 W
WBase station is – according to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – a "land station in the land mobile service."
 W
WThe base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
 W
WThe base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.
 W
WA battery room is a room in a facility used to house batteries for backup or uninterruptible power systems. Battery rooms are found in telecommunication central offices, and to provide standby power to computing equipment in datacenters. Batteries provide direct current (DC) electricity, which may be used directly by some types of equipment, or which may be converted to alternating current (AC) by uninterruptible power supply (UPS) equipment. The batteries may provide power for minutes, hours or days depending on the electrical system design, although most commonly the batteries power the UPS during brief electric utility outages lasting only seconds.
 W
WA cell site, cell tower, or cellular base station is a cellular-enabled mobile device site where antennas and electronic communications equipment are placed—typically on a radio mast, tower, or other raised structure—to create a cell in a cellular network. The raised structure typically supports antenna and one or more sets of transmitter/receivers transceivers, digital signal processors, control electronics, a GPS receiver for timing, primary and backup electrical power sources, and sheltering.
 W
WA cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the last link is wireless. The network is distributed over land areas called "cells", each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, but more normally, three cell sites or base transceiver stations. These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. A cell typically uses a different set of frequencies from neighbouring cells, to avoid interference and provide guaranteed service quality within each cell.
 W
WIn radio communication, a control channel is a central channel that controls other constituent radios by handling data streams. It is most often used in the context of a trunked radio system, where the control channel sends various data which coordinates users in talkgroups.
 W
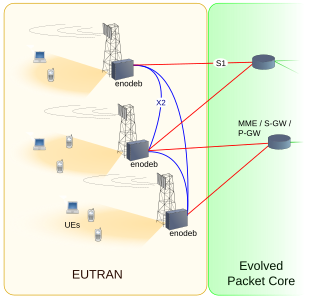
WE-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial Radio Access, also referred to as the 3GPP work item on the Long Term Evolution (LTE) also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the initialism of Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network and is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and E-UTRAN Node B or Evolved Node B (EnodeB).
 W
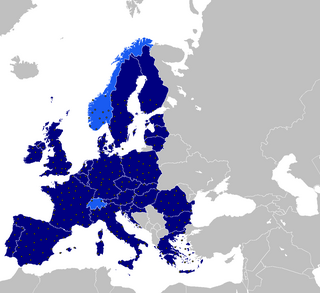
WThe European Aviation Network is a hybrid-network built by Deutsche Telekom and Inmarsat in cooperation with their technological partner Nokia. It is used as a backhaul for in-flight WiFi for domestic flights within Europe and contains a LTE ground network supported by a satellite connection. Because of the LTE technology the network can achieve data rates up to 75 Mbit/s downstream and 20 Mbit/s upstream per airplane, with a total capacity of 50Gbps.
 W
WA telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers.
 W
WIn telecommunications, a femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station, typically designed for use in a home or small business. A broader term which is more widespread in the industry is small cell, with femtocell as a subset. It is also called femto AccessPoint (AP). It connects to the service provider's network via broadband ; current designs typically support four to eight simultaneously active mobile phones in a residential setting depending on version number and femtocell hardware, and eight to sixteen mobile phones in enterprise settings. A femtocell allows service providers to extend service coverage indoors or at the cell edge, especially where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable. Although much attention is focused on WCDMA, the concept is applicable to all standards, including GSM, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, WiMAX and LTE solutions.
 W
WIn electrical engineering, a ground plane is an electrically conductive surface, usually connected to electrical ground. The term has two different meanings in separate areas of electrical engineering. In antenna theory, a ground plane is a conducting surface large in comparison to the wavelength, such as the Earth, which is connected to the transmitter's ground wire and serves as a reflecting surface for radio waves. In printed circuit boards, a ground plane is a large area of copper foil on the board which is connected to the power supply ground terminal and serves as a return path for current from different components on the board.
 W
WA ground segment consists of all the ground-based elements of a spacecraft system used by operators and support personnel, as opposed to the space segment and user segment. The ground segment enables management of a spacecraft, and distribution of payload data and telemetry among interested parties on the ground. The primary elements of a ground segment are:Ground stations, which provide radio interfaces with spacecraft Mission control centers, from which spacecraft are managed Ground networks, which connect the other ground elements to one another Remote terminals, used by support personnel Spacecraft integration and test facilities Launch facilities
 W
WA ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft, or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands. When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft, it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna.
 W
WThe Imperial Wireless Chain was a strategic international communications network of powerful long range radiotelegraphy stations, created by the British government to link the countries of the British Empire. The stations exchanged commercial and diplomatic text message traffic transmitted at high speed by Morse code using paper tape machines. Although the idea was conceived prior to World War I, the United Kingdom was the last of the world's great powers to implement an operational system. The first link in the chain, between Leafield in Oxfordshire and Cairo, Egypt, eventually opened on 24 April 1922, with the final link, between Australia and Canada, opening on 16 June 1928.
 W
WAn information infrastructure is defined by Ole Hanseth (2002) as "a shared, evolving, open, standardized, and heterogeneous installed base" and by Pironti (2006) as all of the people, processes, procedures, tools, facilities, and technology which supports the creation, use, transport, storage, and destruction of information.
