 W
WAllium fistulosum, the Welsh onion, also commonly called bunching onion, long green onion, Japanese bunching onion, and spring onion, is a species of perennial plant, often considered to be a kind of scallion.
 W
WAllium tricoccum is a North American species of wild onion widespread across eastern Canada and the eastern United States. Many of the common English names for this plant are also used for other Allium species, particularly the similar Allium ursinum, which is native to Europe and Asia.
 W
WApios americana, sometimes called the American groundnut, potato bean, hopniss, Indian potato, hodoimo, America-hodoimo, cinnamon vine, or groundnut is a perennial vine that bears edible beans and large edible tubers. Its vine can grow to 1–6 m (3.3–19.7 ft) long, with pinnate leaves 8–15 cm (3.1–5.9 in) long with 5–7 leaflets. The flowers are usually pink, purple, or red-brown, and are produced in dense racemes 7.5–13 cm (3.0–5.1 in) in length. The fruit is a legume (pod) 5–13 cm (2.0–5.1 in) long. Botanically speaking, the tubers are rhizomatous stems, not roots. Its natural range is from Southern Canada down through Florida and West as far as the border of Colorado. It is a larval host for the Epargyreus clarus.
 W
WAralia cordata is an upright herbaceous perennial plant growing up to 2 to 3 metres in height, native to Japan, Korea and eastern China. Its common names include spikenard, herbal aralia, udo, Japanese spikenard, and mountain asparagus. It is commonly found on the slopes of wooded embankments. Aralia cordata is a species of Aralia in the family Araliaceae.
 W
WThe globe artichoke, also known by the names French artichoke and green artichoke in the U.S., is a variety of a species of thistle cultivated as a food.
 W
WAsparagus, or garden asparagus, folk name sparrow grass, scientific name Asparagus officinalis, is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus Asparagus. Its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
 W
WBasella alba is an edible perennial vine in the family Basellaceae. It is found in tropical Asia and Africa where it is widely used as a leaf vegetable. It is native to the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and New Guinea. It is naturalized in China, tropical Africa, Brazil, Belize, Colombia, the West Indies, Fiji and French Polynesia.
 W
WBlitum bonus-henricus, also called Good-King-Henry, poor-man's asparagus, perennial goosefoot, Lincolnshire spinach, Markery, English mercury, or mercury goosefoot, is a species of goosefoot which is native to much of central and southern Europe.
 W
WThe cardoon, Cynara cardunculus, also called the artichoke thistle, is a thistle in the sunflower family. It is a naturally occurring species that also has many cultivated forms, including the globe artichoke. It is native to the western and central Mediterranean region, where it was domesticated in ancient times and still occurs as a wild plant.
 W
WCommon chicory is a somewhat woody, perennial herbaceous plant of the daisy family Asteraceae, usually with bright blue flowers, rarely white or pink. Many varieties are cultivated for salad leaves, chicons, or roots, which are baked, ground, and used as a coffee substitute and food additive. In the 21st century, inulin, an extract from chicory root, has been used in food manufacturing as a sweetener and source of dietary fiber.
 W
WCrambe maritima, common name sea kale, seakale or crambe, is a species of halophytic (salt-tolerant) flowering plant in the genus Crambe of the family Brassicaceae. It grows wild along the coasts of mainland Europe and the British Isles.
 W
WDioscorea bulbifera is a species of true yam in the yam family, Dioscoreaceae. It is native to Africa, Asia and northern Australia. It is widely cultivated and has become naturalized in many regions.
 W
WDiplotaxis tenuifolia is a species of flowering plant in the mustard family known by the common names wild rocket and perennial wall-rocket. This plant is native to Europe and Western Asia. It can be found throughout much of the temperate world where it has naturalized.
 W
WElephant garlic is a perennial plant belonging to the onion genus. It has a tall, solid, flowering stalk and broad, flat leaves. The flavor is milder than garlic, and much more palatable to some people than garlic when used raw as in salads. It is sometimes confused with solo garlic.
 W
WFennel is a flowering plant species in the carrot family. It is a hardy, perennial herb with yellow flowers and feathery leaves. It is indigenous to the shores of the Mediterranean but has become widely naturalized in many parts of the world, especially on dry soils near the sea-coast and on riverbanks.
 W
WFiddleheads or fiddlehead greens are the furled fronds of a young fern, harvested for use as a vegetable.
 W
WGynura procumbens, sometimes called "longevity spinach" or "longevity greens", is an edible vine found in China, Southeast Asia, and Africa. Leaves are ovate-elliptic or lanceolate, 3.5 to 8 centimetres long, and 0.8 to 3.5 centimetres wide. Flowering heads are panicled, narrow, yellow, and 1 to 1.5 centimetres long. The plant grows wild but is also cultivated as a vegetable or medicinal plant. Its young leaves are used for cooking, such as with meat and prawns in a vegetable soup.
 W
WIpomoea aquatica is a semi-aquatic, tropical plant grown as a vegetable for its tender shoots. This plant is known in English as water spinach, river spinach, water morning glory, water convolvulus, or by the more ambiguous names Chinese spinach, Chinese watercress, Chinese convolvulus or swamp cabbage, or kangkong in Southeast Asia and ong choy in Cantonese. Its place of origin is not known.
 W
WThe Jerusalem artichoke, also called sunroot, sunchoke, wild sunflower, topinambur, or earth apple, is a species of sunflower native to central North America. It is cultivated widely across the temperate zone for its tuber, which is used as a root vegetable.
 W
WMatteuccia is a genus of ferns with one species: Matteuccia struthiopteris. The species epithet struthiopteris comes from Ancient Greek words στρουθίων (strouthíōn) "ostrich" and πτερίς (pterís) "fern".
