 W
WNeon lighting consists of brightly glowing, electrified glass tubes or bulbs that contain rarefied neon or other gases. Neon lights are a type of cold cathode gas-discharge light. A neon tube is a sealed glass tube with a metal electrode at each end, filled with one of a number of gases at low pressure. A high potential of several thousand volts applied to the electrodes ionizes the gas in the tube, causing it to emit colored light. The color of the light depends on the gas in the tube. Neon lights were named for neon, a noble gas which gives off a popular orange light, but other gases and chemicals are used to produce other colors, such as hydrogen (red), helium (yellow), carbon dioxide (white), and mercury (blue). Neon tubes can be fabricated in curving artistic shapes, to form letters or pictures. They are mainly used to make dramatic, multicolored glowing signage for advertising, called neon signs, which were popular from the 1920s to 1960s and again in the 1980s.
 W
WAerolux Light Corporation was a manufacturer of artful gas-discharge light bulbs from the 1930s through the 1970s. Aerolux made these bulbs in a factory in New York City. US Patents dating back to the 1930s describe the design and construction of these bulbs. Philip J. Kayatt (1896–1975) was president of the company.
 W
WThe American Sign Museum in Cincinnati, Ohio, preserves, archives, and displays a collection of signs. The museum also displays the equipment utilized in the design and manufacture of signs. Tod Swormstedt began working on the museum in 1999. It opened to the public in 2005.
 W
WGeorges Claude was a French engineer and inventor. He is noted for his early work on the industrial liquefaction of air, for the invention and commercialization of neon lighting, and for a large experiment on generating energy by pumping cold seawater up from the depths. He has been considered by some to be "the Edison of France". Claude was an active collaborator with the German occupiers of France during the Second World War, for which he was imprisoned in 1945 and stripped of his honors.
 W
WThe End of the Red Line is an abstract light sculpture by Alejandro and Moira Sina.
 W
WDouglas Leigh was an American advertising executive and lighting designer, and a pioneer in signage and outdoor advertising. He is famous for making New York City's Times Square the site of some of the world's most famous neon signs, or electric billboards. Leigh also designed the colored lighting scheme for the Empire State Building.
 W
WDaniel McFarlan Moore was a U.S. electrical engineer and inventor. He developed a novel light source, the "Moore lamp", and a business that produced them in the early 1900s. The Moore lamp was the first commercially viable light-source based on gas discharges instead of incandescence; it was the predecessor to contemporary neon lighting and fluorescent lighting. In his later career Moore developed a miniature neon lamp that was extensively used in electronic displays, as well as vacuum tubes that were used in early television systems.
 W
WA neon lamp is a miniature gas discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes. When sufficient voltage is applied and sufficient current is supplied between the electrodes, the lamp produces an orange glow discharge. The glowing portion in the lamp is a thin region near the cathode; the larger and much longer neon signs are also glow discharges, but they use the positive column which is not present in the ordinary neon lamp. Neon glow lamps were widely used as indicator lamps in the displays of electronic instruments and appliances.
 W
WThe Neon Museum in Las Vegas, Nevada, United States, features signs from old casinos and other businesses displayed outdoors on 2.62 acres. The museum features a restored lobby shell from the defunct La Concha Motel as its visitor center, which officially opened on October 27, 2012.
 W
WNeon Museum, also the Museum of Neon is a museum located in Warsaw's Praga-Południe. The institution documents and protects Polish light advertisements created after World War II. It is the first in Poland and one of the few museums of neon signs in the world.
 W
WA neon-sign transformer (NST) is a transformer made for the purpose of powering a neon sign. They convert line voltage from the 120-347 V up to high voltages, in the range of 2 to 15 kV. These transformers supply between 18-30 mA; 60 mA on special order A more general designation would be "luminous tube transformer", because many other gases are used in luminous gas discharge tubes.
 W
WNeonopolis, a 250,000 sq ft (23,000 m2) shopping mall, is a $100 million entertainment complex in Las Vegas, Nevada located on top of a $15 million city parking garage. It is located on Fremont Street, at the corner of Las Vegas Boulevard. In keeping with the complex's name, it contains three miles of neon lights.
 W
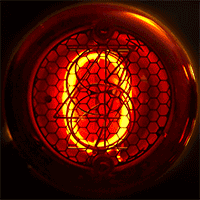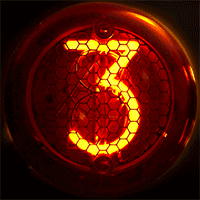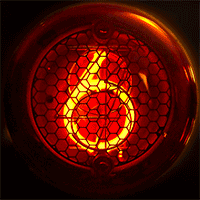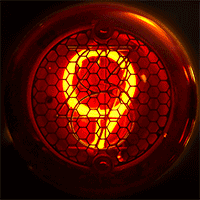
WA Nixie tube, or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
 W
WIn the signage industry, neon signs are electric signs lighted by long luminous gas-discharge tubes that contain rarefied neon or other gases. They are the most common use for neon lighting, which was first demonstrated in a modern form in December 1910 by Georges Claude at the Paris Motor Show. While they are used worldwide, neon signs were popular in the United States from about the 1920s to 1960s. The installations in Times Square, many originally designed by Douglas Leigh, were famed, and there were nearly 2,000 small shops producing neon signs by 1940. In addition to signage, neon lighting is used frequently by artists and architects, and in plasma display panels and televisions. The signage industry has declined in the past several decades, and cities are now concerned with preserving and restoring their antique neon signs.
 W
WYESCO is a privately owned manufacturer of electric signs based in Salt Lake City, founded by Thomas Young in 1920. The company provides design, fabrication, installation and maintenance of signs.