 W
WData Management comprises all disciplines related to managing data as a valuable resource.
 W
WAltitude3.Net is an electronic business development platform that allows to create web and mobile solutions along with interactive communication strategies. The platform has the same functionalities than a content management system (CMS) and communicates with other systems.
 W
WThe Asset Description Metadata Schema (ADMS) is a common metadata vocabulary to describe standards, so-called interoperability assets, on the Web.
 W
WAstroinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of study involving the combination of astronomy, data science, machine learning, informatics, and information/communications technologies.
 W
WAuthor name disambiguation is a type of disambiguation and record linkage applied to the names of individual people. The process could, for example, distinguish individuals with the name "John Smith".
 W
WBig data is a field that treats ways to analyze, systematically extract information from, or otherwise deal with data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data-processing application software. Data with many cases (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data challenges include capturing data, data storage, data analysis, search, sharing, transfer, visualization, querying, updating, information privacy and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: volume, variety, and velocity. When we handle big data, we may not sample but simply observe and track what happens. Therefore, big data often includes data with sizes that exceed the capacity of traditional software to process within an acceptable time and value.
 W
WThe Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) is a standard for organizing, annotating, and describing data collected during neuroimaging experiments. It is based on a formalized file/folder structure and JSON based metadata files with controlled vocabulary. This standard has been adopted by a multitude of labs around the world as well as databases such as OpenNeuro, SchizConnect, Developing Human Connectome Project, and FCP-INDI, and is seeing uptake in an increasing number of studies.
 W
WCambridge Analytica Ltd (CA) was a British political consulting firm that was involved in influencing hundreds of elections globally and that came to prominence through the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data scandal. It was started in 2013 as a subsidiary of the private intelligence company and self-described "global election management agency" SCL Group by long-time SCL executives Nigel Oakes, Alexander Nix and Alexander Oakes, with Nix as CEO. The company had close ties to the Conservative Party (UK), the British royal family and the British military. The firm maintained offices in London, New York City, and Washington, DC. The company closed operations in 2018 in the course of the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data scandal, although related firms still exist.
 W
WCleo is a software company that provides business-to-business (B2B), embedded integration, application-to-application (A2A), cloud integration and big data integration solutions. The privately held company, formally known as Cleo Communications LLC, was founded in 1976, but goes by "Cleo."
 W
WComputer-aided software engineering (CASE) is the domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and were partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE tools are used for developing high-quality, defect-free, and maintainable software. CASE software is often associated with methods for the development of information systems together with automated tools that can be used in the software development process.
 W
WA content format is an encoded format for converting a specific type of data to displayable information. Content formats are used in recording and transmission to prepare data for observation or interpretation. This includes both analog and digitized content. Content formats may be recorded and read by either natural or manufactured tools and mechanisms.
 W
WA control-flow diagram (CFD) is a diagram to describe the control flow of a business process, process or review.
 W
WCouchbase Server, originally known as Membase, is an open-source, distributed multi-model NoSQL document-oriented database software package optimized for interactive applications. These applications may serve many concurrent users by creating, storing, retrieving, aggregating, manipulating and presenting data. In support of these kinds of application needs, Couchbase Server is designed to provide easy-to-scale key-value or JSON document access with low latency and high sustained throughput. It is designed to be clustered from a single machine to very large-scale deployments spanning many machines.
 W
WA dashboard is a type of graphical user interface which often provides at-a-glance views of key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to a particular objective or business process. In other usage, "dashboard" is another name for "progress report" or "report" and considered a form of data visualization.
 W
WData are characteristics or information, usually numerical, that are collected through observation. In a more technical sense, data are a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables about one or more persons or objects, while a datum is a single value of a single variable.
 W
WData analysis is a process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of names, and is used in different business, science, and social science domains. In today's business world, data analysis plays a role in making decisions more scientific and helping businesses operate more effectively.
 W
WA data center or data centre is a building, dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.
