 W
WIn finance, a derivative is a contract that derives its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the "underlying". Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements (hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Some of the more common derivatives include forwards, futures, options, swaps, and variations of these such as synthetic collateralized debt obligations and credit default swaps. Most derivatives are traded over-the-counter (off-exchange) or on an exchange such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, while most insurance contracts have developed into a separate industry. In the United States, after the financial crisis of 2007–2009, there has been increased pressure to move derivatives to trade on exchanges.
 W
WAccumulators are financial derivative products sold by an issuer (seller) to investors that require the buyers to buy shares of some underlying security at a predetermined strike price, settled periodically. This allows the investor to "accumulate" holdings in the underlying security over the term of the contract; this then constitutes a structured product.
 W
WThe Borsa İstanbul is the sole exchange entity of Turkey combining the former Istanbul Stock Exchange (ISE), the Istanbul Gold Exchange and the Derivatives Exchange of Turkey under one umbrella. It was established as an incorporated company with a founding capital of ₺ 423,234,000 on April 3, 2013, and began to operate on April 5, 2013. Its logo is the traditional Ottoman mark for Istanbul, the tulip. Its slogan is worth investing.
 W
WIn options trading, a box spread is a combination of positions that has a certain payoff, considered to be simply "delta neutral interest rate position". For example, a bull spread constructed from calls combined with a bear spread constructed from puts has a constant payoff of the difference in exercise prices assuming that the underlying stock does not go ex-dividend before the expiration of the options. If the underlying asset has a dividend of X, then the settled value of the box will be 10 + x. Under the no-arbitrage assumption, the net premium paid out to acquire this position should be equal to the present value of the payoff.
 W
WIn finance, a butterfly is a limited risk, non-directional options strategy that is designed to have a high probability of earning a limited profit when the future volatility of the underlying asset is expected to be lower or higher than that asset's current implied volatility.
 W
WA cash flow hedge is a hedge of the exposure to the variability of cash flow thatis attributable to a particular risk associated with a recognized asset or liability. Such as all or some future interest payments on variable rate debt or a highly probable forecast transaction and could affect profit or loss
 W
WChain of Blame: How Wall Street Caused the Mortgage and Credit Crisis is a 2008 book about the subprime mortgage crisis in the United States by investigative journalists Paul Muolo of National Mortgage News and Mathew Padilla of the Orange County Register. The book has an accompanying website with some excerpts, author biographies and a roundup of events in the subprime mortgage crisis that occurred after the book was printed.
 W
WA collateralized debt obligation (CDO) is a type of structured asset-backed security (ABS). Originally developed as instruments for the corporate debt markets, after 2002 CDOs became vehicles for refinancing mortgage-backed securities (MBS). Like other private label securities backed by assets, a CDO can be thought of as a promise to pay investors in a prescribed sequence, based on the cash flow the CDO collects from the pool of bonds or other assets it owns. Distinctively, CDO credit risk is typically assessed based on a probability of default (PD) derived from ratings on those bonds or assets.
 W
WA commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.
 W
WConstant proportion portfolio investment (CPPI) is a trading strategy that allows an investor to maintain an exposure to the upside potential of a risky asset while providing a capital guarantee against downside risk. The outcome of the CPPI strategy is somewhat similar to that of buying a call option, but does not use option contracts. Thus CPPI is sometimes referred to as a convex strategy, as opposed to a "concave strategy" like constant mix.
 W
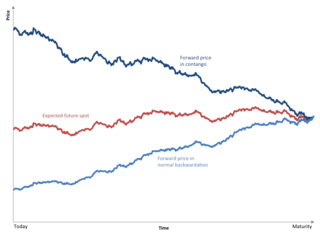
WContango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.
 W
WA credit default swap index is a credit derivative used to hedge credit risk or to take a position on a basket of credit entities. Unlike a credit default swap, which is an over the counter credit derivative, a credit default swap index is a completely standardized credit security and may therefore be more liquid and trade at a smaller bid–offer spread. This means that it can be cheaper to hedge a portfolio of credit default swaps or bonds with a CDS index than it would be to buy many single name CDS to achieve a similar effect. Credit-default swap indexes are benchmarks for protecting investors owning bonds against default, and traders use them to speculate on changes in credit quality.
