 W
WLaboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery is a system used for virtual surgical planning. Starting with 1998, LUCAS was developed at the University of Regensburg, Germany, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. The resulting surgical planning is then reproduced onto the patient by using a navigation system. In fact, LUCAS is integrated into the same platform together with the Surgical Segment Navigator (SSN), the Surgical Tool Navigator (STN), the Surgical Microscope Navigator (SMN) and the 6DOF Manipulator, also from the Carl Zeiss Company.
 W
WThe N-localizer or N-bar is a device that enables guidance of stereotactic surgery or radiosurgery using tomographic images that are obtained via computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or positron emission tomography (PET). The N-localizer comprises a diagonal rod that spans two vertical rods to form an N-shape and permits calculation of the point where a tomographic image plane intersects the diagonal rod. Attaching three N-localizers to a stereotactic instrument allows calculation of three points where a tomographic image plane intersects three diagonal rods. These points determine the spatial orientation of the tomographic image plane relative to the stereotactic frame.
 W
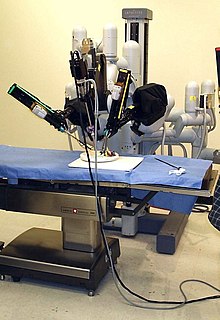
WRobotic surgery are types of surgical procedures that are done using robotic systems. Robotically-assisted surgery was developed to try to overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
 W
WDavid B. Samadi is an American board-certified urologist, a Newsmax contributor, and the former Chairman of Urology and Chief of Robotic Surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital.
 W
WStereolithography is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers. Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1987. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive.
 W
WStereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, biopsy, lesion, injection, stimulation, implantation, radiosurgery (SRS), etc.
 W
WThe surgical planning is the preoperative method of pre-visualising a surgical intervention, in order to predefine the surgical steps and furthermore the bone segment navigation in the context of computer-assisted surgery. The surgical planning is most important in neurosurgery and oral and maxillofacial surgery. The transfer of the surgical planning to the patient is generally made using a medical navigation system.
 W
WThe surgical segment navigator (SSN) is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the surgical tool navigator (STN), the surgical microscope navigator (SMN) and the 6DOF manipulator (MKM), developed by Carl Zeiss.
 W
WThe Vattikuti Urology Institute (VUI) at the Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, Michigan is a clinical and research center for urological care. The VUI is notable for being the first institute to establish robotic surgery as a treatment for patients with prostate cancer. To date, the VUI has performed more than 10,000 robotic procedures. Ranked consistently high by U.S. News & World Report, VUI is also one of the largest and most active urology departments in the United States, with nearly 50,000 patients annually from all 50 states and nearly 25 countries.