 W
WThe Australian pound was the currency of Australia from 1910 until 14 February 1966, when it was replaced by the Australian dollar. As with other £sd currencies, it was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
 W
WThe Dollar has been the currency of Barbados since 1935. The present dollar has the ISO 4217 code BBD and is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign "$" to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents.
 W
WThe Belize dollar is the official currency in Belize. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively BZ$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies.
 W
WThe Biafran pound was the currency of the breakaway Republic of Biafra between 1968 and 1970.
 W
WThe pula is the currency of Botswana. It has the ISO 4217 code BWP and is subdivided into 100 thebe. Pula literally means "rain" in Setswana, because rain is very scarce in Botswana—home to much of the Kalahari Desert—and therefore valuable and a blessing. The word also serves as the national motto of the country.
 W
WThe British West African Pound was the currency of British West Africa, a group of British colonies, protectorates and mandate territories. It was equal to the pound sterling and was similarly subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
 W
WThe Brunei dollar, has been the currency of the Sultanate of Brunei since 1967. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively B$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 sen (Malay) or cents (English). The Brunei dollar is issued by the Autoriti Monetari Brunei Darussalam.
 W
WThe Canadian dollar is the currency of Canada. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or sometimes CA$, Can$ or C$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents (¢).
 W
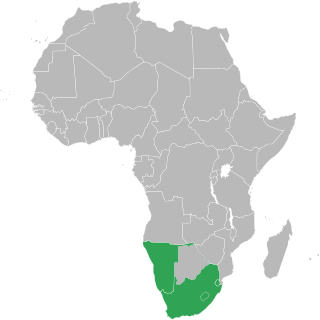
WThe Common Monetary Area (CMA) links South Africa, Namibia, Lesotho and Eswatini into a monetary union. It is allied to the Southern African Customs Union (SACU).
 W
WThe Cook Islands dollar was the former currency of the Cook Islands, which now uses the New Zealand dollar, although some physical cash issued for the Cook Islands dollar remains in use. The dollar was subdivided into 100 cents, with some older 50-cent coins carrying the denomination as "50 tene".
 W
WThe Cypriot pound, also known as the Cypriot lira, was the currency of Cyprus, including the Sovereign Base Areas in Akrotiri and Dhekelia, from 1879 to 2007, when the Republic of Cyprus adopted the euro. However, the self-proclaimed Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus used and still uses on the official level the Turkish lira.
 W
WThe East African shilling was the currency issued for use in British controlled areas in East Africa from 1921 until 1969. It was produced by the East African Currency Board. It is also the proposed name for a common currency that the East African Community plans to introduce.
 W
WThe euro is the official currency of 19 of the 27 member states of the European Union. This group of states is known as the eurozone or euro area and includes about 343 million citizens as of 2019. The euro, which is divided into 100 cents, is the second-largest and second-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar.
 W
WThe Fijian dollar has been the currency of Fiji since 1969 and was also the currency between 1867 and 1873. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively FJ$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents.
 W
WThe pound was the currency of Fiji between 1873 and 1969. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
 W
WThe dalasi is the currency of the Gambia that was adopted in 1971. It is subdivided into 100 bututs. It replaced the Gambian pound at a rate of 1 pound = 5 dalasis, i.e. 1 dalasi = 0.2 pound = 4 shillings.
 W
WThe Ghanaian cedi is the unit of currency of Ghana. It is the fourth historical and only current legal tender in the Republic of Ghana. One cedi is divided into one hundred pesewas (Gp).
 W
WThe Ghanaian pound was the currency of Ghana between 1958 and 1965. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence. Until 1958, Ghana used the British West African pound, after which it issued its own currency. In 1965, Ghana introduced the first cedi at a rate of 1 pound = 2.4 cedis, i.e., 1 cedi = 100 pence.
 W
WThe pound is the currency of Guernsey. Since 1921, Guernsey has been in currency union with the United Kingdom and the Guernsey pound is not a separate currency but is a local issue of banknotes and coins denominated in pound sterling, in a similar way to the banknotes issued in Scotland, England and Northern Ireland. It can be exchanged at par with other sterling coinage and notes.
