 W
WGeneral elections were held in Liberia in 1927. In the presidential election, the result was a victory for Charles D. B. King of the True Whig Party, who was re-elected for a third term after defeating Thomas J. Faulkner of the People's Party.
 W
WGeneral elections were held in Bolivia on 20 October 2019. Voters elected all 130 members of the Chamber of Deputies and 36 senators and cast ballots for a joint slate of president and vice president.
 W
WMoncena Dunn, was a farmer, telegrapher, optometrist, and inventor of the fraud-proof, color-coded coupon ballot.
 W
WElectoral ink, indelible ink, electoral stain or phosphoric ink is a semi-permanent ink or dye that is applied to the forefinger (usually) of voters during elections in order to prevent electoral fraud such as double voting. It is an effective method for countries where identification documents for citizens are not always standardised or institutionalised. One of the more common election ink compositions is based on silver nitrate, which can produce a stain lasting several weeks. It was first used during the 1962 Indian general election, in Mysore State, now the modern-day state of Karnataka.
 W
WFamily voting is when family members enter a voting booth together and collude or direct voting intentions.
 W
WMurphy James Foster was the 31st Governor of the U.S. state of Louisiana, an office he held for two terms from 1892 to 1900. Foster supported the Louisiana Constitution of 1898, which effectively disfranchised the black majority, who were mostly Republicans. This led to Louisiana becoming a one-party Democratic state for several generations and excluding African Americans from the political system.
 W
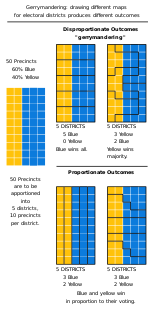
WGerrymandering is a practice intended to establish an arguably unfair political advantage for a particular party or group by manipulating the boundaries of electoral districts, which is most commonly used in first-past-the-post electoral systems.
 W
WThe Infamous Decade was a period in Argentinian history that began with the 1930 coup d'état against President Hipólito Yrigoyen. This decade was marked on one hand by significant rural exodus, with many small rural landowners ruined by the Great Depression, which in turn pushed the country towards import substitution industrialization, and on the other hand, by electoral fraud to perpetuate conservative governments in power. The poor results of economic policies and popular discontent led to another coup in 1943, the Revolution of 1943, by the Grupo de Oficiales Unidos (GOU), a nationalist faction of the Armed Forces, which triggered the rise to power of Juan Perón.
 W
WThis is a list of controversial elections arranged by continent and date.
 W
WAndreas Maurer is a German mail carrier and local politician convicted of electoral fraud.
 W
WMurphy James Foster was the 31st Governor of the U.S. state of Louisiana, an office he held for two terms from 1892 to 1900. Foster supported the Louisiana Constitution of 1898, which effectively disfranchised the black majority, who were mostly Republicans. This led to Louisiana becoming a one-party Democratic state for several generations and excluding African Americans from the political system.
 W
WPolitical corruption is the use of powers by government officials or their network contacts for illegitimate private gain.
 W
WThe Presidential Advisory Commission on Election Integrity, also called the Voter Fraud Commission, was a Presidential Commission established by Donald Trump that ran from May 11, 2017 to January 3, 2018. The Trump administration said the commission would review claims of voter fraud, improper registration, and voter suppression. The establishment of the commission followed Trump's false claim that millions of illegal immigrants had voted in the 2016 presidential election, costing him the popular vote. Vice President Mike Pence was as chair of the commission and Kansas Secretary of State Kris Kobach was vice chair and day-to-day administrator.
 W
WA risk-limiting audit (RLA) is one way of checking whether computers tallied an election accurately. It involves (1) storing paper ballots securely until they can be checked, (2) manually comparing a statistical sample of paper ballots to the computers' records for those same ballots, and (3) checking whether all the computer records of ballots in the election were totalled correctly.
 W
WA rotten or pocket borough, also known as a nomination borough or proprietorial borough, was a parliamentary borough or constituency in England, Great Britain, or the United Kingdom before the Reform Act 1832, which had a very small electorate and could be used by a patron to gain unrepresentative influence within the unreformed House of Commons. The same terms were used for similar boroughs represented in the 18th-century Parliament of Ireland. The Reform Act 1832 abolished these rotten and pocket boroughs.
 W
WBernard "Berny" L. Stone was alderman of the 50th Ward of the City of Chicago, Illinois from 1973 to 2011. The 50th Ward encompasses part of Chicago's far North Side and includes the West Ridge, West Rogers Park and Peterson Park neighborhoods. First elected to the Council in 1973, Stone was the second longest-serving alderman. His tenure spanned the terms of seven Mayors, from Richard J. Daley to Richard M. Daley. Stone was also Vice Mayor of the City of Chicago from 1998 to 2011.
 W
WTreating is the act of serving food, drink, and other refreshments in order to influence people and to gain benefits not easily obtained in the free market. It began as a political term, and came to be used elsewhere.
 W
WIn Spanish politics during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, El Turno Pacífico was an informal system operated by the two major parties for determining in advance the result of a general election. The system ensured that the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party would have alternating periods in power.
 W
WAn unfair election is a concept used by national and international election monitoring groups to identify when the vote of the people for a government is not free and fair. Unfairness in elections encompasses all varieties of electoral fraud, voter suppression or intimidation, unbalanced campaign finance rules, and imbalanced access to the media. Unfair elections violate the right to vote, which is generally recognised as an essential element to a deliberative democracy and representative democracy.
 W
WA voter identification law is a law that requires a person to show some form of identification in order to vote. In many jurisdictions requiring voter IDs, voters who do not have photo ID often must sign a Challenged Voter Affidavit in order to receive a ballot to vote.
 W
WVoter suppression is a strategy used to influence the outcome of an election by discouraging or preventing specific groups of people from voting. It is distinguished from political campaigning in that campaigning attempts to change likely voting behavior by changing the opinions of potential voters through persuasion and organization, activating otherwise inactive voters, or registering new supporters. Voter suppression, instead, attempts to reduce the number of voters who might vote against a candidate or proposition.