 W
WThe ADOX Polo was a consumer-class, viewfinder camera with a completely manual operating system. It was manufactured between 1960 and 1963 by Dr C. Schleussner Fotowerke GmbH following the company's takeover of the Wirgin camera factory of Wiesbaden, Germany. The brothers who were the founders and original owners of the Wirgin company, fled Germany to avoid persecution from the government of the time.
 W
WAn animation camera, a type of rostrum camera, is a movie camera specially adapted for frame-by-frame shooting of animation. It consists of a camera body with lens and film magazines, and is most often placed on a stand that allows the camera to be raised and lowered above a table often having both top and underneath lighting. The artwork to be photographed is placed on this table.
 W
WAn astrograph is a telescope designed for the sole purpose of astrophotography. Astrographs are mostly used in wide-field astronomical surveys of the sky and for detection of objects such as asteroids, meteors, and comets.
 W
WA box camera is a simple type of camera, the most common form being a cardboard or plastic box with a lens in one end and film at the other. They were sold in large numbers during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The lenses are often single element designs meniscus fixed focus lens, or in better quality box cameras a doublet lens with minimal possible adjustments to the aperture or shutter speeds. Because of the inability to adjust focus, the small lens aperture and the low sensitivity of the sensitive materials available, these cameras work best in brightly lit day-lit scenes when the subject is within the hyperfocal distance for the lens and of subjects that move little during the exposure. Eventually, box cameras with photographic flash, shutter and aperture adjustment were introduced, allowing indoor photos.
 W
WA digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a digital imaging sensor.
 W
WA disposable or single-use camera is a simple box camera meant to be used once. Most use fixed-focus lenses. Some are equipped with an integrated flash unit, and there are even waterproof versions for underwater photography. Internally, the cameras use a 135 film or an APS cartridge.
 W
WFemto-photography is a technique for recording the propagation of ultrashort pulses of light through a scene at a very high speed (up to 1013 frames per second). A femto-photograph is equivalent to an optical impulse response of a scene and has also been denoted by terms such as a light-in-flight recording or transient image. Femto-photography of macroscopic objects was first demonstrated using a holographic process in the 1970s by Nils Abramsson at the Royal Institute of Technology (Sweden). A research team at the MIT Media Lab led by Ramesh Raskar, together with contributors from the Graphics and Imaging Lab at the Universidad de Zaragoza, Spain, more recently achieved a significant increase in image quality using a streak camera synchronized to a pulsed laser and modified to obtain 2D images instead of just a single scanline.
 W
WA field camera is a view camera that can be folded in a compact size. Modern designs are little different from the first folding field cameras from the 19th century. In general they have more limited camera movements than monorail cameras, but when folded are relatively compact and portable.
 W
WA folding camera is a camera type. Folding cameras fold into a compact and rugged package for storage. The lens and shutter are attached to a lens-board which is connected to the body of the camera by a light-tight folding bellows. When the camera is fully unfolded it provides the correct focus distance from the film. The key advantage of folding cameras is their excellent physical-size to film-size ratio when the camera is folded for storage.
 W
WThe instant camera is a type of camera which uses self-developing film to create a chemically developed print shortly after taking the picture. Polaroid Corporation pioneered consumer-friendly instant cameras and film, and were followed by various other manufacturers.
 W
WA light field camera, also known as plenoptic camera, captures information about the light field emanating from a scene; that is, the intensity of light in a scene, and also the direction that the light rays are traveling in space. This contrasts with a conventional camera, which records only light intensity.
 W
WMonorail cameras are view cameras with lens mount, bellows, and interchangeable viewing and film backs all fitted along a rigid rail along which they can slide until locked into position.
 W
WThe multiplane camera is a motion-picture camera used in the traditional animation process that moves a number of pieces of artwork past the camera at various speeds and at various distances from one another. This creates a sense of parallax or depth.
 W
WAn on-ride camera is a camera mounted alongside the track of a roller coaster, log flume or other thrill ride that automatically photographs all of the riders on each passing vehicle. They are often mounted at the most intense or fastest part of the ride, resulting in humorously distorted expressions due to fear or wind resistance. The pictures are then available for viewing and purchase as a souvenir.
 W
WA pinhead mirror can be used to create a camera similar to a pinhole camera. Instead of passing through a tiny aperature, the light to form the image is reflected by a small disc-shaped mirror. One advantage is that a pinhead mirror can be swiveled to scan a scene or project a scene to different locations.
 W
WA pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens but with a tiny aperture —effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through the aperture and projects an inverted image on the opposite side of the box, which is known as the camera obscura effect.
 W
WThe PlayStation Camera is a motion sensor and camera accessory for the PlayStation 4 and PlayStation 5, developed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It is the successor to the PlayStation Eye for the PlayStation 3, which was released in 2007. It is also the motion sensor used to track the PlayStation VR virtual reality headset.
 W
WA press camera is a medium or large format view camera that was predominantly used by press photographers in the early to mid-20th century. It was largely replaced for press photography by 35mm film cameras in the 1960s, and subsequently, by digital cameras. The quintessential press camera was the Speed Graphic. Press cameras are still used as portable and rugged view cameras.
