 W
WThe action of 13 May 1944 refers to the sinking of an Imperial Japanese submarine in the Atlantic Ocean during World War II. An American destroyer escort attacked the former German U-boat U-1224, which had been given to the Japanese Navy and renamed RO-501. The boat was the first of two Japanese vessels sunk in the European Theater of Operations.
 W
WThe action of 10 November 1944 was a naval engagement of World War II involving an American submarine and a German U-boat. In a short action north of Lombok Strait, the Americans attacked the German vessel which exploded and sank with all hands.
 W
WThe action of 24 July 1945 was one of the final naval battles during the Pacific Theater of World War II. In an attempt to destroy as many allied ships as possible, the Imperial Japanese Navy began arming their submarine fleet with manned torpedoes called kaitens. The Action of 24 July 1945 concerns the battle between a convoy of U.S. Navy warships off Luzon and the Japanese submarine I-53 and her kaitens.
 W
WThe action of 13 November 1943 was a submarine engagement of World War II. It resulted in the sinking of the Japanese Navy's Kaidai Junsen Type B1 submarine I-34 in the Strait of Malacca by the British Royal Navy submarine HMS Taurus. I-34 was on a Yanagi Mission, an underwater convoy secretly shipping goods between Japan and their German allies.
 W
WThe action of 14 February 1944 refers to the sinking of a German U-boat off the Strait of Malacca during World War II by a British submarine. It was one of the few naval engagements of the Asian and Pacific theater involving German and Italian forces.
 W
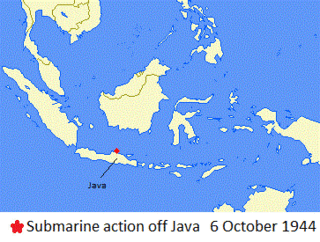
WThe action of 6 October 1944 was an incident of World War II in which a German U-boat was sunk by a Dutch submarine while operating in the Java Sea. The sinking was part of the German U-boat campaign in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
 W
WThe Sinking of U-864 occurred during the action of 9 February 1945, when HMS Venturer – a submarine of the Royal Navy, which was patrolling the waters around Fedje, a Norwegian island in the North Sea – attacked and sank the German U-boat U-864.
 W
WThe action of 23 April 1945 was a submarine engagement of World War II that occurred in the Java Sea between Nazi Germany and the United States. It resulted in the last sinking of a German U-boat in Asian waters during the Pacific War and was one of only a few actions of the theater involving German forces.
 W
WThe action of 8 June 1945, sometimes called the Sinking of Ashigara was a naval action that resulted in the sinking of the heavy cruiser Ashigara of the Imperial Japanese Navy by the British Royal Navy submarine HMS Trenchant. Ashigara was transporting Japanese troops from Indonesia for the defence of Singapore, and the sinking resulted in a heavy loss of life.
 W
WAllied submarines were used extensively during the Pacific War and were a key contributor to the defeat of the Empire of Japan.
 W
WSubmarine warfare in the Black Sea in World War II during 1941 primarily involved engagements between submarines of the Soviet Black Sea Fleet attacking Axis merchantmen defended by Romanian and Bulgarian warships. These engagements were a part of the naval Black Sea campaigns between Axis and Soviet naval forces.
 W
WSubmarine warfare in the Black Sea in World War II during 1943 involved engagements between submarines of the Soviet Black Sea Fleet attacking Axis merchantmen defended by Romanian and German naval warships, as well as and German U-boats attacking Soviet merchants on the eastern Black Sea. These engagements were a part of the Black Sea campaigns between Axis and Soviet naval forces.
 W
WSubmarine warfare in the Black Sea in World War II during 1944 involved engagements between submarines of the Soviet Black Sea Fleet attacking Axis merchantmen, defended by Romanian and German naval warships, as well as German U-boats and Romanian submarines attacking Soviet merchants on the eastern Black Sea. Before the conclusion of the campaign, Romania joined the Allies after King Michael's Coup. These engagements were a part of the naval Black Sea campaigns.
 W
WThe Eastern Sea Frontier (EASTSEAFRON) was a United States Navy operational command during World War II, that was responsible for the coastal waters from Canada to Jacksonville, Florida, extending out for a nominal distance of two hundred miles. The Commander was designated Commander, Eastern Sea Frontier (COMEASTSEAFRON). COMEASTSEAFRON had vessels for convoy use or other uses determined by the commander. In addition to providing escorts for convoys within its frontier, the frontier was responsible for sea-air rescue, harbor defense, shipping lane patrol, minesweeping, and air operations.
 W
WFremantle submarine base was the utilisation of Fremantle Harbour as a submarine base in World War II. The submarine base was second only to Pearl Harbor in the Pacific theater, with US, British and Dutch submarines operating from Fremantle during the war. US submarines operating from Fremantle accounted for approximately one quarter of all US submarine patrols in the Pacific.
 W
WJapanese submarines in the Pacific War consisted of 169 boats of the Imperial Japanese Navy. During the war Japanese submarines sank two US aircraft carriers, a cruiser and numerous other warships. Later they became used to resupply isolated island garrisons. The Japanese began the war with an advanced submarine torpedo design, the Type 95.
 W
WThe Mediterranean U-boat Campaign lasted from about 21 September 1941 to 19 September 1944 during the Second World War. Malta was an active British base strategically located near supply routes from Europe to North Africa. Axis supply convoys across the Mediterranean Sea suffered severe losses, which in turn threatened the fighting ability of the Axis armies in North Africa. The Allies were able to keep their North African armies supplied. The Kriegsmarine tried to isolate Malta but later it concentrated its U-boat operations on disrupting Allied landing operations in southern Europe.
 W
WIn late May and early June 1942, during World War II, submarines belonging to the Imperial Japanese Navy made a series of attacks on the cities of Sydney and Newcastle in New South Wales, Australia. On the night of 31 May – 1 June, three Ko-hyoteki-class midget submarines, each with a two-member crew, entered Sydney Harbour, avoided the partially constructed Sydney Harbour anti-submarine boom net, and attempted to sink Allied warships. Two of the midget submarines were detected and attacked before they could engage any Allied vessels. The crew of M-14 scuttled their submarine, whilst M-21 was successfully attacked and sunk. The crew of M-21 killed themselves. These submarines were later recovered by the Allies. The third submarine attempted to torpedo the heavy cruiser USS Chicago, but instead sank the converted ferry HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors. This midget submarine's fate was unknown until 2006, when amateur scuba divers discovered the wreck off Sydney's northern beaches.
 W
WScouting Squadron 1-D7 (VS-1D7) was a United States Navy anti-submarine warfare squadron in World War II. It was stationed at Naval Air Station Banana River, Florida (USA).
 W
WScouting Squadron 1-D7 (VS-1D7) was a United States Navy anti-submarine warfare squadron in World War II. It was stationed at Naval Air Station Banana River, Florida (USA).
 W
WThe Worek Plan was an operation of the Polish Navy in the first days of World War II, in which its five submarines formed a screen in order to prevent German naval forces from carrying out landings on the Polish coast, and to attack enemy ships bombarding Polish coastal fortifications, in particular the base on the Hel Peninsula.