 W
WAjmer State was a separate state within India from 1950 to 1956 with Ajmer as its capital. Ajmer State was formed in 1950 out of the territory of former province of Ajmer-Merwara, which became a province of the Indian Union on 15 August 1947. It formed an enclave within the state of Rajasthan. Following the States Reorganisation Act in 1956 it was merged with Rajasthan.
 W
WBhopal was a state of India, which existed from 1949 to 1956. The state evolved out of the princely state of Bhopal, and was merged with neighbouring states to form Madhya Pradesh in 1956. Shankar Dayal Sharma of the Indian National Congress served as chief minister of Bhopal state from 1952 to 1956.
 W
WBilaspur State was a state of India from 1950 to 1954 with Bilaspur town as its capital. The state was established after the province of the same name created in 1948 from the princely state of Bilaspur.
 W
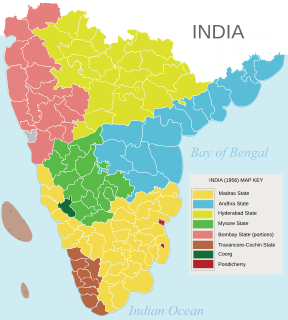
WBombay State was a large Indian state created at the time of India's Independence, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Presidency was merged with the princely states of the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat and Deccan States (which included parts of the present-day Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka.
 W
WHimachal Pradesh is located in north India and became 18th state of India.
 W
WCooch Behar, also known as Koch Bihar, was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state was placed under the Bengal States Agency, part of the Eastern States Agency of the Bengal Presidency. It is located south of the Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan, in present-day West Bengal.
 W
WHyderabad State was a state in Dominion and later Republic of India, formed after the accession of the princely state of Hyderabad into the Indian Union on 17 September 1948. It existed from 1948 to 1956.
 W
WKutch State was a state within India from 1947 to 1956. Its capital was Bhuj.
 W
WMadhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh.
 W
WMadras State was a state of India during the mid-20th century. At the time of its formation in 1950, it included the whole of present-day Tamil Nadu, Coastal Andhra, Rayalaseema, the Malabar region of North and central Kerala, and Bellary, South Canara. Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema were separated to form Andhra State in 1953, while South Canara and Bellary districts were merged with Mysore State, and Malabar District with the State of Travancore-Cochin to form Kerala in 1956. On January 14, 1969, Madras State was renamed to Tamil Nadu, meaning "Tamil country".
 W
WMysore State was a state within the Dominion and the later Republic of India from its formation in 1947, out of the territories of the Kingdom of Mysore, until 1956 with Bangalore as its capital. The state was considerably enlarged in 1956 when it became a linguistically homogeneous Kannada speaking state within the Union of India. It was subsequently renamed as the state of Karnataka.
 W
WThe Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) was a state of India, uniting eight princely states between 1948 and 1956. The capital and principal city was Patiala. The state covered an area of 26,208 km². Shimla, Kasauli, Kandaghat and Chail also became part of the PEPSU.
 W
WSaurashtra, also known as United State of Kathiawar, was a State of India from that existed between 1948 and 1956, on Saurashtra alias Kathiawar peninsula, with Rajkot as its capital,
 W
WTravancore–Cochin or Thiru–Kochi was a short-lived state of India (1949–1956). It was originally called United State of Travancore and Cochin and was created on 1 July 1949 by the merger of two former kingdoms, Travancore and Cochin with Thiruvananthapuram as the capital. It was renamed State of Travancore–Cochin in January 1950.
 W
WVindhya Pradesh was a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948 as Union of Baghelkhand and Bundelkhand States, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named as Vindhya Pradesh on 25 January 1950 after the Vindhya Range, which runs through the centre of the province. The capital of the state was Rewa. It lay between Uttar Pradesh to the north and Madhya Pradesh to the south, and the enclave of Datia, which lay a short distance to the west, was surrounded by the state of Madhya Bharat.