 W
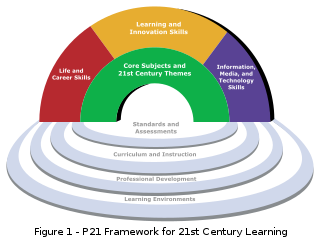
W21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.
 W
WA craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale production of goods, or their maintenance, for example by tinkers. The traditional term craftsman is nowadays often replaced by artisan and by craftsperson (craftspeople).
 W
W"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of experts or gender. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals engage raw and semi-raw materials and parts to produce, transform, or reconstruct material possessions, including those drawn from the natural environment ". DIY behavior can be triggered by various motivations previously categorized as marketplace motivations, and identity enhancement.
 W
WAn expert is somebody who has a broad and deep competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized as a reliable source of technique or skill whose faculty for judging or deciding rightly, justly, or wisely is accorded authority and status by peers or the public in a specific well-distinguished domain. An expert, more generally, is a person with extensive knowledge or ability based on research, experience, or occupation and in a particular area of study. Experts are called in for advice on their respective subject, but they do not always agree on the particulars of a field of study. An expert can be believed, by virtue of credentials, training, education, profession, publication or experience, to have special knowledge of a subject beyond that of the average person, sufficient that others may officially rely upon the individual's opinion on that topic. Historically, an expert was referred to as a sage. The individual was usually a profound thinker distinguished for wisdom and sound judgment.
 W
WExpertization is the process of authentication of an object, usually of a sort that is collected, by an individual authority or a committee of authorities. The expert, or expert committee, examines the collectible and issues a certificate typically including:A statement of: Whether or not the item is authentic Identification of any damage to the item Identification of any repairs to the item Identification of any forgery or faked parts of the item A photo of the item
 W
WIn psychology, the four stages of competence, or the "conscious competence" learning model, relates to the psychological states involved in the process of progressing from incompetence to competence in a skill.
 W
WA game of skill or game of wits is a game where the outcome is determined mainly by mental or physical skill, rather than chance.
 W
WIntellectualism refers to related mental perspectives that emphasize the use, the development, and the exercise of the intellect; and also identifies the life of the mind of the intellectual person. In the field of philosophy, “intellectualism” is synonymous with rationalism, knowledge derived from reason. Moreover, the term intellectualism can also have a socially negative connotation about a man or woman intellectual who gives “too much attention to thinking” and who shows an “absence of affection and feeling”.
 W
WA lineworker is a tradesman who constructs and maintains electric power transmission, telecommunications lines and distribution lines.
 W
WPradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is a skill development initiative scheme of the Government of India for recognition and standardisation of skills.
 W
WSeamanship is the art, knowledge and competence of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water.