 W
WA megastructure is a very large artificial object, although the limits of precisely how large vary considerably. Some apply the term to any especially large or tall building. Some sources define a megastructure as an enormous self-supporting artificial construct. The products of megascale engineering or astroengineering are megastructures. The lower bound of megastructural engineering might be considered any structure that has any single dimension 1 megameter (1000km) in length.
 W
WAn Alderson disk is a hypothetical artificial astronomical megastructure, like Larry Niven's Ringworld and the Dyson sphere. The disk is a giant platter with a thickness of several thousand miles. The Sun rests in the hole at the center of the disk. The outer perimeter of an Alderson disk would be roughly equivalent to the orbit of Mars or Jupiter. According to the proposal, a sufficiently large disk would have a larger mass than its Sun.
 W
WArcology, a portmanteau of "architecture" and "ecology", is a field of creating architectural design principles for very densely populated, ecologically low-impact human habitats.
 W
WAtlantropa, also referred to as Panropa, was a gigantic engineering and colonisation idea that was devised by the German architect Herman Sörgel in the 1920s and promoted by him until his death, in 1952. Its central feature was a hydroelectric dam to be built across the Strait of Gibraltar, which would have provided enormous amounts of hydroelectricity and would have led to the lowering of the surface of the Mediterranean Sea by up to 200 metres (660 ft), opening up large new lands for settlement, such as in the Adriatic Sea. The project proposed four additional major dams as well:Across the Dardanelles to hold back the Black Sea Between Sicily and Tunisia to provide a roadway and lower the inner Mediterranean further On the Congo River below its Kwah River tributary to refill the Mega-Chad basin around Lake Chad to provide fresh water to irrigate the Sahara and create a shipping lane to the interior of Africa Suez Canal extension and locks to maintain a Red Sea connection
 W
WCoruscant is an ecumenopolis planet in the fictional Star Wars universe. It first appeared onscreen in the 1997 Special Edition of Return of the Jedi, but was first depicted and mentioned by name in Timothy Zahn's 1991 novel Heir to the Empire. Coruscant is a prominent location in both canon and Legends media that has been produced. Within the narrative of the films, Coruscant-based locations such as the Jedi Temple and Jedi Archives act as the home for the Jedi and in plot terms are frequently used for exposition or to drive other elements of the plot.
 W
WThe Death Star a fictional mobile space station and galactic superweapon featured in the Star Wars space-opera franchise. The first version, which appears in the original 1977 film Star Wars, is stated to be more than 160 kilometers (99 mi) in diameter, and is crewed by an estimated 1.7 million military personnel and 400,000 droids. The second Death Star appears in Return of the Jedi, and is significantly larger at 900 kilometres (560 mi) in diameter and while unfinished, is technologically more advanced than its predecessor. Built by the Galactic Empire to strengthen its control over the galaxy, both Death Stars are armed with kyber krystal-powered superlasers, which can destroy entire planets. The first Death Star requires significant time to fully recharge the laser.
 W
WA Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure that completely encompasses a star and captures a large percentage of its power output. The concept is a thought experiment that attempts to explain how a spacefaring civilization would meet its energy requirements once those requirements exceed what can be generated from the home planet's resources alone. Only a tiny fraction of a star's energy emissions reach the surface of any orbiting planet. Building structures encircling a star would enable a civilization to harvest far more energy.
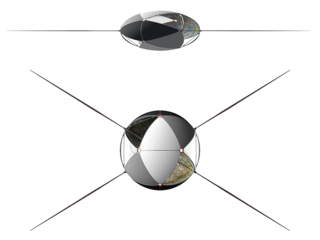 W
WGlobus Cassus is an art project and book by Swiss architect and artist Christian Waldvogel presenting a conceptual transformation of Planet Earth into a much bigger, hollow, artificial world with an ecosphere on its inner surface. It was the Swiss contribution to the 2004 Venice Architecture Biennale and was awarded the Gold Medal in the category "Most beautiful books of the World" at the Leipzig Book Fair in 2005. It consists of a meticulous description of the transformation process, a narrative of its construction, and suggestions on the organizational workings on Globus Cassus.
