 W
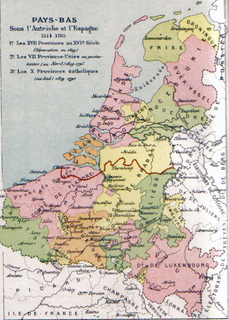
WSpanish Netherlands was the name for the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries held in personal union by the Spanish Crown. This region comprised most of the modern states of Belgium and Luxembourg, as well as parts of northern France, the southern Netherlands, and western Germany with the capital being Brussels.
 W
WThe Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, was the part of the Low Countries largely controlled by Spain (1556–1714), later Austria (1714–1794), and occupied then annexed by France (1794–1815). The region also included a number of smaller states that were never ruled by Spain or Austria: the Prince-Bishopric of Liège, the Imperial Abbey of Stavelot-Malmedy, the County of Bouillon, the County of Horne and the Princely Abbey of Thorn. The Southern Netherlands were part of the Holy Roman Empire until the whole area was annexed by Revolutionary France.
 W
WThe Army of Flanders was a multinational army in the service of the kings of Spain that was based in the Spanish Netherlands during the 16th to 18th centuries. It was notable for being the longest-serving standing army of the period, being in continuous service from 1567 until its disestablishment in 1706. In addition to taking part in numerous battles of the Dutch Revolt (1567–1609) and the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), it also employed many developing military concepts more reminiscent of later military units, enjoying permanent, standing regiments (tercios), barracks, military hospitals and rest homes long before they were adopted in most of Europe. Sustained at huge cost and at significant distances from Spain, the Army of Flanders also became infamous for successive mutinies and its ill-disciplined activity off the battlefield, including the Sack of Antwerp in 1576.
 W
WIn Brussels, like in most European cities, one needed the capacity of bourgeois in order to not only exercise political rights, but also to practice a trade, which, in Brussels, meant to be a member of the Guilds and/or of the Seven Noble Houses. The charter of Brussels, as codified in 1570 in articles 206 and following, provided the conditions of admission to the bourgeoisie of the city. The Bourgeois were the patrician class of the city. This social class was abolished by Napoleon during the French occupation.
 W
WLes Chasses de Maximilien or Les Belles chasses de Guise is a set of twelve tapestries, one per month, depicting hunting scenes in the Sonian Forest, south of Brussels. They were produced in a Brussels workshop, probably commissioned by a member of the Habsburg family: either Charles V, or his aunt Margaret of Austria, or his sister Mary of Hungary who both governed the Low countries in his name. A contract of 1533 probably refers to them. They were in the collection of the Dukes of Guise by 1589, remaining until 1654. After being owned by Cardinal Mazarin, they entered the French royal collection of Louis XIV in 1665. They are now in the Louvre museum, and considered one of the masterpieces of the art of tapestry.
 W
WJohannes "Jan" de Lichte was an 18th-century Flemish outlaw and gang leader. Motivated by poverty during the upheavals of the Austrian War of Succession (1740–48), de Lichte led a gang of bandits who committed burglaries, robberies, and several murders in Flanders. Captured and executed in 1748, he was subsequently rehabilitated in the fictional works of Louis Paul Boon in 1958 and has subsequently inspired a sculpture and film series.
 W
WFort Knokke or Fort de Cnocke or Fort de la Knocque or Fort de Knocke was an important fortification that defended western Flanders from the 1580s until it was demolished in the 1780s. During its 200 year history, the place was held by the Spanish Empire, Kingdom of France, Habsburg Austria and the Dutch Republic. The existing defenses were improved in 1678 by the famous military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. The fort was attacked by the Grand Alliance in 1695 during the Nine Years' War but the French garrison successfully held out. It was captured from the French by a ruse in 1712 during the War of the Spanish Succession. Control of the fort and other strong places in the Austrian Netherlands was a key feature of the so-called Barrier Treaty in 1713. The French captured the fort after a two-month siege in 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession. Emperor Joseph II had the citadel demolished in 1781. The site is on the Yser River about 8 kilometres (5 mi) southwest of Diksmuide, Belgium.
 W
WThe Duchy of Luxemburg was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg, now Duke of Limburg, became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, competing against the House of Habsburg for supremacy in Central Europe. They would be the heirs to the Přemyslid dynasty in the Kingdom of Bohemia, succeeding the Kingdom of Hungary and contributing four Holy Roman Emperors until their own line of male heirs came to an end and the House of Habsburg got the pieces that the two Houses had originally agreed upon in the Treaty of Brünn in 1364.
 W
WThe Renaissance in the Low Countries was a cultural period in the Northern Renaissance that took place in around the 16th century in the Low Countries.
 W
WThe Seven Noble Houses of Brussels were the seven families or clans whose descendants formed the patrician class and urban aristocracy of Brussels.
 W
WThe Spanish Empire, historically known as the Hispanic Monarchy and as the Catholic Monarchy, was one of the largest empires in history. From the late 15th century to the early 19th, Spain controlled a huge overseas territory in the New World, the Asian archipelago of the Philippines, what they called "The Indies" and territories in Europe, Africa and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the 16th and 17th centuries. The Spanish Empire became known as "the empire on which the sun never sets" and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century.
 W
WThe Treaty of Arras of 17 May 1579 was a peace treaty concluded between the Spanish Crown, represented by Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma, and representatives of the County of Hainaut, the County of Artois, and the cities of Douai, Lille, Orchies and Arras, all members of the Union of Arras, that had been formed the previous January, at the Abbey of St Vaast in Arras. It was a separate peace that formally ended the state of war that had existed between these entities during the Eighty Years' War. The provinces that had formed the Union of Utrecht continued the war.