 W
WBiomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare purposes. BME is also traditionally known as "bioengineering", but this term has come to also refer to biological engineering. This field seeks to close the gap between engineering and medicine, combining the design and problem solving skills of engineering with medical biological sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment within hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves making equipment recommendations, procurement, routine testing and preventive maintenance, a role also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or as clinical engineering.
 W
WThe American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE) is a non-profit organization founded in 1991, and headquartered in Washington. It represents 50,000 medical and biomedical engineers, and academic institutions, private industry, and professional engineering societies. J-S Lee has provide a history of the organization of AIMBE.
 W
WApplied Spectral Imaging or ASI is a multinational biomedical company that develops and manufactures microscopy imaging and digital analysis tools for hospitals, service laboratories and research centers. The company provides cytogenetic, pathology and research laboratories with brightfield, fluorescence and spectral imaging clinical applications. Test slides can be scanned, captured, archived, reviewed on screen, analyzed with computer-assisted algorithms and reported. ASI system platforms automate the workflow process to reduce human error in the identification and classification of chromosomal disorders, genome instability, various oncological malignancies, among other diseases.
 W
WArgus retinal prosthesis, also known as a bionic eye, is an electronic retinal implant manufactured by the American company Second Sight Medical Products. It is used as a visual prosthesis to improve the vision of people with severe cases of retinitis pigmentosa. The Argus II version of the system was approved for marketing in the European Union in March 2011, and it received approval in the US in February 2013 under a humanitarian device exemption. The Argus II system costs about US$150,000, excluding the cost of the implantation surgery and training to learn to use the device.
 W
WA cardiac pacemaker, is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to cause the heart muscle chambers to contract and therefore pump blood; by doing so this device replaces and/or regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart.
 W
WBio-MEMS is an abbreviation for biomedical microelectromechanical systems. Bio-MEMS have considerable overlap, and is sometimes considered synonymous, with lab-on-a-chip (LOC) and micro total analysis systems (μTAS). Bio-MEMS is typically more focused on mechanical parts and microfabrication technologies made suitable for biological applications. On the other hand, lab-on-a-chip is concerned with miniaturization and integration of laboratory processes and experiments into single chips. In this definition, lab-on-a-chip devices do not strictly have biological applications, although most do or are amenable to be adapted for biological purposes. Similarly, micro total analysis systems may not have biological applications in mind, and are usually dedicated to chemical analysis. A broad definition for bio-MEMS can be used to refer to the science and technology of operating at the microscale for biological and biomedical applications, which may or may not include any electronic or mechanical functions. The interdisciplinary nature of bio-MEMS combines material sciences, clinical sciences, medicine, surgery, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, optical engineering, chemical engineering, and biomedical engineering. Some of its major applications include genomics, proteomics, molecular diagnostics, point-of-care diagnostics, tissue engineering, single cell analysis and implantable microdevices.
 W
WBioceramics and bioglasses are ceramic materials that are biocompatible. Bioceramics are an important subset of biomaterials. Bioceramics range in biocompatibility from the ceramic oxides, which are inert in the body, to the other extreme of resorbable materials, which are eventually replaced by the body after they have assisted repair. Bioceramics are used in many types of medical procedures. Bioceramics are typically used as rigid materials in surgical implants, though some bioceramics are flexible. The ceramic materials used are not the same as porcelain type ceramic materials. Rather, bioceramics are closely related to either the body's own materials or are extremely durable metal oxides.
 W
WCardiac Pacemakers, Inc.(CPI), doing business as Guidant Cardiac Rhythm Management, manufactured implantable cardiac rhythm management devices, such as pacemakers and defibrillators. It also sold insulin pumps controlled by microprocessors and various equipments to regulate heart rhythm. In addition, Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. developed therapies for the treatment of irregular heartbeats. The company was founded in 1971 and is based in St. Paul, Minnesota. Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. operates as a subsidiary of Boston Scientific Corporation.
 W
WCell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.
 W
WEnding Aging: The Rejuvenation Breakthroughs that Could Reverse Human Aging in Our Lifetime is a 2007 book written by Aubrey de Grey, a biomedical gerontologist, with his research assistant Michael Rae. Ending Aging describes de Grey's proposal for eliminating aging as a cause of debilitation and death in humans, and restoring the body to an indefinitely youthful state, a project plan that he calls the "Strategies for Engineered Negligible Senescence", or "SENS". De Grey argues that defeating aging is feasible, possibly within a few decades, and he outlines steps that can be taken to hasten the development of regenerative medicine treatments that will save lives.
 W
WIn cardiac surgery and vascular surgery, external support is a type of scaffold made of metal or plastic material that is inserted over the outside of the vein graft in order to decrease the intermediate and late vein graft failure after bypass surgery.
 W
WFantastic Voyage: Live Long Enough to Live Forever is a book authored by Ray Kurzweil and Terry Grossman published in 2004. The basic premise of the book is that if middle aged people can live long enough, until approximately 120 years, they will be able to live forever—as humanity overcomes all diseases and old age itself. This might also be considered a break-even scenario where developments made during a year increase life expectancy by more than one year. Biogerontologist Aubrey de Grey called this the "Longevity escape velocity" in a 2005 TED talk.