 W
WThe Halo Array is a group of fictional megastructures and superweapons in the Halo science fiction franchise, consisting of ringworlds known as Halos built by structures known as the Ark. They are referred to as "Installations" by their artificial intelligence caretakers, and were created by an ancient race known as the Forerunners. The series' alien antagonists, the Covenant, refer to the Halos as the "Sacred Rings", believing them to form part of a greater religious prophecy known as "The Great Journey". In the games' stories, the Forerunners built the Halo Array to contain and study the Flood, an infectious alien parasite. The rings act together as a weapon of last resort; when fired, they kill all sentient life in the galaxy capable of falling prey to the Flood, thereby starving the parasite of its food. The battle to prevent their activation forms the crux of the plot progression for the first Halo trilogy of games.
 W
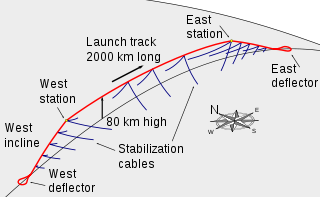
WA launch loop, or Lofstrom loop, is a proposed system for launching objects into orbit using a moving cable-like system situated inside a sheath attached to the Earth at two ends and suspended above the atmosphere in the middle. The design concept was published by Keith Lofstrom and describes an active structure maglev cable transport system that would be around 2,000 km (1,240 mi) long and maintained at an altitude of up to 80 km (50 mi). A launch loop would be held up at this altitude by the momentum of a belt that circulates around the structure. This circulation, in effect, transfers the weight of the structure onto a pair of magnetic bearings, one at each end, which support it.
 W
WThis is a list of buildings and other structures that have been envisioned. The definition of 'vision' is that used by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat.
 W
WLuna Ring is a speculative engineering project which consists in a series of solar generators, disposed around the equator of the Moon, that could send the generated electric energy back to the Earth via microwaves from the near side of the Moon. The project was proposed by Japanese construction firm Shimizu Corporation, after the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami destroyed the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, creating public opposition against nuclear electric energy. Until then, Japan had relied heavily on nuclear power.
 W
WMegastructures is a documentary television series appearing on the National Geographic Channel in the United States and the United Kingdom, Channel 5 in the United Kingdom, France 5 in France, and 7mate in Australia.
 W
WThe O'Neill cylinder is a space settlement concept proposed by American physicist Gerard K. O'Neill in his 1976 book The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space. O'Neill proposed the colonization of space for the 21st century, using materials extracted from the Moon and later from asteroids.
 W
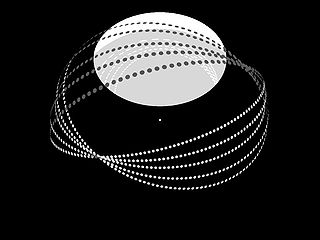
WAn orbital ring is a concept of an enormous artificial ring placed around the Earth that rotates at an angular rate that is faster than the rotation of the Earth.
 W
WRingworld is a 1970 science fiction novel by Larry Niven, set in his Known Space universe and considered a classic of science fiction literature. Ringworld tells the story of Louis Wu and his companions on a mission to the Ringworld, a rotating wheel space station, an alien construct in space 186 million miles in diameter. Niven later added three sequel novels and then cowrote, with Edward M. Lerner, four prequels and a final sequel; the five latter novels constitute the Fleet of Worlds series. All the Ringworld novels tie into numerous other books set in Known Space. Ringworld won the Nebula Award in 1970, as well as both the Hugo Award and Locus Award in 1971.
 W
WA skyhook is a proposed momentum exchange tether that aims to reduce the cost of placing payloads into low Earth orbit. A heavy orbiting station is connected to a cable which extends down towards the upper atmosphere. Payloads, which are much lighter than the station, are hooked to the end of the cable as it passes, and are then flung into orbit by rotation of the cable around the center of mass. The station can then be reboosted to its original altitude by electromagnetic propulsion, rocket propulsion, or by deorbiting another object with the same kinetic energy as transferred to the payload.
 W
WA space elevator is a proposed type of planet-to-space transportation system. The main component would be a cable anchored to the surface and extending into space. The design would permit vehicles to travel along the cable from a planetary surface, such as the Earth's, directly into space or orbit, without the use of large rockets. An Earth-based space elevator would consist of a cable with one end attached to the surface near the equator and the other end in space beyond geostationary orbit. The competing forces of gravity, which is stronger at the lower end, and the outward/upward centrifugal force, which is stronger at the upper end, would result in the cable being held up, under tension, and stationary over a single position on Earth. With the tether deployed, climbers could repeatedly climb the tether to space by mechanical means, releasing their cargo to orbit. Climbers could also descend the tether to return cargo to the surface from orbit.