 W
WThe Guyanese dollar has been the unit of account in Guyana since 29 January 1839. Originally it was intended as a transitional unit to facilitate the changeover from the Dutch guilder system of currency to the British pound sterling system. The Spanish dollar was already prevalent throughout the West Indies in general, and from 1839, the Spanish dollar unit operated in British Guiana in conjunction with British sterling coins at a standard conversion rate of one dollar for every four shillings and twopence. In 1951 the British sterling coinage was replaced with a new decimal coinage which was simultaneously introduced through all the British territories in the Eastern Caribbean. When sterling began to depreciate in the early 1970s, a switch to a US dollar peg became increasingly attractive as an anti-inflationary measure and the Eastern Caribbean Currency Authority made the switch in October 1975. The Guyanese dollar is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively G$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies.
 W
WThe Indian rupee is the official currency of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 paise, though as of 2019, coins of denomination of 1 rupee is the lowest value in use. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve Bank manages currency in India and derives its role in currency management on the basis of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
 W
WThe Irish pound was the currency of Ireland until 2002. Its ISO 4217 code was IEP, and the usual notation was the prefix £. The Irish pound was replaced by the euro on 1 January 1999. Euro currency did not begin circulation until the beginning of 2002.
 W
WThe Jamaican pound was the official currency of Jamaica between 1840 and 1969. It circulated as a mixture of British currency and local issues and was always equal to the British pound. The Jamaican pound was also used by the Cayman Islands and Turks and Caicos Islands.
 W
WThe shilling is the currency of Kenya. It is divided into 100 cents.
 W
WThe Australian dollar is the official currency of Kiribati. The Kiribati coins are pegged at 1:1 ratio to the Australian dollar. Coins were issued in 1979 and circulate alongside banknotes and coins of the Australian dollar. Kiribati coins are nowadays very few in comparison to Australian coins, the last minor emission has been made in 1992, and these old coins are generally collected. The complete emissions of coins were made in 1979 and in 1989 for the tenth anniversary of independence.
 W
WThis is a list of countries that have used postal orders.
 W
WThe Livatu is a unit used by the Turaga indigenous movement and the Tangbunia Bank in Vanuatu to reckon the worth of items of traditional currency such as pigs and textiles. One livatu is equivalent to one fully curved boar's tusk, a symbolic item of value in Vanuatu culture. Long dyed mats, a less valuable item of exchange, are worth up to a half a livatu.
 W
WThe kwacha is the currency of Malawi as of 1971, replacing the Malawian pound. It is divided into 100 tambala. The kwacha replaced other types of currency, namely the British pound sterling, the South African rand, and the Rhodesian dollar, that had previously circulated through the Malawian economy. The exchange rate of the kwacha undergoes fixed periodical adjustments, but since 1994 the exchange rate has floated. In 2005, administrative measures were put in place by Bingu wa Mutharika to peg the exchange rate with other currencies. Banknotes are issued by the Reserve Bank of Malawi. In May 2012, the Reserve Bank of Malawi devalued the kwacha by 34% and unpegged it from the United States dollar.
 W
WThe Malaya and British Borneo dollar was the currency of Malaya, Singapore, Sarawak, North Borneo, Brunei and Riau archipelago from 1953 to 1967 and was the successor of the Malayan dollar and Sarawak dollar, replacing them at par. The currency was issued by the Board of Commissioners of Currency, Malaya and British Borneo. Prior to 1952, the board was known as the Board of Commissioners of Currency, Malaya.
 W
WThe Malaysian ringgit is the currency of Malaysia. It is divided into 100 sen (cents). The ringgit is issued by the Central Bank of Malaysia.
 W
WThe Maldivian rufiyaa is the currency of the Maldives. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Maldives Monetary Authority (MMA). The most commonly used symbols for the rufiyaa are MVR and Rf. The ISO 4217 code for Maldivian rufiyaa is MVR. The rufiyaa is subdivided into 100 laari.