 W
WA data grid is an architecture or set of services that gives individuals or groups of users the ability to access, modify and transfer extremely large amounts of geographically distributed data for research purposes. Data grids make this possible through a host of middleware applications and services that pull together data and resources from multiple administrative domains and then present it to users upon request. The data in a data grid can be located at a single site or multiple sites where each site can be its own administrative domain governed by a set of security restrictions as to who may access the data. Likewise, multiple replicas of the data may be distributed throughout the grid outside their original administrative domain and the security restrictions placed on the original data for who may access it must be equally applied to the replicas. Specifically developed data grid middleware is what handles the integration between users and the data they request by controlling access while making it available as efficiently as possible. The adjacent diagram depicts a high level view of a data grid.
 W
WThe Data Reference Model (DRM) is one of the five reference models of the Federal Enterprise Architecture.
 W
WData storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. DNA and RNA, handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Recording may be accomplished with virtually any form of energy. Electronic data storage requires electrical power to store and retrieve data.
 W
WData Transformation Services, or DTS, is a set of objects and utilities to allow the automation of extract, transform and load operations to or from a database. The objects are DTS packages and their components, and the utilities are called DTS tools. DTS was included with earlier versions of Microsoft SQL Server, and was almost always used with SQL Server databases, although it could be used independently with other databases.
 W
WIn computing, a data warehouse, also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis, and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise.
 W
WDigital obsolescence is a situation where a digital resource is no longer readable because of its archaic format. There are two main categories of digital obsolescence:Software: the software needed to access the digital file becomes obsolete. An example here would be WordStar, a word processor popular in the 1980s which used a closed data format. WordStar is no longer readily available and modern machines are not configured to read data in this format. Hardware: the hardware needed to access the digital file becomes obsolete and thus no longer available. One example is the floppy disk and floppy disk drive; the disks are no longer commercially available and modern computers no longer have the drives to read them built in as standard.
 W
WA database is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Where databases are more complex they are often developed using formal design and modeling techniques.
 W
WFAIR data are data which meet principles of findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability. A March 2016 publication by a consortium of scientists and organizations specified the "FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship" in Scientific Data, using FAIR as an acronym and making the concept easier to discuss.
 W
WA flat-file database is a database stored in a file called a flat file. Records follow a uniform format, and there are no structures for indexing or recognizing relationships between records. The file is simple. A flat file can be a plain text file, or a binary file. Relationships can be inferred from the data in the database, but the database format itself does not make those relationships explicit.
 W
WA key–value database, or key–value store, is a data storage paradigm designed for storing, retrieving, and managing associative arrays, and a data structure more commonly known today as a dictionary or hash table. Dictionaries contain a collection of objects, or records, which in turn have many different fields within them, each containing data. These records are stored and retrieved using a key that uniquely identifies the record, and is used to find the data within the database.
 W
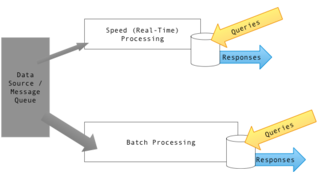
WLambda architecture is a data-processing architecture designed to handle massive quantities of data by taking advantage of both batch and stream-processing methods. This approach to architecture attempts to balance latency, throughput, and fault-tolerance by using batch processing to provide comprehensive and accurate views of batch data, while simultaneously using real-time stream processing to provide views of online data. The two view outputs may be joined before presentation. The rise of lambda architecture is correlated with the growth of big data, real-time analytics, and the drive to mitigate the latencies of map-reduce.
 W
WLearning Object Metadata is a data model, usually encoded in XML, used to describe a learning object and similar digital resources used to support learning. The purpose of learning object metadata is to support the reusability of learning objects, to aid discoverability, and to facilitate their interoperability, usually in the context of online learning management systems (LMS).
 W
WIn computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database.
 W
WMaPS S.A. is a software editor founded in 2011 by Thierry Muller. The company is headquartered in Luxembourg. Its platform, called MaPS System, provides Data Management solutions for Multichannel Marketing.
