 W
WBrain implants, often referred to as neural implants, are technological devices that connect directly to a biological subject's brain – usually placed on the surface of the brain, or attached to the brain's cortex. A common purpose of modern brain implants and the focus of much current research is establishing a biomedical prosthesis circumventing areas in the brain that have become dysfunctional after a stroke or other head injuries. This includes sensory substitution, e.g., in vision. Other brain implants are used in animal experiments simply to record brain activity for scientific reasons. Some brain implants involve creating interfaces between neural systems and computer chips. This work is part of a wider research field called brain-computer interfaces.
 W
WIn September 2018, the Center for Sensorimotor Neural Engineering (CSNE) changed its name to the Center for Neurotechnology (CNT) to highlight the role of neurotechnologies in healing the brain and spinal cord.
 W
WEduardo Reck Miranda is a Brazilian composer of chamber and electroacoustic pieces but is most notable in the United Kingdom for his scientific research into computer music, particularly in the field of human-machine interfaces where brain waves will replace keyboards and voice commands to permit the disabled to express themselves musically.
 W
WThe neurotrophic electrode is an intracortical device designed to read the electrical signals that the brain uses to process information. It consists of a small, hollow glass cone attached to several electrically conductive gold wires. The term neurotrophic means "relating to the nutrition and maintenance of nerve tissue" and the device gets its name from the fact that it is coated with Matrigel and nerve growth factor to encourage the expansion of neurites through its tip. It was invented by neurologist Dr. Philip Kennedy and was successfully implanted for the first time in a human patient in 1996 by neurosurgeon Roy Bakay.
 W
WThe Shannon criteria constitute an empirical rule in neural engineering that is used for evaluation of possibility of damage from electrical stimulation to nervous tissue.
 W
WA Spinal Cord Stimulator (SCS) or Dorsal Column Stimulator (DCS) is a type of implantable neuromodulation device that is used to send electrical signals to select areas of the spinal cord for the treatment of certain pain conditions. SCS is a consideration for people who have a pain condition that has not responded to more conservative therapy.
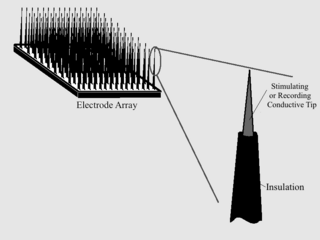 W
WAs with any material implanted in the body, it is important to minimize or eliminate foreign body response and maximize effectual integration. Neural implants have the potential to increase the quality of life for patients with such disabilities as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, epilepsy, depression, and migraines. With the complexity of interfaces between a neural implant and brain tissue, adverse reactions such as fibrous tissue encapsulation that hinder the functionality, occur. Surface modifications to these implants can help improve the tissue-implant interface, increasing the lifetime and effectiveness of the implant.
 W
WWireheading is a term associated with fictional or futuristic applications of brain stimulation reward, the act of directly triggering the brain's reward center by electrical stimulation of an inserted wire, for the purpose of 'short-circuiting' the brain's normal reward process and artificially inducing pleasure. Scientists have successfully performed brain stimulation reward on rats (1950s) and humans (1960s). This stimulation does not appear to lead to tolerance or satiation in the way that sex or drugs do. The term is sometimes associated with science fiction writer Larry Niven, who used the term as early as the 1950s. In the philosophy of artificial intelligence, the term is used to refer to AI systems that hack their own reward channel.