 W
WThe County of Mark was a county and state of the Holy Roman Empire in the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. It lay on both sides of the Ruhr river along the Volme and Lenne rivers.
 W
WLa Marck was a noble family, which from about 1200 appeared as the counts of Mark.
 W
WAltena Castle is a medieval hill castle in the town of Altena in North Rhine-Westphalia. Built on a spur of Klusenberg hill, the castle lies near the Lenne in the Märkischer Kreis.
 W
WThe Battle of Worringen was fought on 5 June 1288 near the town of Worringen, which is now the northernmost borough of Cologne. It was the decisive battle of the War of the Limburg Succession, fought for the possession of the Duchy of Limburg between Archbishop Siegfried II of Cologne and Duke John I of Brabant, and one of the largest battles in Europe in the Middle Ages.
 W
WBilstein Castle is a hill castle in the Sauerland in Germany. It is located in the eponymous quarter of Bilstein in the town of Lennestadt. Since 1927 the building has been a youth hostel.
 W
WBlankenstein Castle is a castle located on the south side of the river Ruhr in Hattingen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
 W
WCappenberg Castle is a former Premonstratensian monastery, Cappenberg Abbey in Cappenberg, a part of Selm, North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. It stands on an elevation, the Cappenberg, near Lünen and Werne, and is a vantage point offering views over the eastern Ruhrgebiet.
 W
WEssen Abbey was a monastery of secular canonesses for women of high nobility in Essen, Germany. It was founded about 845 by the Saxon Altfrid, later Bishop of Hildesheim and saint, near a royal estate called Astnidhi, which later gave its name to the religious house and to the town. The first abbess was Altfrid's kinswoman, Gerswit.
 W
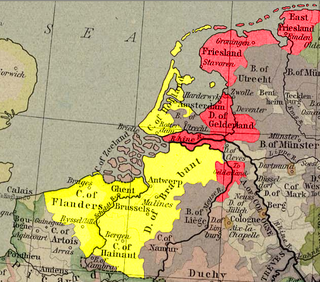
WThe Guelders Wars were a series of conflicts in the Low Countries between the Duke of Burgundy, who controlled Holland, Flanders, Brabant, and Hainaut on the one side, and Charles, Duke of Guelders, who controlled Guelders, Groningen, and Frisia on the other side.
 W
WHardenstein Castle is a ruined castle in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The remains lie east of Herbede on the Ruhr River, surrounded by mountains, and are not easily accessible. Nearby ruins show that the castle was once part of an important mining centre, probably dating to the Middle Ages; the earliest records, from the 16th century, support this. The castle features in the legend of the Nibelungs.
 W
WHusen Castle is a medieval tower house of a castle in the Dortmund borough of Syburg in North Rhine-Westphalia.
 W
WKlusenstein is a castle in Hemer, Germany, located on a 60m high cliff above the valley of the Hönne river. The castle was built in 1353 as a boundary fortification of the earldom Mark.
 W
WOsmond iron was wrought iron made by a particular process. This is associated with the first European production of cast iron in furnaces such as Lapphyttan in Sweden.
 W
WThe Soest Feud, or Feud of Soest, was a feud that took place from 1444 to 1449 in which the town of Soest claimed its freedom from Archbishop Dietrich of Cologne (1414–1463), who tried to restore his rule. The town of Soest opposed this attempt on 5 June 1444 by accepting a new suzerain, John I, the Duke of Cleves-Mark, who guaranteed the town its old rights as well as new ones. As a result Emperor Frederick III imposed the imperial ban on the town. The victory of the town meant that Soest had de facto more freedom than a free imperial city until it was annexed by Prussia, but at the same time it had to forfeit its economic power because it was now an enclave within Cologne's territory.
 W
WThe War of the Jülich Succession was a military conflict over the right of succession to the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg. It lasted between 10 June 1609 and 24 October 1610, resuming in May 1614 and finally ending in 13 October 1614. The first round of the conflict pitted Catholic Archduke Leopold V against the combined forces of the Protestant Margraviate of Brandenburg and Palatinate-Neuburg, ending in the former's military defeat. The representatives of the Brandenburg and Neuburg later entered into a direct conflict after their religious conversion to Calvinism and Catholicism respectively. The conflict was further complicated by the involvement of Spain and the Netherlands making it part of the Eighty Years' War. It was finally settled by the Treaty of Xanten, provisions of which favored Spain.
 W
WWerden Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Essen-Werden (Germany), situated on the Ruhr.