 W
WThe 6264 is a JEDEC-standard static RAM integrated circuit. It has a capacity of 64 Kbit. It is produced by a wide variety of different vendors, including Hitachi, Hynix, and Cypress Semiconductor. It is available in a variety of different configurations, such as DIP, SPDIP, and SOIC. Some versions of the 6264 can run in ultra-low-power mode and retain memory when not in use, thus making them suitable for battery backup applications.ZMD U6264 SRAM
 W
WFREDDIE is the name for a 40-pin LSI found in later model Atari 8-bit computers. It is a RAM address multiplexer, used for DRAM access. Atari created this chip to replace several other chips to cut costs and to enhance CPU and ANTIC memory access.
 W
WThe Commodore 1540 introduced in 1982 is the companion floppy disk drive for the Commodore VIC-20 home computer. It uses single-sided 5¼" floppy disks, on which it stores roughly 170 kB of data utilizing Commodore's GCR data encoding scheme.
 W
WDigital Tape Format is a magnetic tape data storage format developed by Sony. It uses a 1/2" wide tape, in a cassette with two reels, which is written and read with a helical scan process. The format is described by the ECMA 248 and ISO/IEC 15731 standards. There are two sizes of tape cassettes, "S" and "L".
 W
WDVD-Ds, also referred to as disposable DVDs, are a type of digital versatile disc/digital video disc that is designed to be used for a maximum 48 hours after the containing package is opened. After this time, the DVDs become unreadable to DVD players because they contain a chemical that, after the set period of time, will prevent the underlying data from being read by DVD drives. The medium in itself is copy protection neutral and does not require additional Digital Rights Management types of applications to be installed for the content to be accessible. The technology used for DVD-Ds is different from that for earlier disposable DVDs. DVD-D has a reservoir in the central area of the disc which contains the chemical agent. When the disc spins for the first time the chemical agent moves and gets in contact with the reflective layer of the disc. After approximately 48 hours, the reflective layer becomes unreadable as the laser cannot reflect on the layer.
 W
WGfarm file system is an open-source distributed file system, generally used for large-scale cluster computing and wide-area data sharing, and provides features to manage replica location explicitly. The name is derived from the Grid Data Farm architecture it implements.
 W
WHigh-Definition Versatile Disc (HVD) is an Asian standard of advanced high-definition technology originally developed in China by AMLogic Inc., for high-definition video. The format supports 720p, 1080i, or 1080p video on version 1 discs. Version 2 of the format added high-resolution beyond the standard fare of HD for use on non-TV monitors that support higher resolutions, up to 1080p.
 W
WThe Hyper CD-ROM is an optical data storage device similar to the CD-ROM with a multilayer 3D structure, invented by Romanian scientist Dr. Eugen Pavel.
 W
WThe IBM 727 Magnetic Tape Unit was announced for the IBM 701 and IBM 702 on September 25, 1953. It became IBM's standard tape drive for their early vacuum tube era computer systems. Later vacuum tube machines and first-generation transistor computers used the IBM 729-series tape drive. The 727 was withdrawn on May 12, 1971.
 W
WThe IBM 3590 is a series of tape drives and corresponding magnetic tape data storage media formats developed by IBM. The first drive, having the IBM product number 3590, was introduced in 1995 under the nickname Magstar. The 3590 series of tape drives and media are not compatible with the IBM 3592 line of drives that replaced it. They can store up to 60 GB of data (uncompressed). This family superseded the IBM 3480 Family of tape drives popular in 1980s and 1990s.
 W
WThe IBM 7330 Magnetic Tape Unit was IBM's low cost tape mass storage system through the 1960s. Part of the IBM 7 track family of tape units, it was used mostly on 1400 series computers and the IBM 7040/7044. The 7330 used 1⁄2 inch (12.7 mm) magnetic tape up to 2,400 feet (730 m) long wound on reels up to 10 1⁄2 inches (266.7 mm) diameter.
 W
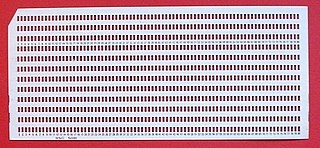
WA lace card is a punched card with all holes punched. They were mainly used as practical jokes to cause disruption in card readers. Card readers tended to jam when a lace card was inserted, as the resulting card had too little structural strength to avoid buckling inside the mechanism. Card punches could also jam trying to produce cards with all holes punched, owing to power-supply problems. When a lace card was fed through the reader, a card knife or card saw was needed to clear the jam.
 W
WIn communications and computing a machine-readable medium, or computer-readable medium, is a medium capable of storing data in a format readable by a mechanical device.
 W
WMaynard Electronics was an American company based in Lake Mary, Florida that produced magnetic tape data storage related products.
 W
WA Memory Technology Device (MTD) is a type of device file in Linux for interacting with flash memory. The MTD subsystem was created to provide an abstraction layer between the hardware-specific device drivers and higher-level applications. Although character and block device files already existed, their semantics don't map well to the way that flash memory devices operate.
 W
WPhase-change Dual is a rewritable optical disc and its standard developed by Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. in April 1995.
 W
WPLY is a computer file format known as the Polygon File Format or the Stanford Triangle Format. It was principally designed to store three-dimensional data from 3D scanners. The data storage format supports a relatively simple description of a single object as a list of nominally flat polygons. A variety of properties can be stored, including: color and transparency, surface normals, texture coordinates and data confidence values. The format permits one to have different properties for the front and back of a polygon. There are two versions of the file format, one in ASCII, the other in binary.
 W
WThe Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) is a registered 501(c)(6)non-profit trade association incorporated in December 1997.[1] SNIA has more than 185 unique members, 2,000 active contributing members and over 50,000 IT end users and storage professionals. The SNIA absorbed the Small Form Factor Committee
 W
WStrataFlash is a NOR flash memory technology first developed by Intel.
 W
WThe USB Flash Drive Alliance, founded in December 2003 by Samsung, Lexar Media, Kingston Technology and others, is a group of companies promoting the use of USB flash drives.