine and Belarus. The duchy of Vladimir arose in the course of the 12th century along with the duchy of Halitch (Halicz).
 W
WThe Secret State Conference was the de jure advisory body to Emperor Ferdinand I of Austria and the de facto ruling cabinet of the Austrian Empire from 1836 to 1848 during the Vormärz era.
 W
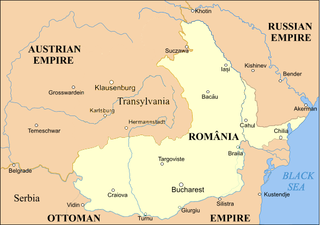
WThe Principality of Transylvania, from 1765 the Grand Principality of Transylvania, was a realm of the Hungarian Crown and from 1804 an Austrian crownland ruled by the Habsburg and Habsburg-Lorraine monarchs of the Habsburg Monarchy. During the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary. In 1867, as a result of the Austro-Hungarian Compromise, the principality was reunited with Hungary proper.
 W
WThe Venetian Province was the name of the territory of former Republic of Venice ceded by the French First Republic to the Habsburg Monarchy under the terms of the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio that ended the War of the First Coalition. The province's capital was Venice.
 W
WThe Vienna Literary Agreement was the result of a meeting held in March 1850, when writers from Croatia, Serbia and Carniola (Slovenia) met to discuss the extent to which their literatures could be conjoined and united to standardize the Serbo-Croatian language. The agreement recognized the commonality of South Slavic dialects and enumerated a basic set of grammar rules which they shared.
 W
WVormärz was a period in the history of Germany preceding the 1848 March Revolution in the states of the German Confederation. The beginning of the period is less well-defined: some place the starting point directly after the fall of Napoleon and the establishment of the German Confederation in 1815; others, typically those emphasizing the Vormärz as a period of political uprising, place the beginning at the French July Revolution of 1830.