 W
WSound recording and reproduction is an electrical, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording.
 W
WSound recording and reproduction is an electrical, mechanical, electronic, or digital inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording.
 W
WAmbisonics is a full-sphere surround sound format: in addition to the horizontal plane, it covers sound sources above and below the listener.
 W
WAudio editing software is software which allows editing and generating of audio data. Audio editing software can be implemented completely or partly as a library, as a computer application, as a web application, or as a loadable kernel module. Wave Editors are digital audio editors and there are many sources of software available to perform this function. Most can edit music, apply effects and filters, adjust stereo channels, etc.
 W
WAuro 11.1 is one of the cinematic speaker layouts of the Auro-3D format, invented in 2005 by Wilfried Van Baelen. The Auro 11.1 cinema audio format is supported by Barco, a global visualization technology and digital cinema projection company.
 W
WA bat detector is a device used to detect the presence of bats by converting their echolocation ultrasound signals, as they are emitted by the bats, to audible frequencies, usually about 120 Hz to 15 kHz. There are other types of detectors which record bat calls so that they can be analysed afterward, but these are more commonly referred to by their particular function.
 W
WCenter channel refers to an audio channel common to many surround sound formats. It is the channel that is mostly, or fully, dedicated to the reproduction of the dialogue of an audiovisual program. The speaker(s) connected to the center channel are placed in the center of and behind the perforated projection screen, to give the effect that sounds from the center channel are coming from the screen. In many home surround sound units, the center channel is positioned above or below the video screen.
 W
WFred Roy Cizek was an American inventor, hi-fi designer, and manufacturer.
 W
WDigital room correction is a process in the field of acoustics where digital filters designed to ameliorate unfavorable effects of a room's acoustics are applied to the input of a sound reproduction system. Modern room correction systems produce substantial improvements in the time domain and frequency domain response of the sound reproduction system.
 W
WThe University of Southampton is a research university in Southampton, England. The university's origins date back to the founding of the Hartley Institution in 1862. In 1902, the Institution developed into the Hartley University College, awarding degrees from the University of London. On 29 April 1952, the institution was granted full university status, allowing it to award its own degrees.
 W
WAn isolation booth is a cabinet used to prevent a person or people from seeing or hearing certain events, usually for television programs or for blind testing of products.
 W
WMultichannel Audio Digital Interface (MADI) or AES10 is an Audio Engineering Society (AES) standard that defines the data format and electrical characteristics of an interface that carries multiple channels of digital audio. The AES first documented the MADI standard in AES10-1991, and updated it in AES10-2003 and AES10-2008. The MADI standard includes a bit-level description and has features in common with the two-channel AES3 interface.
 W
WMonaural or monophonic sound reproduction is sound intended to be heard as if it were emanating from one position. This contrasts with stereophonic sound or stereo, which uses two separate audio channels to reproduce sound from two microphones on the right and left side, which is reproduced with two separate loudspeakers to give a sense of the direction of sound sources. In mono, only one loudspeaker is necessary, but, when played through multiple loudspeakers or headphones, identical signals are fed to each speaker, resulting in the perception of one-channel sound "imaging" in one sonic space between the speakers. Monaural recordings, like stereo ones, typically use multiple microphones fed into multiple channels on a recording console, but each channel is "panned" to the center. In the final stage, the various center-panned signal paths are usually mixed down to two identical tracks, which, because they are identical, are perceived upon playback as representing a single unified signal at a single place in the soundstage. In some cases, multitrack sources are mixed to a one-track tape, thus becoming one signal. In the mastering stage, particularly in the days of mono records, the one- or two-track mono master tape was then transferred to a one-track lathe intended to be used in the pressing of a monophonic record. Today, however, monaural recordings are usually mastered to be played on stereo and multi-track formats, yet retain their center-panned mono soundstage characteristics.
 W
WProducing Great Sound for Film and Video: Expert Tips from Preproduction to Final Mix is a non-fiction book and filmmaking handbook. The book is also used as a university textbook. It covers the process of acquiring professional quality sound for motion picture productions.
 W
WProfessional audio, abbreviated as pro audio, refers to both an activity and a category of high quality, studio-grade audio equipment. Typically it encompasses sound recording, sound reinforcement system setup and audio mixing, and studio music production by trained sound engineers, audio engineers, record producers, and audio technicians who work in live event support and recording using mixing consoles, recording equipment and sound reinforcement systems. Professional audio is differentiated from consumer- or home-oriented audio, which are typically geared toward listening in a non-commercial environment.
 W
WQuadrafile was an LP recording released in 1976 intended as a demonstration of four different systems of quadraphonic sound reproduction on phonograph records.
 W
WA road case, ATA case or flight case is a shipping container specifically built to protect musical instruments, motion picture equipment, audio and lighting production equipment, properties, firearms, or other sensitive equipment when it must be frequently moved between locations by ground or air. Many varying-sized road cases can be built to outfit the needs of an entire concert tour, or custom designed individually for a specific industry or product.
 W
WShowco was a sound equipment provider of touring sound reinforcement equipment and services to the concert touring industry. It was based in Dallas, Texas, United States. In 2000, Showco was acquired by Clair Global.
 W
WA soundcheck is the preparation that takes place before a concert, speech, or similar performance to adjust the sound on the venue's sound reinforcement system or PA system. The performer and the sound crew run through a small portion of the upcoming show to make sure that the venue's front of house and stage monitor sound systems are producing clear sound, that they are set at the proper volume, and that they have the correct mix and tonal balance.
 W
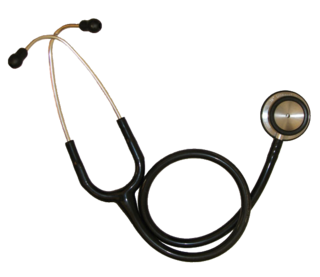
WThe stethoscope is an acoustic medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure.
 W
WA telegraph sounder is an antique electromechanical device used as a receiver on electrical telegraph lines during the 19th century. It was invented by Alfred Vail after 1850 to replace the previous receiving device, the cumbersome Morse register and was the first practical application of the electromagnet. When a telegraph message comes in it produces an audible "clicking" sound representing the short and long keypresses – "dots" and "dashes" – which are used to represent text characters in Morse code. A telegraph operator would translate the sounds into characters representing the telegraph message.