 W
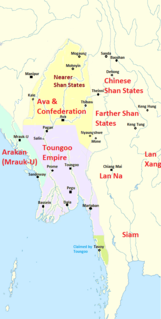
WThe First Toungoo Empire was the dominant power in mainland Southeast Asia in the second half of the 16th century. At its peak, Toungoo "exercised suzerainty from Manipur to the Cambodian marches and from the borders of Arakan to Yunnan" and was "probably the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia." The "most adventurous and militarily successful" dynasty in Burmese history was also the "shortest-lived."
 W
WBayinnaung Kyawhtin Nawrahta was king of the Toungoo Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1550 to 1581. During his 31-year reign, which has been called the "greatest explosion of human energy ever seen in Burma", Bayinnaung assembled what was probably the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia, which included much of modern-day Burma, the Chinese Shan states, Lan Na, Lan Xang, Manipur and Siam.
 W
WThe Burmese–Siamese War (1547–1549) was the first war fought between the Toungoo Dynasty of Burma and the Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam, and the first of the Burmese–Siamese wars that would continue until the middle of the 19th century. The war is notable for the introduction of early modern warfare to the region. It is also notable in Thai history for the death in battle of Siamese Queen Suriyothai on her war elephant; the conflict is often referred to in Thailand as the War that Led to the Loss of Queen Suriyothai (สงครามคราวเสียสมเด็จพระสุริโยไท).
 W
WThe Burmese-Siamese War of 1563-1564, also known as the War over the White Elephants, was a war between the Toungoo Dynasty of Burma and the Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam. It was the second of twenty wars fought between the Burmese and Siamese that lasted well into the 19th century. The cause of the war was an attempt by the Toungoo king Bayinnaung to force the Ayutthaya kingdom into submission under his rule, as part of his campaign that later created the largest empire ever to exist in Southeast Asia. 13 years into Bayinnaung's reign, his second attempt at invasion of Siam and first as king succeeded after an extensive siege of the city of Ayutthaya. Siam became a vassal of the Toungoo Dynasty, this status lasting until a 1568 revolt by Ayutthaya resulting in a short-lived independence.
 W
WThe Burmese–Siamese War (1568–1569) was a military conflict fought between the Kingdom of Ayutthaya (Siam) and the Kingdom of Burma. The war began in 1568 when Ayutthaya unsuccessfully attacked Phitsanulok, a Burmese vassal state. The event was followed by a Burmese intervention which resulted in the 2 August 1569 defeat of Ayutthaya, which became a Burmese vassal state. Burma then moved towards Lan Xang, occupying the country for a short period of time until retreating in 1570.
 W
WThe Burmese–Siamese War (1593–1600) was the war fought between the Toungoo Dynasty of Burma and the Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam. The war was the culmination of Siam's move towards independence following subjugation after the Burmese–Siamese War (1584–1593). The war ended with a victory by Siam, which seized the cities of Tavoy and Tenasserim, and laid siege to two major cities of the Toungoo Dynasty.
 W
WPadethayaza, also spelt Padesarājā, was a minister who served the last three monarchs at the Nyaungyan court, and was a prominent writer and poet. He is known for composing pyo, lyrical poems based on the Jataka tales. While he wrote traditional works pertaining to Buddhism, he was also known for expanding his repertoire, drawing from Hindu tales, apocryphal birth stories of the Buddha, current events such as the arrival of Thai envoys to the Burmese court, and village life for peasants. After the demise of the Nyaungyan court in 1754, Padethayaza was captured and taken to Bago Region.
 W
WThe Shwezigon Pagoda Bell is a temple bell located at the Shwezigon Pagoda in Bagan, Myanmar. The 3423 kg bell was dedicated to the pagoda by King Bayinnaung of Toungoo Dynasty in 1557. The inscriptions on the bell in Burmese, Mon, and Pali describe the important events of the first six years of his reign.
 W
WThe Shwezigon Pagoda Bell Inscription is a multi-language inscription found on the Shwezigon Pagoda Bell, donated by King Bayinnaung of Toungoo Dynasty and located at the Shwezigon Pagoda in Bagan, Burma (Myanmar). Written in Burmese, Mon, and Pali, the inscription lists the important events in the first six years of his reign. It is the only contemporary record in Burmese that calls the king "Conqueror of the Ten Directions", the title by which he is widely known in Mon and Thai.
 W
WThe Toungoo dynasty, and also known as the Restored Toungoo dynasty, was the ruling dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from the mid-16th century to 1752. Its early kings Tabinshwehti and Bayinnaung succeeded in reunifying the territories of the Pagan Kingdom for the first time since 1287 and in incorporating the Shan States for the first time. At its peak, the First Toungoo Empire also included Manipur, Chinese Shan States, Siam and Lan Xang. But the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia collapsed in the 18 years following Bayinnaung's death in 1581.
 W
WThe Toungoo–Ava War (1538–1545) was a military conflict that took place in present-day Lower and Central Burma (Myanmar) between the Toungoo Dynasty, and the Ava-led Confederation of Shan States, Hanthawaddy Pegu, and Arakan (Mrauk-U). Toungoo's decisive victory gave the upstart kingdom control of all of central Burma, and cemented its emergence as the largest polity in Burma since the fall of Pagan Empire in 1287.
 W
WThe Toungoo–Hanthawaddy War (1534–1541) was a military conflict between the Toungoo Kingdom, and the Hanthawaddy Kingdom and its allies the Prome Kingdom and the Confederation of Shan States that took place in present-day Lower Burma (Myanmar) between 1534 and 1541. In a series of improbable events, the upstart Burmese-speaking kingdom defeated Mon-speaking Hanthawaddy, the most prosperous and powerful of all post-Pagan kingdoms before the war. In the following years, Toungoo used the newly acquired kingdom's wealth and manpower to reunify the various petty states that had existed since the fall of Pagan Empire in 1287.
 W
WThe Taungoo–Mrauk-U War (1545–1547) was a military conflict that took place in Arakan from 1545 to 1547 between the Taungoo Dynasty and the Kingdom of Mrauk U. The western kingdom successfully fended off the Taungoo invasions, and kept its independence. The war had a deterrence effect: Mrauk U would not see another Taungoo invasion until 1580.