 W
WPedro de Alvarado y Contreras was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Guatemala. He participated in the conquest of Cuba, in Juan de Grijalva's exploration of the coasts of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Gulf of Mexico, and in the conquest of Mexico led by Hernán Cortés. He is considered the conquistador of much of Central America, including Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador. Although renowned for his skill as a soldier, Alvarado is known also for the cruelty of his treatment of native populations, and mass murders committed in the subjugation of the native peoples of Mexico.
 W
WAntigua Guatemala, commonly referred to as just Antigua or la Antigua, is a city in the central highlands of Guatemala known for its preserved Spanish Baroque-influenced architecture as well as a number of ruins of colonial churches. It served as the capital of the Kingdom of Guatemala. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage site.
 W
WVasco Núñez de Balboa was a Spanish explorer, governor, and conquistador. He is best known for having crossed the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific Ocean in 1513, becoming the first European to lead an expedition to have seen or reached the Pacific from the New World.
 W
WThe Duchy of Veragua was a Spanish hereditary domain created in 1537 in the reign of King Charles I in a small section of the territory of Veragua. The first Duke of Veragua was Admiral Luis Colón y Toledo, grandson and heir of Christopher Columbus. Holders of this title also lay claim to the title Admiral of the Ocean Sea. The establishment of the duchy was the resolution of a longstanding dispute between the Spanish Crown and the heirs of Columbus, who had claimed a greater area. Luis Colón was also made Marquess of Jamaica.
 W
WNuevo Cartago y Costa Rica was a province of the Kingdom of Guatemala, created in 1540 during the reign of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. It was formed from two earlier Spanish territories. The first of these was Royal Veragua, the territories on the Caribbean coast that had been part of Columbian Veragua before the creation of the Duchy of Veragua in 1537 for Admiral Luis Colón y Toledo, namely present-day Nicaragua, Costa Rica and part of Panama. The second was the Pacific coast that had constituted Castilla de Oro, namely from the Gulf of Nicoya on the west to the borders of the Duchy of Veragua.
 W
WPanamá Viejo, also known as Panamá la Vieja, is the remaining part of the original Panama City, the former capital of the country. It is located in the suburbs of the current capital. Together with the historical district of Panamá, it has been a World Heritage Site since 1997.
 W
WPedro de Portocarrero was a Spanish conquistador who was active in the early 16th century in Guatemala, and Chiapas in southern Mexico. He was one of the few Spanish noblemen that took part in the early stages of the Spanish conquest of the Americas, and was distantly related to prominent conquistador Pedro de Alvarado, who appointed him as an official in early colonial Guatemala.
 W
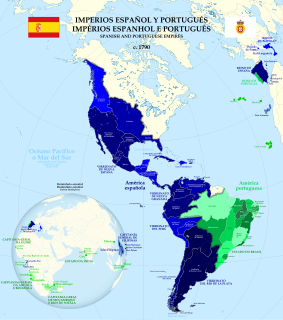
WThe Spanish colonization of the Americas began under the Crown of Castile and spearheaded by the Spanish conquistadors. The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions in South America and the Caribbean. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer this vast territory. The main motivations for colonial expansion were profit through resource extraction and the spread of Catholicism through indigenous conversions.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of El Salvador was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Central American nation of El Salvador. El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America, and is dominated by two mountain ranges running east–west. Its climate is tropical, and the year is divided into wet and dry seasons. Before the conquest the country formed a part of the Mesoamerican cultural region, and was inhabited by a number of indigenous peoples, including the Pipil, the Lenca, the Xinca, and Maya. Native weaponry consisted of spears, bows and arrows, and wooden swords with inset stone blades; they wore padded cotton armour.
 W
WThe Spanish conquest of Guatemala was a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, in which Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries.
 W
WDuring Spain's New World Empire, its mainland coastal possessions surrounding the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico were referred to collectively as the Spanish Main. The southern portion of these coastal possessions were known as the Province of Tierra Firme, or the "Mainland province". The Province of Tierra Firme, or simply Tierra Firme, was also called Costa Firme.