 W
WIn finance, a credit derivative refers to any one of "various instruments and techniques designed to separate and then transfer the credit risk" or the risk of an event of default of a corporate or sovereign borrower, transferring it to an entity other than the lender or debtholder.
 W
WDelta one products are financial derivatives that have no optionality and as such have a delta of one – meaning that for a given instantaneous move in the price of the underlying asset there is expected to be an identical move in the price of the derivative. Delta one products can sometimes be synthetically assembled by combining options. For instance, you can be long a forward on WTI crude oil at price X by buying a X strike call and selling a X strike put. This is known as put call parity. Delta one products often incorporate a number of underlying securities and thus give the holder an easy way to gain exposure to a basket of securities in a single product.
 W
WThe derivatives market is the financial market for derivatives, financial instruments like futures contracts or options, which are derived from other forms of assets.
 W
WIn finance, a derivative is a contract that derives its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the "underlying". Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements (hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Some of the more common derivatives include forwards, futures, options, swaps, and variations of these such as synthetic collateralized debt obligations and credit default swaps. Most derivatives are traded over-the-counter (off-exchange) or on an exchange such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, while most insurance contracts have developed into a separate industry. In the United States, after the financial crisis of 2007–2009, there has been increased pressure to move derivatives to trade on exchanges.
 W
WFinancial instruments are monetary contracts between parties. They can be created, traded, modified and settled. They can be cash (currency), evidence of an ownership interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver in the form of currency (forex); debt ; equity (shares); or derivatives.
 W
WIn finance, a forward contract or simply a forward is a non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed on at the time of conclusion of the contract, making it a type of derivative instrument. The party agreeing to buy the underlying asset in the future assumes a long position, and the party agreeing to sell the asset in the future assumes a short position. The price agreed upon is called the delivery price, which is equal to the forward price at the time the contract is entered into.
 W
WFundamental analysis, in accounting and finance, is the analysis of a business's financial statements ; health; and competitors and markets. It also considers the overall state of the economy and factors including interest rates, production, earnings, employment, GDP, housing, manufacturing and management. There are two basic approaches that can be used: bottom up analysis and top down analysis. These terms are used to distinguish such analysis from other types of investment analysis, such as quantitative and technical.
 W
WIn finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell something at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future, between parties not known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price the parties agree to buy and sell the asset for is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future—which is when delivery and payment occur—is known as the delivery date. Because it is a function of an underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative product.
 W
WA hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
 W
WHedge accounting is an accountancy practice, the aim of which is to provide an offset to the mark-to-market movement of the derivative in the profit and loss account. There are two types of hedge recognized. For a fair value hedge, the offset is achieved either by marking-to-market an asset or a liability which offsets the P&L movement of the derivative. For a cash flow hedge, some of the derivative volatility is placed into a separate component of the entity's equity called the cash flow hedge reserve. Where a hedge relationship is effective, most of the mark-to-market derivative volatility will be offset in the profit and loss account. Hedge accounting entails much compliance - involving documenting the hedge relationship and both prospectively and retrospectively proving that the hedge relationship is effective.
 W
WIAS 39: Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement was an international accounting standard which outlined the requirements for the recognition and measurement of financial assets, financial liabilities, and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial items. It was released by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) in 2003, and was replaced in 2014 by IFRS 9, which became effective in 2018.
 W
WIFRS 4 is an International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) providing guidance for the accounting of insurance contracts. The standard was issued in March 2004, and was amended in 2005 to clarify that the standard covers most financial guarantee contracts. Paragraph 35 of IFRS also applies the standard to financial instruments with discretionary participation features.
 W
WIFRS 9 is an International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) published by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). It addresses the accounting for financial instruments. It contains three main topics: classification and measurement of financial instruments, impairment of financial assets and hedge accounting. The standard came into force on 1 January 2018, replacing the earlier IFRS for financial instruments, IAS 39.
 W
WIn finance an iron butterfly, also known as the ironfly, is the name of an advanced, neutral-outlook, options trading strategy that involves buying and holding four different options at three different strike prices. It is a limited-risk, limited-profit trading strategy that is structured for a larger probability of earning smaller limited profit when the underlying stock is perceived to have a low volatility.
 W
WIVX is a volatility index providing an intraday, VIX-like measure for any of US securities and exchange traded instruments. IVX is the abbreviation of Implied Volatility Index and is a popular measure of the implied volatility of each individual stock. IVX represents the cost level of the options for a particular security and comparing to its historical levels one can see whether IVX is high or low and thus whether options are more expensive or cheaper. IVX values can be compared for the stocks within one industry to find names which significantly differ from what is observed in overall sector.