 W
WNasturtium microphyllum, the onerow yellowcress, is an aquatic plant species widespread across Europe and Asia, and naturalized in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Central America, Australia, New Zealand and other places. It occurs in wet locations generally at elevations less than 1500 m. It has been reported from every Canadian province except Nova Scotia and Saskatchewan. In the US, it is fairly common in New England, New York, and Michigan, with scattered populations in the southern and western parts of the country.
 W
WOenanthe javanica, commonly Java waterdropwort, water celery, water dropwort, Chinese celery, and Japanese parsley, is a plant of the genus Oenanthe originating from East Asia. It has a widespread native distribution in temperate Asia and tropical Asia, and is also native to Queensland, Australia.
 W
WOxalis tuberosa is a perennial herbaceous plant that overwinters as underground stem tubers. These tubers are known as uqa in Quechua, oca in Spanish, yam in New Zealand and a number of other alternative names. The plant was brought into cultivation in the central and southern Andes for its tubers, which are used as a root vegetable. The plant is not known in the wild, but populations of wild Oxalis species that bear smaller tubers are known from four areas of the central Andean region. Oca was introduced to Europe in 1830 as a competitor to the potato, and to New Zealand as early as 1860.
 W
WPetasites japonicus, also known as butterbur, giant butterbur, great butterbur and sweet-coltsfoot, is an herbaceous perennial plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to China, Japan, Korea and Sakhalin and introduced in Europe and North America. It was introduced to southern British Columbia in Canada by Japanese migrants.
 W
WPhaseolus coccineus, known as runner bean, scarlet runner bean, or multiflora bean, is a plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. Another common name is butter bean, which, however, can also refer to the lima bean, a different species.
 W
WRadicchio is a perennial cultivated form of leaf chicory sometimes known as Italian chicory because of its common use in Italian cuisine. It is grown as a leaf vegetable and usually has colorful white-veined red leaves that form a head. Radicchio has a bitter and spicy taste which mellows if it is grilled or roasted.
 W
WRhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks (petioles) of species and hybrids of Rheum in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The whole plant – a herbaceous perennial growing from short, thick rhizomes – is also called rhubarb. Historically, different plants have been called "rhubarb" in English. The large, triangular leaves contain high levels of oxalic acid and anthrone glycosides, making them inedible. The small flowers are grouped in large compound leafy greenish-white to rose-red inflorescences.
 W
WSanguisorba minor, the salad burnet, garden burnet, small burnet, or burnet, is a plant in the family Rosaceae that is native to western, central and southern Europe; northwest Africa and southwest Western Asia; and which has naturalized in most of North America.
 W
WThe shallot is a botanical variety of the onion. Until 2010, the shallot was classified as a separate species, Allium ascalonicum, a name that is a synonym of Allium cepa, the species name of the onion. A. cepa is the correct name for the shallot species.
 W
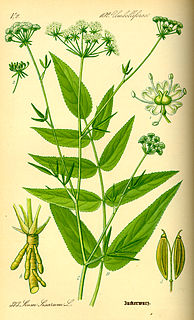
WSium sisarum, commonly known as skirret, is a perennial plant of the family Apiaceae sometimes grown as a root vegetable. The English name skirret is derived from the Middle English 'skirwhit' or 'skirwort', meaning 'white root'. In Scotland it is known as crummock. Its Danish name sukkerrod, Dutch name suikerwortel and German name "Zuckerwurzel" translate as 'sugar root'.
 W
WSorrel, also called common sorrel or garden sorrel, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Polygonaceae. Other names for sorrel include spinach dock and narrow-leaved dock.
 W
WTaraxacum officinale, the dandelion or common dandelion, is a flowering herbaceous perennial plant of the dandelion genus in the family Asteraceae. The common dandelion is well known for its yellow flower heads that turn into round balls of many silver-tufted fruits that disperse in the wind. These balls are usually called "clocks" in both British and American English. The name "blowball" is also used.
 W
WTree onion, topsetting onions, walking onions, or Egyptian onions, Allium × proliferum, are similar to common onions (A. cepa), but with a cluster of bulblets where a normal onion would have flowers. Genomic evidence has conclusively shown that they are a hybrid of the common onion and the Welsh onion (A. fistulosum). However, some sources may still treat the tree onion as A. cepa var. proliferum or A. cepa Proliferum Group. Tree onion bulblets will sprout and grow while still on the original stalk. They may bend down under the weight of the new growth and take root some distance from the parent plant, giving rise to the name "walking onion." It has been postulated that the name "Egyptian onion" derived from Romani people bringing tree onions to Europe from the Indian subcontinent.
 W
WTropaeolum tuberosum is a species of flowering plant in the family Tropaeolaceae, grown in the Andes, particularly in Peru and Bolivia, and to a lesser extent in Ecuador as well as in some areas of Colombia, for its edible tubers, which are eaten cooked or roasted as a vegetable. It is a minor food source, especially to native Amerindian populations. Mashua is a herbaceous perennial climber growing to 2–4 m (7–13 ft) in height. It is related to garden nasturtiums, and is occasionally cultivated as an ornamental for its brightly coloured tubular flowers.
 W
WWatercress or yellowcress is a species of aquatic flowering plant in the cabbage family Brassicaceae. Its botanical name is Nasturtium officinale.
 W
WThe yacón is a species of perennial daisy traditionally grown in the northern and central Andes from Colombia to northern Argentina for its crisp, sweet-tasting, tuberous roots. Their texture and flavour are very similar to jícama, mainly differing in that yacón has some slightly sweet, resinous, and floral undertones to its flavour, probably due to the presence of inulin, which produces the sweet taste of the roots of elecampane, as well. Another name for yacón is Peruvian ground apple, possibly from the French name of potato, pomme de terre. The tuber is composed mostly of water and fructooligosaccharide.