 W
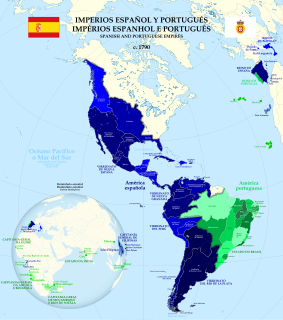
WThe history of Spain dates back to the Antiquity when the pre-Roman peoples of the Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula made contact with the Greeks and Phoenicians and the first writing systems known as Paleohispanic scripts were developed. In 1516, Habsburg Spain unified a number of disparate predecessor kingdoms; its modern form of a constitutional monarchy was introduced in 1813, and the current democratic constitution dates to 1978. After the completion of the Reconquista, the Crown of Castile began to explore across the Atlantic Ocean in 1492, expanding into the New World and marking the beginning of the Golden Age under the Spanish Empire. The kingdoms of Spain were united under Habsburg rule in 1516, that unified the Crown of Castile, the Crown of Aragon and smaller kingdoms under the same rule. Until the 1650s, Habsburg Spain was the most powerful state in the world and remained among the most powerful until early 19th century.
 W
WThe Spanish colonization of the Americas began under the Crown of Castile and spearheaded by the Spanish conquistadors. The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions in South America and the Caribbean. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer this vast territory. The main motivations for colonial expansion were profit and the spread of Catholicism through indigenous conversions.
 W
WHabsburg Spain was the Spain of the 16th and 17th centuries (1516–1700) when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. The Habsburg rulers reached the zenith of their influence and power. They controlled territory that included the Americas, the East Indies, the Low Countries, Belgium, Luxembourg, Italy, and territories now in France and Germany in Europe, the Portuguese Empire from 1580 to 1640, and various other territories such as small enclaves like Ceuta and Oran in North Africa. This period of Spanish history has also been referred to as the "Age of Expansion".
 W
WJusticia mayor was a title bestowed upon a person in 19th century Spanish Empire which authorized him to perform law enforcement and judicial functions within a town, city of region. It is similar to the position of sheriff in some jurisdictions.
 W
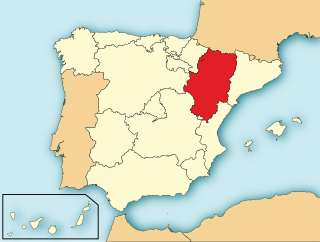
WThe Kingdom of Aragon was a medieval and early modern kingdom on the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, in Spain. It should not be confused with the larger Crown of Aragon, that also included other territories — the Principality of Catalonia, the Kingdom of Valencia, the Kingdom of Majorca, and other possessions that are now part of France, Italy, and Greece — that were also under the rule of the King of Aragon, but were administered separately from the Kingdom of Aragon.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Navarre, originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on either side of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Valencia, located in the eastern shore of the Iberian Peninsula, was one of the component realms of the Crown of Aragon. When the Crown of Aragon merged by dynastic union with the Crown of Castile to form the Kingdom of Spain, the Kingdom of Valencia became a component realm of the Spanish monarchy.
 W
WMaestranzas de caballería are noble militias created in the early modern era by the Spanish Crown, with the aim of giving the nobility practice in horsemanship and the use of weapons. In the sixteenth century, the caballería or cavalry, was the typical military branch for nobles to follow, but the aforementioned skills had become less common as the Spanish aristocracy converted into a class of courtiers. These noble institutions created a dedicated cavalry corps that was directly funded by its members. The participating nobles, or maestrantes, organized themselves under the advocacy of a holy patron and took the internal form of a confraternity.
 W
WThe Polysynodial System or Polysynodial Regime or System of Councils was a political organization of the authoritarian system during rule of the Catholic Monarchs and Habsburg Spain. It was replaced after the promulgation of the Bourbon Reforms in the 18th century, which organized the central administration in a group of collegiate bodies that receive the name of Councils already existing or created ex novo. "The Spanish Crown in the sixteenth century governed its wide and diverse kingdoms through a series of councils. Most of these bodies were composed predominantly of lawyers, men trained in academic study of Roman law."
 W
WThe Principality of Catalonia was a medieval and early modern state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of its history it was in dynastic union with the Kingdom of Aragon, constituting together the Crown of Aragon. Between the 13th and the 18th centuries, it was bordered by the Kingdom of Aragon to the west, the Kingdom of Valencia to the south, the Kingdom of France and the feudal lordship of Andorra to the north and by the Mediterranean sea to the east. The term Principality of Catalonia remained in use until the Second Spanish Republic, when its use declined because of its historical relation to the monarchy. Today, the term Principat (Principality) is used primarily to refer to the autonomous community of Catalonia in Spain, as distinct from the other Catalan Countries, and usually including the historical region of Roussillon in southern France.
 W
WSpanish Baroque Painting refers to the style of painting which developed in Spain throughout the 17th century and the first half of the 18th century. The style appeared in early 17th century paintings, and arose in response to Mannerist distortions and idealisation of beauty in excess, appearing in early 17th century paintings. Its main objective was, above all, to allow the viewer to easily understand the scenes depicted in the works through the use of realism, while also meeting the Catholic Church's demands for 'decorum' during the Counter-Reformation.
 W
WThe Spanish Golden Age is a period of flourishing in arts and literature in Spain, coinciding with the political rise of the Spanish Empire under the Catholic Monarchs of Spain and the Spanish Habsburgs. The greatest patron of Spanish art and culture during this period was King Philip II (1556-1598), whose royal palace, El Escorial, invited the attention of some of Europe's greatest architects and painters such as El Greco, who infused Spanish art with foreign styles and helped create a uniquely Spanish style of painting.
 W
WThe War of the Portuguese Succession, a result of the extinction of the Portuguese royal line after the Battle of Alcácer Quibir and the ensuing Portuguese succession crisis of 1580, was fought from 1580 to 1583 between the two main claimants to the Portuguese throne: António, Prior of Crato, proclaimed in several towns as King of Portugal, and his first cousin Philip II of Spain, who eventually succeeded in claiming the crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.