 W
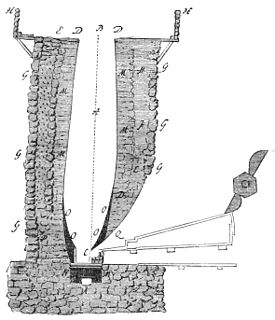
WA blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. Blast refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric pressure.
 W
WA blowing engine is a large stationary steam engine or internal combustion engine directly coupled to air pumping cylinders. They deliver a very large quantity of air at a pressure lower than an air compressor, but greater than a centrifugal fan.
 W
WThe Bourbon Iron Works, near Owingsville in Bath County, Kentucky, date from 1791. The works was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.
 W
WThe Cambria Iron Company of Johnstown, Pennsylvania was a major 19th-century industrial producer of iron and steel. Founded in 1852, it had the nation's largest steel foundry in the 1870s, and was renamed the Cambria Steel Company in 1898. The company used many innovations in the steelmaking process, including those of William Kelly and Henry Bessemer. The company was acquired in 1923 by the Bethlehem Steel Company. The company's historic facilities, extending some 12 miles (19 km) along the Conemaugh and Little Conemaugh Rivers, are a National Historic Landmark District.
 W
WCold blast, in ironmaking, refers to a furnace where air is not preheated before being blown into the furnace. This represents the earliest stage in the development of ironmaking. Until the 1820s, the use of cold air was thought to be preferable to hot air for the production of high-quality iron; this effect was due to the reduced moisture in cool winter air.
 W
WFundidora Park is an urban park located in the Mexican city of Monterrey, built in what once where the grounds of the Fundidora Monterrey steel foundry company.
 W
WThe Govăjdia Blast Furnace is a disused blast furnace in Govăjdia village, Ghelari Commune, Hunedoara County, in the Transylvania region of Romania.
 W
WHot blast refers to the preheating of air blown into a blast furnace or other metallurgical process. As this considerably reduced the fuel consumed, hot blast was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution. Hot blast also allowed higher furnace temperatures, which increased the capacity of furnaces.
 W
WThe Reșița works are two companies, TMK Reșița and UCM Reșița, located in Reșița, in the Banat region of Romania. Founded in 1771 and operating under a single structure until 1948 and then from 1954 to 1962, during the Communist era they were known respectively as the Reșița Steel Works and as the Reșița Machine Building Plant, the latter renamed in 1973 as the Reșița Machine Building Enterprise. They have played a crucial role in the industrial development both of the region and of Romania as a whole, and their evolution has been largely synonymous with that of their host city.
 W
WThe Royal Ironworks of St John, Ipanema was the first ironworks to be continuously operated in Brazil. It is located in Sorocaba region, near the city of Iperó, state of São Paulo. Ruins of the twin blast furnaces are well preserved and nearby is Fazenda Ipanema, a small settlement.