 W
WA heart rate monitor (HRM) is a personal monitoring device that allows one to measure/display heart rate in real time or record the heart rate for later study. It is largely used to gather heart rate data while performing various types of physical exercise. Measuring electrical heart information is referred to as Electrocardiography.
 W
WThe Institute of Biomedical Engineering (BME) is an academic unit at the University of Toronto. The main goal of the institute is provide graduate education and advance research in the field of biomedical engineering. Established in 1962 by Dr. Norman Moody under the moniker 'Institute of Biomedical Electronics', the Institute has taken on several other names in the past.
 W
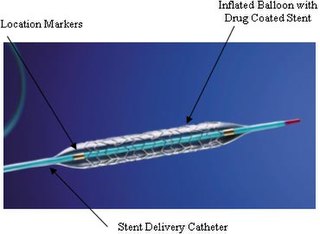
WAn implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are bioactive, such as subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents.
 W
WThe International Federation of Medical and Biological Engineering (IFMBE) was initially formed as International Federation for Medical Electronics and Biological Engineering during the 2nd International Conference of Medical and Biological Engineering, in the UNESCO Building, Paris, France in 1959. It is primarily a federation of national and transnational organizations. These organizations represent national interests in medical and biological engineering.
 W
WMetabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.
 W
WMaterialise Mimics is an image processing software for 3D design and modeling, developed by Materialise NV, a Belgian company specialized in additive manufacturing software and technology for medical, dental and additive manufacturing industries. Materialise Mimics is used to create 3D surface models from stacks of 2D image data. These 3D models can then be used for a variety of engineering applications. Mimics is an acronym for Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System. It is developed in an ISO environment with CE and FDA 510k premarket clearance. Materialise Mimics is commercially available as part of the Materialise Mimics Innovation Suite, which also contains Materialise 3-matic, a design and meshing software for anatomical data. The current version is 20.0, it supports Windows 10, Windows 7, Vista and XP in x64.
 W
WA needle remover is a device used to physically remove a needle from a syringe. In developing countries, there is still a need for improvements in needle safety in hospital settings as most of the needle removal processes are done manually and under severe risk of hazard from needles puncturing skin risking infection. These countries cannot afford needles with individual safety devices attached, so needle-removers must be used to remove the needle from the syringe. This lowers possible pathogen spread by preventing the reuse of the syringes, reducing incidents of accidental needle-sticks, and facilitating syringe disposal.
 W
WThe Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal that covers the field of biomedical engineering. It was established in 1971 as Engineering in Medicine, obtaining its current title in 1989. The journal is published by Sage Publications on behalf of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers.
 W
WIn medicine, a prosthesis or prosthetic implant is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth. Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools.
 W
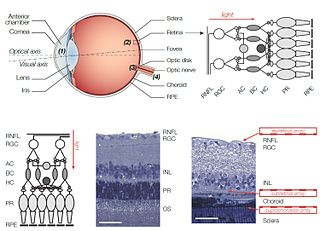
WRetinal prostheses for restoration of sight to patients blinded by retinal degeneration are being developed by a number of private companies and research institutions worldwide. The system is meant to partially restore useful vision to people who have lost their photoreceptors due to retinal diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa (RP) or age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Three types of retinal implants are currently in clinical trials: epiretinal, subretinal, and suprachoroidal. Retinal implants introduce visual information into the retina by electrically stimulating the surviving retinal neurons. So far, elicited percepts had rather low resolution, and may be suitable for light perception and recognition of simple objects.
 W
WSynopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
 W
WSix degrees of freedom (6DoF) refers to the freedom of movement of a rigid body in three-dimensional space. Specifically, the body is free to change position as forward/backward (surge), up/down (heave), left/right (sway) translation in three perpendicular axes, combined with changes in orientation through rotation about three perpendicular axes, often termed yaw, pitch, and roll. Three degrees of freedom (3DOF), a term often used in the context of virtual reality, refers to tracking of rotational motion only: pitch, yaw, and roll.
 W
WThe Starling resistor was invented by English physiologist Ernest Starling and used in an isolated-heart preparation during work which would later lead to the "Frank–Starling law of the heart".
 W
WSurface and bulk erosion are two different forms of erosion that describe how a degrading polymer erodes. In surface erosion, the polymer degrades from the exterior surface. The inside of the material does not degrade until all the surrounding material around it has been degraded. In bulk erosion, degradation occurs throughout the whole material equally. Both the surface and the inside of the material degrade. Surface erosion and bulk erosion are not exclusive, many materials undergo a combination of surface and bulk erosion. Therefore, surface and bulk erosion can be thought of as a spectrum instead of two separate categories.
 W
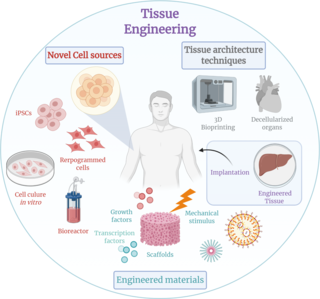
WTissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own.