 W
WMarkLogic Server is a document-oriented database developed by MarkLogic. It is a NoSQL multi-model database that evolved from an XML database to natively store JSON documents and RDF triples, the data model for semantics. MarkLogic is designed to be a data hub for operational and analytical data.
 W
WMetadata management involves managing metadata about other data, whereby this "other data" is generally referred to as content data. The term is used most often in relation to digital media, but older forms of metadata are catalogs, dictionaries, and taxonomies. For example, the Dewey Decimal Classification is a metadata management systems developed in 1876 for libraries.
 W
WMetadata is "data that provides information about other data". In other words, it is "data about data". Many distinct types of metadata exist, including descriptive metadata, structural metadata, administrative metadata, reference metadata and statistical metadata.Descriptive metadata is descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. Structural metadata is metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships and other characteristics of digital materials. Administrative metadata is information to help manage a resource, like resource type, permissions, and when and how it was created. Reference metadata is information about the contents and quality of statistical data. Statistical metadata, also called process data, may describe processes that collect, process, or produce statistical data.
 W
WThe Open Compute Project (OCP) is an organization that shares designs of data center products and best practices among companies, including Facebook, IBM, Intel, Nokia, Google, Microsoft, Seagate Technology, Dell, Rackspace, Cisco, Goldman Sachs, Fidelity, Lenovo and Alibaba Group.
 W
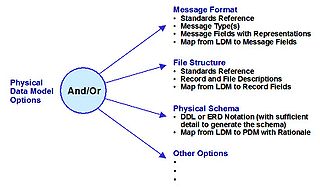
WA physical data model is a representation of a data design as implemented, or intended to be implemented, in a database management system. In the lifecycle of a project it typically derives from a logical data model, though it may be reverse-engineered from a given database implementation. A complete physical data model will include all the database artifacts required to create relationships between tables or to achieve performance goals, such as indexes, constraint definitions, linking tables, partitioned tables or clusters. Analysts can usually use a physical data model to calculate storage estimates; it may include specific storage allocation details for a given database system.
 W
WQuickPar is a computer program that creates parchives used as verification and recovery information for a file or group of files, and uses the recovery information, if available, to attempt to reconstruct the originals from the damaged files and the PAR volumes.
 W
WA recording format is a format for encoding data for storage on a storage medium. The format can be container information such as sectors on a disk, or user/audience information (content) such as analog stereo audio. Multiple levels of encoding may be achieved in one format. For example, a text encoded page may contain HTML and XML encoding, combined in a plain text file format, using either EBCDIC or ASCII character encoding, on a UDF digitally formatted disk.
 W
WSmall Data: the Tiny Clues that Uncover Huge Trends is Martin Lindstrom's seventh book. It chronicles his work as a branding expert, working with consumers across the world to better understand their behavior. The theory behind the book is that businesses can better create products and services based on observing consumer behavior in their homes, as opposed to relying solely on big data.
 W
WA storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
 W
WA super column is a tuple with a binary super column name and a value that maps it to many columns. They consist of a key–value pairs, where the values are columns. Theoretically speaking, super columns are (sorted) associative array of columns. Similar to a regular column family where a row is a sorted map of column names and column values, a row in a super column family is a sorted map of super column names that maps to column names and column values.
 W
WA Virtual Facility (VF) is a highly realistic digital representation of a data center (primarily). The term virtual in Virtual Facility refers to the use of the word as in Virtual Reality rather than the abstraction of computer resources as in platform virtualization. The VF mirrors the characteristics of the physical facility over time and allows modeling all relevant characteristics of a physical data center with a high degree of precision.
 W
WWestminster Digital is a British social media agency which combines video production, data analysis and strategic communication. The firm was used by Boris Johnson during his successful leadership campaign in the 2019 Conservative Party leadership election and during the successful 2019 United Kingdom general election.