 W
WThe federal administration of Switzerland is the ensemble of agencies that constitute, together with the Swiss Federal Council, the executive branch of the Swiss federal authorities. The administration is charged with executing federal law and preparing draft laws and policy for the Federal Council and the Federal Assembly.
 W
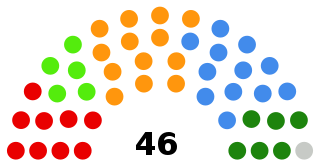
WThe Federal Assembly is Switzerland's federal legislature. It meets in Bern in the Federal Palace.
 W
WThe Swiss federal budget refers to the annual revenue and expenditures of the Swiss Confederation. As budget expenditures are issued on a yearly basis by the government, the federal council, and have to be approved by the parliament, they reflect the country's Fiscal policy.
 W
WThe Federal Chancellor is the head of the Federal Chancellery of Switzerland, the oldest Swiss federal institution, established at the initiative of Napoleon in 1803. The officeholder acts as the general staff of the seven-member Federal Council. The Swiss Chancellor is not a member of the government; the office of Chancellor is not at all comparable to that of the Chancellor of Germany or the Chancellor of Austria.
 W
WThe Federal Council is the seven-member executive council that constitutes the federal government of the Swiss Confederation and serves as the collective head of state and government of Switzerland. It meets in the west wing of the Federal Palace in Bern.
 W
WThe Federal Office of Civil Aviation is the Swiss civil aviation agency, a division of the Federal Department of Environment, Transport, Energy and Communications. Its head office is in Bern, and it has an office at Zurich Airport.
 W
WThe Federal Office of Culture (FOC) is an administrative unit of the Federal Department of Home Affairs, based in Bern, Switzerland. The agency has two extensive areas of responsibility: promoting Swiss culture and preserving the country’s cultural heritage. In 2014, its total budget was close to 170 million francs. The FOC promotes culture in the fields of literature, theatre, dance, music, film, the visual arts and design. It helps preserve the cultural heritage by supporting the protection of monuments and archeological research, and it also maintains valuable collections, libraries, archives, and museums.
 W
WThe Federal Office of Transport is a division of the Swiss Federal Department of Environment, Transport, Energy and Communications. It is the supervisory authority for the fields of public and freight transport in Switzerland, covering rail transport, cableways, ships, trams and buses. The FOT is responsible for safety, finance and infrastructure, as well as the legal and political frameworks of all said transport modes.
 W
WThe Federal Palace refers to the building in Bern housing the Swiss Federal Assembly (legislature) and the Federal Council (executive). It has a total length of more than 300 metres (980 ft) consisting of a central assembly building and two wings housing government departments and a library. The name in German and Romansh both mean "federal house", whereas the French and Italian names both translate to "Federal Palace". The Latin word curia originates from Ancient Rome and originally meant an assembly, and later used for where the Roman Senate met, both meanings being relevant to the Federal Palace.
 W
WThe Investigation Bureau for Railway, Funicular and Boat Accidents was an agency of the government of Switzerland. In 2011, it was replaced by the Swiss Transportation Safety Investigation Board.
 W
WThis is a list of 2005 Swiss incumbents.
 W
WThe National Emergency Operations Centre (NEOC) is a government organisation of the Swiss Confederation based in Zürich.
 W
WThe president of the Swiss Confederation, also known as the president of the Confederation or colloquially as the president of Switzerland, is the head of Switzerland's seven-member Federal Council, the country's executive branch. Elected by the Federal Assembly for one year, the officeholder chairs the meetings of the Federal Council and undertakes special representational duties.
 W
WThe Spiritual national defence was a political-cultural movement in Switzerland which was active from circa 1932 into the 1960s. It was supported by the Swiss authorities, certain institutions, scholars, the press and intellectuals. Its aim was the strengthening of values and customs perceived to be ‘Swiss’ and thus create a defence against totalitarian ideologies.
 W
WThe State Secretariat for International Financial Matters is an administrative unit of the Swiss Confederation. It is an office of the federal administration of Switzerland under the responsibility of the Federal Department of Finance, and was established on 1 March 2010.
 W
WThe Swiss Transportation Safety Investigation Board is a government agency of Switzerland. It investigates civil aviation accidents and incidents and cableway, roadway, waterway, and railway accidents. The head office is in Bern. The aviation division is based at Payerne Airport in Payerne and the rail/navigation division is based in Bern.