 W
WThe INOC-DBA hotline phone system is a global voice telephony network deployed and managed by Packet Clearing House that connects the network operations centers and security incident response teams of critical Internet infrastructure providers such as backbone carriers, Internet service providers, and Internet exchanges as well as critical individuals within the policy, regulatory, Internet governance, security and vendor communities.
 W
WA mobile station (MS) comprises all user equipment and software needed for communication with a mobile network.
 W
WThe mobile switching station, abbreviated as MSC Server or MSS, is a 2G core network element which controls the network switching subsystem elements. Alternatively or adaptively, MSS can be used in GSM networks as well, if the manufacturer has implemented support for GSM networks in the MSS. Since an immediate upgrade of existing GSM network to 3G is not viable due to various issues like handset incompatibilities and high expenditure, most manufacturers do implement GSM support in MSS. In fact, MSS along with other 3G network elements such as media gateway (MGW), can be configured to support GSM network exclusively and can be considered as an upgraded version of existing GSM mobile switching centres. The MSC Server is standards-based and communicates with other distributed elements using industry open standards such as media gateway control protocol, megaco/H.248, session initiation protocol, M2UA and M3UA. The MSC server incorporates industry standards as defined by ETSI, ITU, GSM, 3GPP and 3GPP2 and other leading standard bodies. The MSS supports the regulatory environment set by governing bodies via its support for E911, CALEA/legal intercept, wireless and local number portability, TTY/TTD, and Number Pooling requirements.
 W
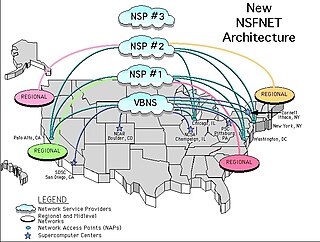
WA Network Access Point (NAP) was a public network exchange facility where Internet service providers (ISPs) connected with one another in peering arrangements. The NAPs were a key component in the transition from the 1990s NSFNET era to the commercial Internet providers of today. They were often points of considerable Internet congestion.
 W
WOppenheimer poles are galvanised iron telegraph poles. They consist of three oval sections that collapse into each other telescope style for transportation. Once extended the joints between the sections are clamped with collars. The pole is fixed to a base for support with a u-bolt.
 W
WIn telecommunication, the term outside plant has the following meanings:In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure, and any associated hardware located between a demarcation point in a switching facility and a demarcation point in another switching center or customer premises. In the United States, the DOD defines outside plant as the communications equipment located between a main distribution frame (MDF) and a user end instrument.
 W
WAn overhead cable is a cable for the transmission of information, laid on utility poles. Overhead telephone and cable TV lines are common in North America. These poles sometimes carry overhead power lines for the supply of electric power. Power supply companies may also use them for an in-house communication network. Sometimes these cables are integrated in the ground or power conductor. Otherwise an additional line is strung on the masts.
 W
WA passive repeater or passive radio link deflection, is a reflective or sometimes refractive panel or other object that assists in closing a radio or microwave link, in places where an obstacle in the signal path blocks any direct, line of sight communication.
 W
WA remote radio head (RRH), also called a remote radio unit (RRU) in wireless networks, is a remote radio transceiver that connects to an operator radio control panel via electrical or wireless interface. When used to describe aircraft radio cockpit radio systems, the control panel is often called the radio head.
 W
WDue to economy of scale property of telecommunication industry, sharing of telecom infrastructure among telecom service providers is becoming the requirement and process of business in the telecom industry where competitors are becoming partners in order to lower their increasing investments. The degree and method of infrastructure sharing can vary in each country depending on regulatory and competitive climate.
 W
WTelecommunication networks can generate a vast amount of transactions where each transaction contains information about a particular subscriber's activity. Telecommunication network consist of various interacting devices and platforms. Any transaction carried out by a subscriber is often recorded in multiple devices as it passes through the network. Telecommunication organizations generally need to be able to extract transaction information from these various network elements in order to correctly bill subscribers for the usage on the network. Transaction processing system is a subset of information systems, and in the telecommunications industry, forms an integral part of the management information system. TPS can be regarded as the link between the various network elements and platforms and the information management uses to drive the business.
 W
WA telecommunications network is a group of nodes interconnected by links that are used to exchange messages between the nodes. The links may use a variety of technologies based on the methodologies of circuit switching, message switching, or packet switching, to pass messages and signals. For each message, multiple nodes may cooperate to pass the message from an originating node to the a destination node, via multiple network hops. For this routing function each node in the network is assigned a network address for identification and locating it on the network. The collection of addresses in the network is called the address space of the network.
 W
WA telephone line or telephone circuit is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. This is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver landline telephone service and Digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network.
 W
WA utility pole is a column or post used to support overhead power lines and various other public utilities, such as electrical cable, fiber optic cable, and related equipment such as transformers and street lights. It can be referred to as a transmission pole, telephone pole, telecommunication pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post, depending on its application. A Stobie pole is a multi-purpose pole made of two steel joists held apart by a slab of concrete in the middle, generally found in South Australia.
 W
WIn computer networking, a wireless access point (WAP), or more generally just access point (AP), is a networking hardware device that allows other Wi-Fi devices to connect to a wired network. As a standalone device, the AP may have a wired connection to a router, but, in a wireless router, it can also be an integral component of the router itself. An AP is differentiated from a hotspot which is a physical location where Wi-Fi access is available.