 W
WActive mobility, active travel, active transport or active transportation is the transport of people or goods, through non-motorized means, based around human physical activity. The best-known forms of active mobility are walking and cycling, though other modes include running, skateboarding, kick scooters and roller skates. Due to its prevalence, cycling is sometimes considered separately from the other forms of active mobility.
 W
WAdventure travel is a type of niche tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk, and which may require special skills and physical exertion. In the United States, adventure tourism has grown in recent decades as tourists seek out-of-the-ordinary or "roads less traveled" vacations, but lack of a clear operational definition has hampered measurement of market size and growth. According to the U.S.-based Adventure Travel Trade Association, adventure travel may be any tourist activity that includes physical activity, a cultural exchange, and connection with nature.
 W
WAir travel is a form of travel in vehicles such as airplanes, jet aircraft, helicopters, hot air balloons, blimps, gliders, hang gliders, parachutes, or anything else that can sustain flight. Use of air travel has greatly increased in recent decades – worldwide it doubled between the mid-1980s and the year 2000. Modern air travel is much safer than road travel.
 W
WBackpacking is a form of low-cost, independent travel, which often includes staying in inexpensive lodgings and carrying all necessary possessions in a backpack. Once seen as a marginal form of travel undertaken only through necessity, it has since become a mainstream form of tourism.
 W
WBusiness travel is travel undertaken for work or business purposes, as opposed to other types of travel, such as for leisure purposes or regularly commuting between one's home and workplace. According to a survey 88% small business owners enjoy business travel.
 W
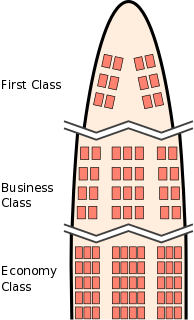
WA travel class is a quality of accommodation on public transport. The accommodation could be a seat or a cabin for example. Higher travel classes are designed to be more comfortable and are typically more expensive.
 W
WCommuting is periodically recurring travel between one's place of residence and place of work or study, where the traveler leaves the boundary of their home community. It sometimes refers to any regular or often repeated traveling between locations, even when not work-related. The modes of travel, time taken and distance traveled in commuting varies widely across the globe. Most people in least-developed countries continue to walk to work, as the ancestors of all people did until the nineteenth century. The cheapest method of commuting after walking is usually by bicycle, so this is common in low-income countries, but is also increasingly practised by people in wealthier countries for environmental and health reasons. In middle-income countries, motorcycle communing is very common. The next technology adopted as countries develop is more dependent on location: in more populous, older cities, especially in Eurasia mass transit predominates, while in smaller, younger cities, and large parts of North America and Australasia, communing by personal automobile is more common. A small number of very wealthy people, and those working in remote locations across the world, also commute by air travel, often for a week or more at a time rather the more typical daily commute. Transportation links that enable commuting also impact the physical layout of cities and regions, allowing a distinction to arise between mostly-residential suburbs and the more economically-focused urban core of a city, but the specifics of how that distinction is realized remain drastically different between societies, with Eurasian "suburbs" often being more densely populated than North American "urban cores".
 W
WCruising by boat is an activity that involves living for extended time on a vessel while traveling from place to place for pleasure. Cruising generally refers to trips of a few days or more, and can extend to round-the-world voyages.
 W
WA field trip or excursion is a journey by a group of people to a place away from their normal environment.
 W
WFirst class is a travel class on some passenger airliners intended to be more luxurious than business class, premium economy, and economy class. Originally all planes offered only one class of service, with a second class appearing first in 1955, when TWA introduced two different types of service on its Super Constellations.
 W
WFlight shame or flygskam is an anti-flying social movement, with the aim of reducing the environmental impact of aviation. It started in 2018 in Sweden and gained traction the following year throughout northern Europe. Flygskam is a Swedish word that literally means “flight shame”. The movement discourages people from flying to lower carbon emissions to thwart climate change.
 W
WThe Grand Tour was the 17th- and 18th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank when they had come of age.
 W
WPark and Pedal commuting is a bimodal form of commuting involving a motor vehicle and bicycle. Park and Pedal systems establish parking lots or spaces a comfortable cycling distance from city or employment centers. At the beginning of the workday, commuters leave their cars parked in the lots and pedal their bicycles the rest of the way to work. At the end of their workday, they do the reverse.
 W
WRecreational travel involves travel for pleasure and recreation.
 W
WA repositioning cruise is a cruise in which the embarkation port and the disembarkation port are different. This is a less common type of cruise; in the majority of cruises the ship's final destination is the same as the starting point.
 W
WA river cruise is a voyage along inland waterways, often stopping at multiple ports along the way. Since cities and towns often grew up around rivers, river cruise ships frequently dock in the center of cities and towns.
 W
WA safari is an overland journey to hunt or observe wild animals, especially in east or southern Africa. Particularly the so-called Big Five game animals of Africa – lion, leopard, rhinoceros, elephant, and Cape buffalo – form an important part of the safari market, both for wildlife viewing and big-game hunting.
 W
WTrain surfing is the act of riding on the outside of a moving train, tram or another rail transport. In a number of countries, the term train hopping is used synonymously with freight hopping, which means riding on the outside of a freight train, while train surfing can be practiced on any type of train. This type of travelling can be dangerous and even life-threatening, because there is a risk of death or serious injury from falling off a moving train, electrocution from power supply, colliding with railway infrastructure while riding outside off structure gauge on the side or on the roof of a train, or unsuccessful attempts to jump on a moving train or off it. Today, the practice is forbidden by statutes on many railroads in the world. Despite this, it is still practiced, especially on those railroads where the trains are overcrowded.
 W
WA vacation, or holiday, is a leave of absence from a regular job, or a specific trip or journey, usually for the purpose of recreation or tourism. People often take a vacation during specific holiday observances, or for specific festivals or celebrations. Vacations are often spent with friends or family.