 W
WA rangefinder camera is a camera fitted with a rangefinder, typically a split-image rangefinder: a range-finding focusing mechanism allowing the photographer to measure the subject distance and take photographs that are in sharp focus. Most varieties of rangefinder show two images of the same subject, one of which moves when a calibrated wheel is turned; when the two images coincide and fuse into one, the distance can be read off the wheel. Older, non-coupled rangefinder cameras display the focusing distance and require the photographer to transfer the value to the lens focus ring; cameras without built-in rangefinders could have an external rangefinder fitted into the accessory shoe. Earlier cameras of this type had separate viewfinder and rangefinder windows; later the rangefinder was incorporated into the viewfinder. More modern designs have rangefinders coupled to the focusing mechanism so that the lens is focused correctly when the rangefinder images fuse; compare with the focusing screen in non-autofocus SLRs.
 W
WA reflex camera is a camera that permits the photographer to view the image that will be seen through the lens, and therefore to see exactly what will be captured, contrary to viewfinder cameras where the image could be significantly different from what will be captured.
 W
WRicoh Theta is a line of 360-degree cameras by Japanese manufacturer Ricoh.
 W
WA rostrum camera is a specially designed camera used in television production and filmmaking to animate a still picture or object. It consists of a moving lower platform on which the article to be filmed is placed, while the camera is placed above on a column. Many visual effects can be created from this simple setup, although it is most often used to add interest to static objects. The camera can, for example, traverse across a painting, and using wipes and zooms, change a still picture into a sequence suitable for television or movie productions.
 W
WA Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.
 W
WA single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a camera that typically uses a mirror and prism system that permits the photographer to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path, allowing light to pass through to the light receptor and the image to be captured.
 W
WPetri TTL was a manual 35 mm SLR camera with TTL metering. It was built by Petri Camera Company, Japan, from 1974. It is unknown when the production stopped.
 W
WA stereo camera is a type of camera with two or more lenses with a separate image sensor or film frame for each lens. This allows the camera to simulate human binocular vision, and therefore gives it the ability to capture three-dimensional images, a process known as stereo photography. Stereo cameras may be used for making stereoviews and 3D pictures for movies, or for range imaging. The distance between the lenses in a typical stereo camera is about the distance between one's eyes and is about 6.35 cm, though a longer base line produces more extreme 3-dimensionality.
 W
WSubminiature photography is photographic technologies and techniques working with film material smaller in size than 35mm film, such as 16mm, 9.5mm, 17mm, or 17.5mm films. It is distinct from photomicrography, photographing microscopic subjects with a camera which is not particularly small.
 W
WA superzoom or hyperzoom lens is a type of photographic zoom lens with unconventionally large focal length factors, typically ranging from wide angle to extreme long lens focal lengths in one lens. There is no clear definition of a superzoom lens, but the name generally covers lenses that have a range well above the 3× or 4× of a standard zoom lens, with lenses being 10×, 12×, 18×, or above considered superzoom.
 W
WA thermographic camera is a device that creates an image using infrared radiation, similar to a common camera that forms an image using visible light. Instead of the 400–700 nanometre range of the visible light camera, infrared cameras are sensitive to wavelengths from about 1,000 nm (1 μm) to about 14,000 nm (14 μm). The practice of capturing and analyzing the data they provide is called thermography.
 W
WWithin the field of photography, a toy camera is a simple, inexpensive film camera.
 W
WA traffic enforcement camera is a camera which may be mounted beside or over a road or installed in an enforcement vehicle to detect motoring offenses, including speeding, vehicles going through a red traffic light, vehicles going through a toll booth without paying, unauthorized use of a bus lane, or for recording vehicles inside a congestion charge area. It may be linked to an automated ticketing system.
 W
WA twin-lens reflex camera (TLR) is a type of camera with two objective lenses of the same focal length. One of the lenses is the photographic objective or "taking lens", while the other is used for the viewfinder system, which is usually viewed from above at waist level.
 W
WIn A World History of Photography, Naomi Rosenblum states that a view camera is: "A large-format camera in which the lens forms an inverted image on a ground glass screen directly at the plane of the film. The image viewed is exactly the same as the image on the film, which replaces the viewing screen during exposure." However, Rosenblum didn't give size limits for "large format"; and the book includes view camera formats smaller than 4x5, which are commonly seen as the smallest of the large format cameras.
 W
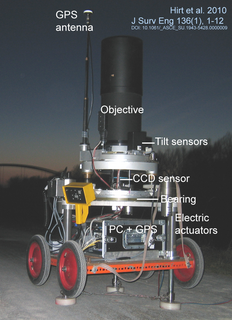
WA zenith camera is an astrogeodetic telescope used today primarily for the local surveys of Earth's gravity field. Zenith cameras are designed as transportable field instruments for the direct observation of the plumb line and vertical deflections.
 W
WA zoom-lens reflex (ZLR) camera is a low-end single-lens reflex (SLR) camera having an integrated zoom lens rather than the interchangeable lenses found on other SLR cameras.