 W
Wcal is a standard program on Unix and Unix-like operating systems that prints an ASCII calendar of the given month or year. If the user does not specify any command-line options, cal will print a calendar of the current month.
 W
WIn Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects. It is also used to change special mode flags. The request is filtered by the umask. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Modes are the filesystem permissions given to "user", "group" and "others" classes to access files under Unix. They are shown when listing files in long format, or, if access-control lists are in use, using getfacl. Modes can be changed with chmod or with setfacl.
 W
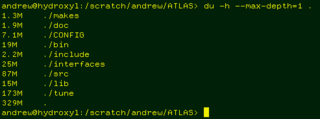
Wdu is a standard Unix program used to estimate file space usage—space used under a particular directory or files on a file system.
 W
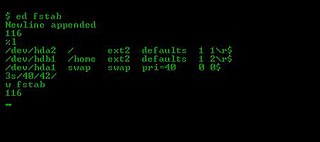
Wed is a line editor for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It was one of the first parts of the Unix operating system that was developed, in August 1969. It remains part of the POSIX and Open Group standards for Unix-based operating systems, alongside the more sophisticated full-screen editor vi.
 W
Wgrep is a command-line utility for searching plain-text data sets for lines that match a regular expression. Its name comes from the ed command g/re/p, which has the same effect. grep was originally developed for the Unix operating system, but later available for all Unix-like systems and some others such as OS-9.
 W
Wgzip is a file format and a software application used for file compression and decompression. The program was created by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler as a free software replacement for the compress program used in early Unix systems, and intended for use by GNU. Version 0.1 was first publicly released on 31 October 1992, and version 1.0 followed in February 1993.
 W
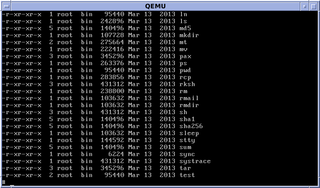
WIn computing, ls is a command to list computer files in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. ls is specified by POSIX and the Single UNIX Specification. When invoked without any arguments, ls lists the files in the current working directory. The command is also available in the EFI shell. In other environments, such as DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, similar functionality is provided by the dir command. The numerical computing environments MATLAB and GNU Octave include an ls function with similar functionality.
 W
WThe mkdir command in the Unix, DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems is used to make a new directory. It is also available in the EFI shell and in the PHP scripting language. In DOS, OS/2, Windows and ReactOS, the command is often abbreviated to md.
 W
WIn computing, netstat is a command-line network utility that displays network connections for Transmission Control Protocol, routing tables, and a number of network interface and network protocol statistics. It is available on Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems including macOS, Linux, Solaris and BSD. It is also available on IBM OS/2 and on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10.
 W
WIn Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.
 W
WIn computing, rm is a basic command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems used to remove objects such as computer files, directories and symbolic links from file systems and also special files such as device nodes, pipes and sockets, similar to the del command in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. The command is also available in the EFI shell.
 W
WIn computing, sort is a standard command line program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems, that prints the lines of its input or concatenation of all files listed in its argument list in sorted order. Sorting is done based on one or more sort keys extracted from each line of input. By default, the entire input is taken as sort key. Blank space is the default field separator. The command supports a number of command-line options that can vary by implementation. For instance the "-r" flag will reverse the sort order.
 W
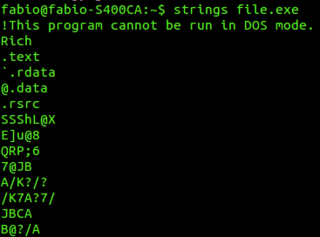
WIn computer software, strings is a program in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems that finds and prints text strings embedded in binary files such as executables. It can be used on object files and core dumps.
 W
Wtr is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. It is an abbreviation of translate or transliterate, indicating its operation of replacing or removing specific characters in its input data set.
 W
Wwc is a command in Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems. The program reads either standard input or a list of computer files and generates one or more of the following statistics: newline count, word count, and byte count. If a list of files is provided, both individual file and total statistics follow.