 W
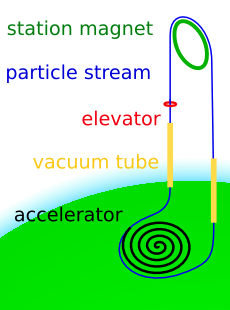
WA space fountain is a proposed form of an extremely tall tower extending into space. As known materials cannot support a static tower with this height, a space fountain has to be an active structure: A stream of pellets is accelerated upwards at a ground station. At the top it is deflected downwards. The necessary force for this deflection supports the station at the top and payloads going up the structure. Spacecraft could launch from the top without having to deal with the atmosphere. This could reduce the cost of placing payloads into orbit. As downside the tower will collapse if the containment systems fail and the stream is broken. This risk could be reduced by several redundant streams.
 W
WA space gun, sometimes called a Verne gun because of its appearance in From the Earth to the Moon by Jules Verne, is a method of launching an object into space using a large gun- or cannonlike structure. Space guns could thus potentially provide a method of non-rocket spacelaunch. It has been conjectured that space guns could place satellites into Earth's orbit, and could also launch spacecraft beyond Earth's gravitational pull and into other parts of the Solar System by exceeding Earth's escape velocity of about 11.20 km/s. However, these speeds are too far into the hypersonic range for most practical propulsion systems and also would cause most objects to burn up due to aerodynamic heating or be torn apart by aerodynamic drag. Therefore, a more likely future use of space guns would be to launch objects into near Earth orbit, from where attached rockets could be fired or the objects could be "collected" by maneuverable orbiting satellites.
 W
WThe Stanford torus is a proposed NASA design for a space habitat capable of housing 10,000 to 140,000 permanent residents.
 W
WStarTram is a proposed space launch system propelled by maglev. The initial Generation 1 facility would launch cargo only, launching from a mountain peak at an altitude of 3 to 7 kilometres with an evacuated tube staying at local surface level; it has been claimed that about 150,000 tons could be lifted to orbit annually. More advanced technology would be required for the Generation 2 system for passengers, with a longer track instead gradually curving up at its end to the thinner air at 22 kilometres (14 mi) altitude, supported by magnetic levitation, reducing g-forces when each capsule transitions from the vacuum tube to the atmosphere. A SPESIF 2010 presentation stated that Generation 1 could be completed by the year 2020 or later if funding began in 2010, and Generation 2 by 2030 or later.
 W
WStellar engines are a class of hypothetical megastructures which use a star's radiation to create usable energy. The concept has been introduced by Badescu and Cathcart. Some variants use this energy to produce thrust, and thus accelerate a star, and anything orbiting it, in a given direction. The creation of such a system would make its builders a Type-II civilization on the Kardashev scale.
 W
WA topopolis is a proposed tube-like space habitat, rotating to produce artificial gravity via centrifugal force on the inner surface, which is extended into a loop around the local star. Topopoles can be looped several times around the local star, in a geometric figure known as a torus knot. The concept was invented by Pat Gunkel and mentioned by Larry Niven in the essay "Bigger Than Worlds" (1974). Topopolises are also called cosmic spaghetti.
 W
WUnicron is a fictional supervillain from the many continuities in the Transformers universe and toyline. Designed by Floro Dery, he was introduced in the 1986 animated film The Transformers: The Movie and has since reappeared in Transformers: Armada, Transformers: Energon, Transformers: Cybertron, Transformers: Prime, Transformers: The Last Knight and Atari's 2004 Transformers video game. Unicron is a prodigiously large robot whose scale reaches planetary proportions, and he is also able to transform into a giant planet. Unicron's origin has expanded over the years from simply being a large robot to being a god of chaos who devours realities. He often employs the help of Decepticons in his work, and in some stories is considered part of the origin of the Decepticon forces.
 W
WThe X-Seed 4000 was a visionary skyscraper. The idea was initially created and developed by Martin Pascoe. Its proposed 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) height, 6-kilometre-wide (3.7 mi) sea-base, and 800-floor capacity could accommodate 500,000 to 1,000,000 inhabitants. This structure would be composed of over 3,000,000 tons of steel.