 W
WMercado Abierto Electrónico (MAE) is an electronic securities and foreign-currency trading market in Argentina. It is based on a modular electronic platform running on specific IT supports, where both government and private fixed-income securities, foreign currencies and swaps are transacted, as well as currency and interest rate futures. In addition, this technological support is used to trade bills of exchange and bonds issued by Banco Central de la República Argentina (BCRA) and for the initial public offering of bonds issued by the National State.
 W
WNormal backwardation, also sometimes called backwardation, is the market condition where the price of a commodity's forward or futures contract is trading below the expected spot price at contract maturity. The resulting futures or forward curve would typically be downward sloping, since contracts for further dates would typically trade at even lower prices. In practice, the expected future spot price is unknown, and the term "backwardation" may refer to "positive basis", which occurs when the current spot price exceeds the price of the future.
 W
WNovation, in contract law and business law, is the act of –replacing an obligation to perform with another obligation; or adding an obligation to perform; or replacing a party to an agreement with a new party.
 W
WOver-the-counter (OTC) or off-exchange trading is done directly between two parties, without the supervision of an exchange. It is contrasted with exchange trading, which occurs via exchanges. A stock exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity, providing transparency, and maintaining the current market price. In an OTC trade, the price is not necessarily publicly disclosed.
 W
WIn finance, partial return reverse swap (PRRS) is a type of derivative swap, a financial contract that transfers a percentage of both the credit risk and market risk of an underlying asset, usually half, while also transferring all of the ownership liabilities for estate planning, tax purposes, and insider trading rules.
 W
WIn finance, a position is the amount of a particular security, commodity or currency held or owned by a person or entity.
 W
WA repurchase agreement, also known as a repo, RP, or sale and repurchase agreement, is a form of short-term borrowing, mainly in government securities. The dealer sells the underlying security to investors and, by agreement between the two parties, buys them back shortly afterwards, usually the following day, at a slightly higher price.
 W
WShort-term European paper (STEP) is a short-term financing instrument and investment tool, and also a tool for the European Union to align the market standards and practices to promote the integration of the European market. The EU has accepted the STEP market as a non-regulated market due to collateral purposes; meanwhile, this will not influence the existing national and European legislative, regulatory and supervisory systems. As a short-term financial instrument, Short-Term European Paper could be issued by Treasury, banks, funds and so on, with a minimum amount of EUR 100,000. It is normally issued at a discount price, which is lower than face value, and matured within a year.
 W
WIn finance, the strike price of an option is a fixed price at which the owner of the option can buy, or sell, the underlying security or commodity. The strike price may be set by reference to the spot price, which is the market price of the underlying security or commodity on the day an option is taken out. Alternatively, the strike price may be fixed at a discount or premium.
 W
WA swap, in finance, is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments or cashflows or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.
 W
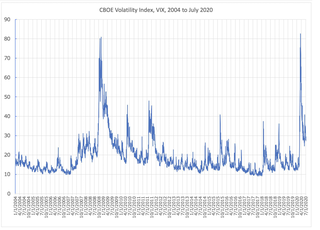
WVIX is the ticker symbol and the popular name for the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index, a popular measure of the stock market's expectation of volatility based on S&P 500 index options. It is calculated and disseminated on a real-time basis by the CBOE, and is often referred to as the fear index or fear gauge.
 W
WAn X-Value Adjustment is a collective term referring to a number of different “valuation adjustments” that banks must make when assessing the value of derivative contracts that they have entered into. The purpose of these is twofold: primarily to hedge for possible losses due to other parties' failures to pay amounts due on the derivative contracts; but also to determine the amount of capital required under the bank capital adequacy rules. XVA has led to the creation of specialized desks in many banking institutions to manage XVA exposures.
 W
WThe Year-on-Year Inflation-Indexed Swap (YYIIS) is a standard derivative product over Inflation rate. The underlying is a single Consumer price index (CPI).
 W
WThe Zero-Coupon Inflation Swap (ZCIS) is a standard derivative product which payoff depends on the Inflation rate realized over a given period of time. The underlying asset is a single Consumer price index (CPI).
 W
W