 W
WEvents in the main sequence of the Odyssey take place in the Peloponnese and in what are now called the Ionian Islands. Incidental mentions of Troy and its house, Phoenicia, Egypt, and Crete hint at geographical knowledge equal to, or perhaps slightly more extensive than that of the Iliad. However, scholars both ancient and modern are divided as to whether or not any of the places visited by Odysseus were real.
 W
WAeaea, Ææa or Eëä was a mythological island said to be the home of the goddess-sorceress Circe. In Homer's Odyssey, Odysseus tells Alcinous that he stayed here for one year on his way home to Ithaca. He says that he could not resist the need to be on this island, not so much for Circe but so that he does not resist the pull. The modern Greek scholar Ioannis Kakridis insists that any attempt at realistic identification is in vain, arguing that Homer vaguely located Aeaea somewhere in the eastern part of his world, perhaps near Colchis, since Circe was the sister of Aeëtes, king of Colchis, and because their paternal aunt the goddess Eos had her palace there.
 W
WIn mythology, the Greek underworld is an otherworld where souls go after death. The original Greek idea of afterlife is that, at the moment of death, the soul is separated from the corpse, taking on the shape of the former person, and is transported to the entrance of the underworld. Good people and bad people would then separate. The underworld itself—sometimes known as Hades, after its patron god—is described as being either at the outer bounds of the ocean or beneath the depths or ends of the earth. It is considered the dark counterpart to the brightness of Mount Olympus with the kingdom of the dead corresponding to the kingdom of the gods. Hades is a realm invisible to the living, made solely for the dead.
 W
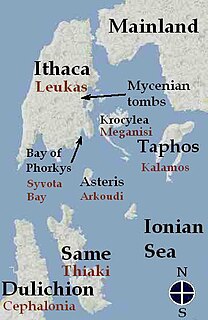
WIthaca was, in Greek mythology, the island home of the hero Odysseus. The specific location of the island, as it was described in Homer's Odyssey, is a matter for debate. There have been various theories about its location. Modern Ithaki has traditionally been accepted to be Homer's island. One recent alternative candidate is Paliki, which may have been an island separated from the rest of Kefalonia, as argued by Bittlestone, Diggle and Underhill in Odysseus Unbound. This theory has not been generally accepted, however, on grounds of geology, archaeology, philology, or historical and Homeric analysis. “What is clearly missing,” wrote Dr Christine Haywood reviewing Odysseus Unbound, “is a good knowledge of the complexities of Homeric language, and the support of archaeology.”
 W
WIsmarus or Ismaros was a city of the Cicones, in ancient Thrace, mentioned by Homer in the Odyssey.
 W
WIn Greek mythology the lotus-eaters, were a race of people living on an island dominated by the lotus tree, a plant whose botanical identity is uncertain. The lotus fruits and flowers were the primary food of the island and were a narcotic, causing the inhabitants to sleep in peaceful apathy. After they ate the lotus they would forget their home and loved ones. Those who ate the plant never cared to report, nor return.
 W
WOgygia is an island mentioned in Homer's Odyssey, Book V, as the home of the nymph Calypso, the daughter of the Titan Atlas. In Homer's Odyssey, Calypso detained Odysseus on Ogygia for seven years and kept him from returning to his home of Ithaca, wanting to marry him.
 W
WSame, also Samos (Σάμος) is an Ancient Greek name of a Homeric island in the Ionian Sea, near Ithaca and Cephalonia. In Homer's Odyssey Same is described as part of Odysseus's kingdom together with Ithaca, Dulichium, and Zacynthus. The Iliad, book II, in the Catalogue of Ships, contains a different list of islands comprising Odysseus's kingdom. Same is included together with Ithaca, Neritum, Krocylea, Aegilips and Zacynthus, indicating that the "Catalogue of Ships" could be a later addition to the Iliad.
 W
WTelepylos or Telepylus was the mythological city of the Laestrygonians. In the Odyssey, it is described as the rocky stronghold of Lamos. When Odysseus reaches the city in the Odyssey, he sends three scouts to explore the island. They come across the king, a giant cannibal, who then eats one of the men, causing the other scouts to run away. Most of Odysseus' men are killed in the incident, but his boat is moored outside the Laestrygonians' harbour. He is able to sail away, without the bombardment of rocks received by the rest of the fleet who did moor within the harbour. Only forty-five men escape.
 W
WThrinacia is the island home of the Cattle of Helios in Book XII of Homer's Odyssey, guarded by Helios' daughters Lampetia and Phaethusa.