 W
WThe Nabataeans, also Nabateans, were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu —gave the name Nabatene to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea.
 W
WArabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Empire beginning in the 2nd century; it consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom in Jordan, southern Levant, the Sinai Peninsula and northwestern Arabian Peninsula. Its capital was Petra. It was bordered on the north by Syria, on the west by Iudaea and Aegyptus, and on the south and east by the rest of Arabia, known as Arabia Deserta and Arabia Felix.
 W
WBosra, also spelled Bostra, Busrana, Bozrah, Bozra and officially called Busra al-Sham, is a town in southern Syria, administratively belonging to the Daraa District of the Daraa Governorate and geographically part of the Hauran region.
 W
WDushara, also transliterated as Dusares, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh.
 W
WHegra, also known as Mada’in Salih, or Al-Ḥijr (ٱلْحِجْر) is an archaeological site located in the area of AlUla within Al Madinah Region in the Hejaz, Saudi Arabia. A majority of the remains date from the Nabatean kingdom. The site constitutes the kingdom's southernmost and largest settlement after Petra, its capital. Traces of Lihyanite and Roman occupation before and after the Nabatean rule, respectively, can also be found.
 W
WThe incense trade route included a network of major ancient land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant and Egypt through Northeastern Africa and Arabia to India and beyond. The incense land trade from South Arabia to the Mediterranean flourished between roughly the 7th century BC and the 2nd century AD. The incense trade route served as a channel for the trading of goods such as Arabian frankincense and myrrh; from Southeast Asia Indian spices, precious stones, pearls, ebony, silk and fine textiles; and from the Horn of Africa, rare woods, feathers, animal skins, Somali frankincense, and gold.
 W
WLeuke Kome was a Nabataean port city located on the Incense Route. The location currently is called "Wadi Ainounah".
 W
WThe Nabataean alphabet is an abjad that was used by the Nabataeans in the second century BC. Important inscriptions are found in Petra, the Sinai Peninsula, and other archaeological sites including Avdat and Mada'in Saleh in Saudi Arabia.
 W
WNabataean Aramaic was the Western Aramaic variety used in inscriptions by the Nabataeans of the Negev, the east bank of the Jordan River and the Sinai Peninsula.
 W
WNabatean architecture refers to the building traditions of the Nabateans in Jordan. It includes the temple and tombs of Petra in the sandstone cliffs of Jordan’s Negev desert. The style appears a mix of Mesopotamian and Hellenistic (Greek) influences.
 W
WNabataean art is the art of the Nabataeans of North Arabia. They are known for finely-potted painted ceramics, which became dispersed among Greco-Roman world, as well as contributions to sculpture and Nabataean architecture. Nabataean art is most well known for the archaeological sites in Petra, specifically monuments such as Al Khazneh and Ad Deir.
 W
WThe coinage of Nabataea began under the reign of Aretas II, c. 110 – 96 BC but it was his heir Aretas III, who at the time was in control of land extending to Damascus. The silver coinage is based on the weight of the Roman Denarius or Greek Drachma, as the adjacent areas around Nabataea used the Greek weight system, it is presumed the coins are of this standard. The local name of the denominations are not known so the Latin denarius and Greek drachma equivalents are used interchangeably.
 W
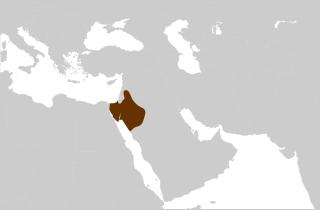
WThe Nabataean Kingdom, also named Nabatea, was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity.
 W
WPetra, originally known to its inhabitants in Nabataean Aramaic as ̢𐢚𐢛𐢓𐢈 rqmw Raqēmō, is a historical and archaeological city in southern Jordan. Petra lies around Jabal Al-Madbah in a basin surrounded by mountains which form the eastern flank of the Arabah valley that runs from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and the Nabataeans might have settled in what would become the capital city of their kingdom, as early as the 4th century BC. However, archaeological work has only discovered evidence of Nabataean presence dating back to the second century BC, by which time Petra had become their capital. The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who invested in Petra's proximity to the trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub.
 W
WThe Port of Gaza is a small port near the Rimal district of Gaza City. It is the home port of Palestinian fishing-boats and the base of the Palestinian Naval Police, a branch of the Palestinian National Security Forces. Under the Oslo II Accord, the activities of the Palestinian Naval Police are restricted to 6 nautical miles from the coast. Since 2007, the Port of Gaza has been under an Israeli-imposed naval blockade as part of a blockade of the Gaza Strip, and activities at the port have been restricted to small-scale fishing.