 W
WAcetyl nitrate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)ONO2. It is classified as the mixed anhydride of nitric and acetic acids. It is a colorless explosive liquid that fumes in moist air.
 W
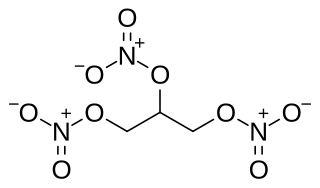
W1,2,4-Butanetriol trinitrate (BTTN), also called butanetriol trinitrate, is an important military propellant. It is a colorless to brown explosive liquid.
 W
WDiacetyl peroxide is the organic peroxide with the formula (CH3CO2)2. It is a white solid or oily liquid with a sharp odor. Since the pure material poses an explosion hazard, it is often used as a solution, e.g., in dimethyl phthalate as a solvent.
 W
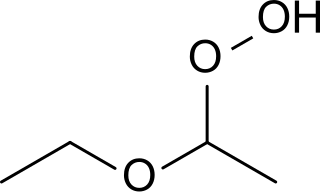
WDiethyl ether hydroperoxide is the organic compound with the formula C2H5OCH(OOH)CH3. It is a colorless, distillable liquid. Diethyl ether hydroperoxide and its condensation products are blamed for the explosive organic peroxides that slowly form upon exposure of diethyl ether to ambient air and temperature conditions.
 W
WDiethylene glycol dinitrate is a nitrated alcohol ester produced by the action of concentrated nitric acid on diethylene glycol, normally with an excess of strong sulfuric acid as a dehydrating agent.
 W
WEthyl azide (C2H5N3) is an explosive compound sensitive to rapid heating, shock or impact. It has exploded when heated to room temperature. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
 W
WEthylene glycol dinitrate, abbreviated EGDN and NGc, also known as nitroglycol, is a chemical compound a colorless, oily explosive liquid obtained by nitrating ethylene glycol. It is similar to nitroglycerin in both manufacture and properties, though it is more volatile and less viscous. Unlike nitroglycerine, the chemical has a perfect (0) oxygen balance, meaning that its ideal exothermic decomposition would completely convert it to low energy CO2, H2O, and N2, with no excess unreacted O2, H2, C, or other high-energy substances, without needing to react with anything else.
 W
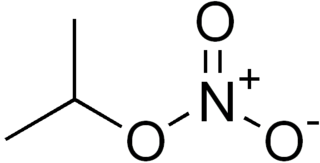
WIsopropyl nitrate is a colorless liquid monopropellant. It is used as a diesel cetane improver. IPN is a low-sensitivity explosive, with a detonation velocity of approximately 5400 m/s.
 W
WAn explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.
 W
WMethyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) is an organic peroxide, a high explosive similar to acetone peroxide. MEKP is a colorless, oily liquid whereas acetone peroxide is a white powder at STP; MEKP is slightly less sensitive to shock and temperature, and more stable in storage. Depending on the experimental conditions, several different adducts of methyl ethyl ketone and hydrogen peroxide are known. The first to be reported was a cyclic dimer, C8H16O4, in 1906. Later studies found that a linear dimer is the most prevalent in the mixture of products typically obtained, and this is the form that is typically quoted in the commercially available material from chemical supply companies.
 W
WMethyl nitrate is the methyl ester of nitric acid and has the chemical formula CH3NO3. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is explosive.
 W
WNitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure. Pure nitroethane is colorless and has a fruity odor.
 W
WNitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water.
 W
WNitroglycerin (NG), also known as nitroglycerine, trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating glycerol with white fuming nitric acid under conditions appropriate to the formation of the nitric acid ester. Chemically, the substance is an organic nitrate compound rather than a nitro compound, yet the traditional name is often retained. Invented in 1847, nitroglycerin has been used ever since as an active ingredient in the manufacture of explosives, mostly dynamite, and as such it is employed in the construction, demolition, and mining industries. Since the 1880s, it has been used by the military as an active ingredient, and a gelatinizer for nitrocellulose, in some solid propellants, such as cordite and ballistite. It is a major component in double-based smokeless gunpowders used by reloaders. Combined with nitrocellulose, hundreds of powder combinations are used by rifle, pistol, and shotgun reloaders.
 W
WPeroxymonosulfuric acid, (H2SO5), also known as persulfuric acid, peroxysulfuric acid, or Caro's acid. In this acid, the S(VI) center adopts its characteristic tetrahedral geometry; the connectivity is indicated by the formula HO–O–S(O)2–OH. It is one of the strongest oxidants known (E0 = +2.51 V) and is highly explosive.
 W
WPropylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN, ttup 1,2-propylene glycol dinitrate, or 1,2-propanediol dinitrate) is an organic chemical, an ester of nitric acid and propylene glycol. It is structurally similar to nitroglycerin, except that it has one fewer nitrate group. It is a characteristically and unpleasantly smelling colorless liquid, which decomposes at 121 °C, below its boiling point. It is flammable and explosive. It is shock-sensitive and burns with a clean flame producing water vapor, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen gas.C3H6(ONO2)2 → 3 CO + 3 H2O + N2
 W
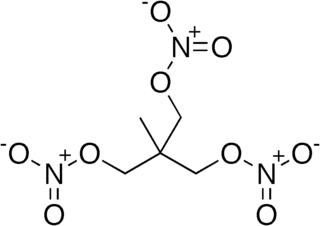
WTrimethylolethane trinitrate (TMETN), also known as metriol trinitrate (METN, MTN, METRTN) or nitropentaglycerin, is a nitrate ester. It is a high explosive similar to nitroglycerin. It is a transparent oily liquid, colorless to light brown. It is odorless. It is used in some solid propellants and smokeless powders as a plasticizer. Its chemical formula is CH3-C(CH2-O-NO2)3.
 W
WTrinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (C6H3N3O9S) is a nitroaryl oxidizing acid. Due to its extreme oxidative properties, if mixed with reducing agents including hydrides, sulfides, and nitrides, it may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in almost immediate detonation. The aromatic nitro compounds may explode in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide even in the presence of water or organic solvents because of the explosive tendencies of aromatic nitro compounds which increase in the presence of multiple nitro groups. Not much is known about this compound, but it is used as a peptide terminal amino group neutralizer and is currently being investigated for its effects on the immune system.