 W
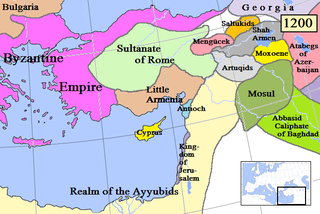
WThe Artuqids or Artuqid dynasty was a Turkmen dynasty originated from Döğer tribe that ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqid dynasty took its name from its founder, Zaheer-ul-Daulah Artuk, who was of the Döger branch of the Oghuz Turks and ruled one of the Turkmen beyliks of the Seljuk Empire. Artuk's sons and descendants ruled the three branches in the region: Sökmen's descendants ruled the region around Hasankeyf between 1102 and 1231; Ilghazi's branch ruled from Mardin and Mayyafariqin between 1106 and 1186 and Aleppo from 1117–1128; and the Harput line starting in 1112 under the Sökmen branch, and was independent between 1185 and 1233.
 W
WThe Banu Shayban is an Arab tribe, a branch of the Bakr ibn Wa'il group. Throughout the early Islamic era, the tribe was settled chiefly in the Jazira, and played an important role in its history.
 W
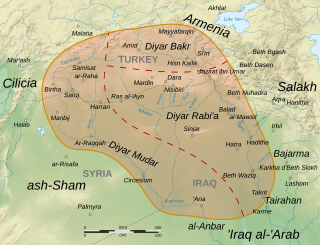
WDiyar Bakr is the medieval Arabic name of the northernmost of the three provinces of the Jazira, the other two being Diyar Mudar and Diyar Rabi'a. According to the medieval geographer al-Baladhuri, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by Mu'awiyah in the course of the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Diyar Bakr was settled by the Rabi'a subgroup of the Banu Bakr, and hence the two provinces are sometimes referred to collectively as "Diyar Rabi'a". In later Turkish usage, "Diyar Bakr" referred to the western portion of the former province, around Amid.
 W
WDiyar Mudar is the medieval Arabic name of the westernmost of the three provinces of al-Jazira, the other two being Diyar Bakr and Diyar Rabi'a. According to the medieval geographer al-Baladhuri, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by Mu'awiya I in the course of the early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Diyar Mudar was settled by the Mudar tribe.
 W
WDiyar Rabi'a is the medieval Arabic name of the easternmost and largest of the three provinces of the Jazira, the other two being Diyar Bakr and Diyar Mudar. According to the medieval geographer al-Baladhuri, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by Mu'awiyah in the course of the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Diyar Rabi'a was settled by the Rabi'a tribe.
 W
WGökböri, or Muzaffar ad-Din Gökböri, was a leading emir and general of Sultan Saladin, and ruler of Erbil. He served both the Zengid and Ayyubid rulers of Syria and Egypt. He played a pivotal role in Saladin's conquest of Northern Syria and the Jazira and later held major commands in a number of battles against the Crusader states and the forces of the Third Crusade. He was known as Manafaradin to the Franks of the Crusader states.
 W
WAn incantation bowl, also known as a demon bowl, devil-trap bowl, or magic bowl, is a form of early protective magic found in what is now Iraq and Iran. Produced in the Middle East during late antiquity from the sixth to eighth centuries, particularly in Upper Mesopotamia and Syria, the bowls were usually inscribed in a spiral, beginning from the rim and moving toward the center. Most are inscribed in Jewish Babylonian Aramaic.
 W
WGeorge Maniakes was a prominent general of the Byzantine Empire during the 11th century. He was the catepan of Italy in 1042. He is known as Gyrgir in Scandinavian sagas. He is popularly said to have been extremely tall and well built, almost a giant.
 W
WThe Marwanids were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty in the Diyar Bakr region of Upper Mesopotamia and Armenia, centered on the city of Amid (Diyarbakır). Other cities under their rule were Arzan, Mayyāfāriqīn, Hisn Kayfa (Hasankeyf), Khilāṭ, Manzikart, Arjish.
 W
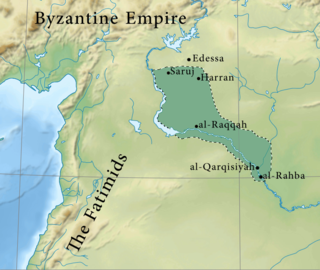
WThe Numayrids were an Arab dynasty based in Diyar Mudar. They were emirs (princes) of their namesake tribe, the Banu Numayr. The senior branch of the dynasty, founded by Waththab ibn Sabiq in 990, ruled the Euphrates cities of Harran, Saruj and Raqqa more or less continuously until the late 11th century. In the early part of Waththab's reign, the Numayrids also controlled Edessa until the Byzantines conquered it in the early 1030s. In 1062, the Numayrids lost Raqqa to their distant kinsmen and erstwhile allies, the Mirdasids, while by 1081, their capital Harran and nearby Saruj were conquered by the Turkish Seljuks and their Arab Uqaylid allies. Numayrid emirs continued to hold isolated fortresses in Upper Mesopotamia, such as Qal'at an-Najm and Sinn Ibn Utayr near Samosata until the early 12th century, but nothing is heard of them after 1120.
 W
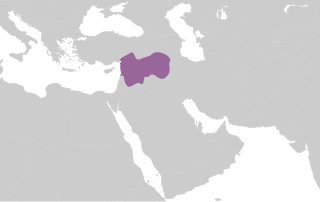
WThe Uqaylid dynasty was a Shi'a Arab dynasty with several lines that ruled in various parts of Al-Jazira, northern Syria and Iraq in the late tenth and eleventh centuries. The main line, centered in Mosul, ruled from 990 to 1096.