 W
WThe lira or pound was the currency of Malta from 1972 until 31 December 2007. After 1986 the lira was abbreviated as Lm, although the original ₤M sign was often used locally. In English the currency was still frequently called the pound even after its official English language name was changed to lira.
 W
WThe Mauritian rupee is the currency of Mauritius. One rupee is subdivided into 100 cents. Several other currencies are also called rupee.
 W
WThe Namibian dollar has been the currency of Namibia since 1993. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively N$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is divided into 100 cents.
 W
WThe pound was the currency of New Zealand from 1840 until 1967, when it was replaced by the New Zealand dollar.
 W
WThe naira is the currency of Nigeria. One naira is divided into 100 kobo.
 W
WThe Pakistani rupee has been the official currency of Pakistan since 1948. The coins and notes are issued and controlled by the central bank, namely State Bank of Pakistan.
 W
WThe kina is the currency of Papua New Guinea. It is divided into 100 toea. The kina was introduced on 19 May 1975, and circulated along with the Australian dollar until 31 December 1975. The next day, the dollar ceased to be legal tender.
 W
WThe pound sterling, known in some contexts simply as the pound or sterling, is the official currency of the United Kingdom, Jersey, Guernsey, the Isle of Man, Gibraltar, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, the British Antarctic Territory, and Tristan da Cunha. It is subdivided into 100 pence. The "pound sterling" is the oldest currency in continuous use. Some nations that do not use sterling also have currencies called the pound.
 W
WThe Rhodesian dollar was the currency of Rhodesia between 1970 and 1980. It was subdivided into 100 cents.
 W
WThe pound was the currency of Southern Rhodesia from 1964 to 1965 and Rhodesia from 1965 until 1970. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
 W
WThe Rwandan franc is the currency of Rwanda. It is subdivided into 100 centimes.
 W
WThe rupee is the currency of the Seychelles. It is subdivided into 100 cents. In the local Seychellois Creole (Seselwa) language, it is called the roupi and roupie in French. The international currency code is SCR. The abbreviation SR is sometimes used. By population, Seychelles is the smallest country to have an independent monetary policy. Several other currencies are also called rupee.
 W
WThe pound was the currency of the Union of South Africa from the creation of the country as a British Dominion in 1910. It was replaced by the rand in 1961, the same year that South Africa became a republic.
 W
WThe Sri Lankan rupee is the currency of Sri Lanka, divided into 100 cents. It is issued by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka. The symbol ₨ is generally used, but the currency code "LKR" is occasionally used to distinguish it from other currencies also called rupee.
 W
WThe sterling area was a group of countries that either pegged their currencies to the pound sterling, or actually used the pound as their own currency.
 W
WThe lilangeni is the currency of Eswatini and is subdivided into 100 cents. It is issued by the Central Bank of Eswatini. Similarly in situation to the Lesotho loti, there are singular and plural abbreviations, namely L and E, so where one might have an amount L1, it would be E2, E3, or E4.
 W
WThe shilingi is the currency of Tanzania. It is subdivided into 100 senti . The Tanzanian shilling replaced the East African shilling on 14 June 1966 at par.
 W
WThe paʻanga is the currency of Tonga. It is controlled by the National Reserve Bank of Tonga in Nukuʻalofa. The paʻanga is not convertible and is pegged to a basket of currencies comprising the Australian, New Zealand, and United States dollars and the Japanese yen.
 W
WThe Trinidad and Tobago dollar is the currency of Trinidad and Tobago. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively TT$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is subdivided into 100 cents. Cents are abbreviated with the cent sign ¢, or TT¢ to distinguish from other currencies that use cents. Its predecessor currencies are the Trinidadian dollar and the Tobagonian dollar.
 W
WThe shilling is the currency of Uganda. Officially divided into cents until 2013, the shilling now has no subdivision.
 W
WThe Zambian pound was the currency in Zambia from independence in 1964 until decimalization on January 16, 1968. It was subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence.
 W
WThe Zimbabwean dollar was the name of four official currencies of Zimbabwe from 1980 to 12 April 2009. During this time, it was subject to periods of extreme inflation, followed by a period of hyperinflation.