 W
WA railway signal is a visual display device that conveys instructions or provides advance warning of instructions regarding the driver’s authority to proceed. The driver interprets the signal's indication and acts accordingly. Typically, a signal might inform the driver of the speed at which the train may safely proceed or it may instruct the driver to stop.
 W
WRailway signalling is a system used to direct railway traffic and keep trains clear of each other at all times. Trains move on fixed rails, making them uniquely susceptible to collision. This susceptibility is exacerbated by the enormous weight and momentum of a train, which makes it difficult to quickly stop when encountering an obstacle. In the UK, the Regulation of Railways Act 1889 introduced a series of requirements on matters such as the implementation of interlocked block signalling and other safety measures as a direct result of the Armagh rail disaster in that year.
 W
WThe application of railway signals on a rail layout is determined by various factors, principally the location of points of potential conflict, as well as the speed and frequency of trains and the movements they require to make.
 W
WThe Bardic Rail Signalling Lamp was the original name of a particular type of electric railway signalling handlamp made from 1962 by Bardic, Ltd. for use by rail and trackside workers. The lamp provided the colours red, green, yellow and white. Today, it refers to any lamp used for signalling that gives red, green, yellow and white colours that is in use by British railways to provide signalling.
 W
WCab signaling is a railway safety system that communicates track status and condition information to the cab, crew compartment or driver's compartment of a locomotive, railcar or multiple unit. The information is continually updated giving an easy to read display to the train driver or engine driver.
 W
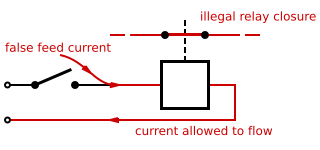
WDouble switching, double cutting, or double breaking is the practice of using a multipole switch to close or open both the positive and negative sides of a DC electrical circuit, or both the hot and neutral sides of an AC circuit. This technique is used to prevent shock hazard in electric devices connected with unpolarised AC power plugs and sockets. Double switching is a crucial safety engineering practice in railway signalling, wherein it is used to ensure that a single false feed of current to a relay is unlikely to cause a wrong-side failure. It is an example of using redundancy to increase safety and reduce the likelihood of failure, analogous to double insulation. Double switching increases the cost and complexity of systems in which it is employed, for example by extra relay contacts and extra relays, so the technique is applied selectively where it can provide a cost-effective safety improvement.
 W
WOn the railroads, a flagman is an employee of the railroad who is assigned to protect contractors or anyone performing work on a railroad right of way. A flagman is also assigned to protect a train that has stopped on a section of track. When a train approaches a location a flagman is posted, the train crew will have to get permission from the flagman to pass the area.
 W
WJack was a chacma baboon who attained some fame for acting as an assistant to a disabled railway signalman in South Africa.
 W
WRailway semaphore signal is one of the earliest forms of fixed railway signals. This semaphore system involes signals that display their different indications to train drivers by changing the angle of inclination of a pivoted 'arm'. Semaphore signals were patented in the early 1840s by Joseph James Stevens, and soon became the most widely used form of mechanical signal. Designs have altered over the intervening years, and colour light signals have replaced semaphore signals in most countries, but in a few they remain in use.
 W
WA signalman or signaller is an employee of a railway transport network who operates the points and signals from a signal box in order to control the movement of trains.
 W
WOn a railway, single-line working refers to the practice where, when one line out of the two lines is blocked, trains are able to use the other in either direction. This is usually when a line is out of use for maintenance, or because of damage, obstruction or train failure.
 W
WThe Système d'aide à la conduite, à l'exploitation et à la maintenance (SACEM) is an embedded, automatic speed train protection system for rapid transit railways. The name means "Driver Assistance, Operation, and Maintenance System".
 W
WA train dispatcher (US), rail traffic controller (Canada), train controller (Australia), train service controller (Singapore) or signalman (UK), is employed by a railroad to direct and facilitate the movement of trains over an assigned territory, which is usually part, or all, of a railroad operating division. The dispatcher is also responsible for cost effective movement of trains and other on-track railroad equipment to optimize physical (trains) and human resource (crews) assets.
 W
WA whistle post or whistle board, in railroad usage, is a sign marking a location where a locomotive engineer is required to sound the horn or whistle.
 W
WThe ZUB 1xx system is a family of train protection systems produced by Siemens. Its ZUB balises were deployed in the ZUB 121 train protection system in the Swiss railway network, in the ZUB 122 tilting control system in the German railway network, and in the ZUB 123 train protection system in the Danish railway network. Some of these were adapted for other railway lines before the next generation ZUB 2xx family was introduced which is based on Eurobalises - the earlier ZUB balises are not compatible with those.