 W
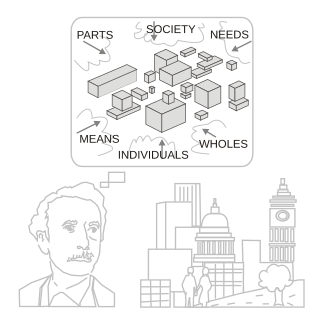
WSystems science is an interdisciplinary field that studies the nature of systems—from simple to complex—in nature, society, cognition, engineering, technology and science itself. To systems scientists, the world can be understood as a system of systems. The field aims to develop interdisciplinary foundations that are applicable in a variety of areas, such as psychology, biology, medicine, communication, business management, technology, computer science, engineering, and social sciences.
 W
WSystems art is art influenced by cybernetics, and systems theory, that reflects on natural systems, social systems and social signs of the art world itself.
 W
WA cascading failure is a process in a system of interconnected parts in which the failure of one or few parts can trigger the failure of other parts and so on. Such a failure may happen in many types of systems, including power transmission, computer networking, finance, transportation systems, organisms, the human body, and ecosystems.
 W
WComplex systems biology (CSB) is a branch or subfield of mathematical and theoretical biology invented by Robert Rosen concerned with complexity of both structure and function in biological organisms, as well as the emergence and evolution of organisms and species, with emphasis being placed on the interconnectivity of, and within, biological network inference, and on modelling the fundamental relations inherent to life.
 W
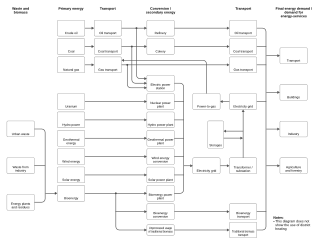
WAn energy system is a system primarily designed to supply energy-services to end-users. Taking a structural viewpoint, the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report defines an energy system as "all components related to the production, conversion, delivery, and use of energy". The field of energy economics includes energy markets and treats an energy system as the technical and economic systems that satisfy consumer demand for energy in the forms of heat, fuels, and electricity.
 W
WLearning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event, but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved.
 W
WThe plateau effect is a force of nature that lessens the effectiveness of once effective measures over time. An example of the plateau effect is when someone's exercise fails to be as effective as in the past, similar to the concept of diminishing returns. A person enters into a period where there is no improvement or a decrease in performance.
 W
WSystems modeling or system modeling is the interdisciplinary study of the use of models to conceptualize and construct systems in business and IT development.