 W
WA smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card is a physical electronic authorization device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, mobile phones (SIM), public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.
 W
WA contactless smart card is a contactless credential whose dimensions are credit-card size. Its embedded integrated circuits can store data and communicate with a terminal via NFC. Commonplace uses include transit tickets, bank cards and passports.
 W
WSome widely used contactless smart cards include Melbourne's myki, Sydney's Opal Card, London's Oyster card, South Korea's T-money, Hong Kong's Octopus card, Stockholm's Access card, Japan's Suica and Pasmo cards, Singapore's NETS FlashPay and EZ-Link cards, Manila's Beep cards, Nigeria's ETC Card, Paris's Calypso/Navigo, the Dutch OV-Chipkaart, Greater Toronto's Presto card and Lisbon's LisboaViva card, which predate the ISO/IEC 14443 standard. The following tables list smart cards used for public transport and other electronic purse applications.
 W
WThe SUBE card is a contactless smart card system introduced in Argentina in February 2009. It is used on public transport services within the Buenos Aires metropolitan area and other Argentine cities and was promoted by the Argentine Secretary of Transportation. It is valid on a number of different travel systems across the city including the Underground, buses and trains.
 W
WA card enclosure is a container for smart cards, credit cards, debit cards, telephone cards, visiting cards, business cards and other cards of similar size. Most cards have dimensions that follow the ID-1 format of the ISO/IEC 7810 standard which specify the physical dimensions for cards to be 85.60 × 53.98 mm. The enclosures can be made of metal, leather, or plastic and come in various colors and designs. Sometimes having a laser engraved design for aesthetic purposes.
 W
WCarta Worldwide is a Canadian financial technology company that offers digital payments technology and modern card issuer processing for banks and financial technology "fintech" companies. In addition to their Canadian headquarters in Toronto, Carta has offices in London and Casablanca. Carta operates internationally, providing financial technology and digital payment software and cloud API issuer processing.
 W
WCarte Bleue was a major debit card payment system operating in France. Unlike Visa Electron or Maestro debit cards, Carte Bleue allowed transactions without requiring authorization from the cardholder's bank. In many situations, the card worked like a credit card but without fees for the cardholder. The system has now been integrated into a wider scheme called CB or carte bancaire. All Carte Bleue cards were part of CB, but not all CB cards were Carte Bleue.
 W
WThe Chip Authentication Program (CAP) is a MasterCard initiative and technical specification for using EMV banking smartcards for authenticating users and transactions in online and telephone banking. It was also adopted by Visa as Dynamic Passcode Authentication (DPA). The CAP specification defines a handheld device with a smartcard slot, a numeric keypad, and a display capable of displaying at least 12 characters. Banking customers who have been issued a CAP reader by their bank can insert their Chip and PIN (EMV) card into the CAP reader in order to participate in one of several supported authentication protocols. CAP is a form of two-factor authentication as both a smartcard and a valid PIN must be present for a transaction to succeed. Banks hope that the system will reduce the risk of unsuspecting customers entering their details into fraudulent websites after reading so-called phishing emails.
 W
WChipknip was an electronic cash system used in the Netherlands until 1 January 2015. All ATM cards issued by Dutch banks had smart cards that could be loaded with value via Chipknip loading stations next to ATMs. For people who did not have Dutch bank accounts, pre-paid Chipknip cards could be purchased at various locations in the Netherlands. Chipknip was used for payments at parking machines, office canteens, and for other small retail transactions. No network access was required by the payment collection terminal. The system was complementary to the online electronic point-of-sale payment system known in the Netherlands as PIN which transfers money between bank accounts in real-time. The maximum value of Chipknip storage and transactions was quite limited but adequate for small retail transactions.
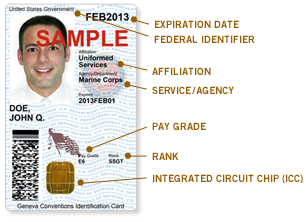 W
WThe Common Access Card, also commonly referred to as the CAC is a smart card about the size of a credit card. It is the standard identification for Active Duty United States Defense personnel, to include the Selected Reserve and National Guard, United States Department of Defense (DoD) civilian employees, United States Coast Guard (USCG) civilian employees and eligible DoD and USCG contractor personnel. It is also the principal card used to enable physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and it provides access to defense computer networks and systems. It also serves as an identification card under the Geneva Conventions. In combination with a personal identification number, a CAC satisfies the requirement for two-factor authentication: something the user knows combined with something the user has. The CAC also satisfies the requirements for digital signature and data encryption technologies: authentication, integrity and non-repudiation.
 W
WDubai Plus is a city smart card program for government and semi-government employees in Dubai. It was announced on May 12, 2015 by the Department of Economic Development (DED) in Dubai and the Dubai Government Human Resources Department (DGHR) together with National Plus and Network International, a payment service provider.
 W
WThe Estonian identity card is a mandatory identity document for citizens of Estonia. In addition to regular identification of a person, an ID-card can also be used for establishing one's identity in electronic environment and for giving one's digital signature. Within Europe as well as French overseas territories and Georgia, the Estonian ID Card can be used by the citizens of Estonia as a travel document.
 W
WGemalto was an international digital security company providing software applications, secure personal devices such as smart cards and tokens, and managed services. Formed in June 2006 by the merger of two companies, Axalto and Gemplus International. Gemalto N.V.'s revenue in 2018 was €2.969 billion.
 W
WHelmut Gröttrup was a German engineer, rocket scientist and inventor of the smart card. During World War II, he worked in the German V-2 rocket program under Wernher von Braun. From 1946 to 1953 he headed a group of 170 German scientists who were forced to work for the Soviet rocketry program under Sergei Korolev. After returning to West Germany in December 1953, he developed data processing systems and contributed to early commercial applications of computer science. In 1967 Gröttrup invented the basic principles of the smart card as a forgery-proof "key" for secure identification and access control.
 W
WGroupement des cartes bancaires CB, also known as simply CB, is France's national interbank network, with over 46,000 ATMs and over 1 million EFTPOS acceptance points.
 W
WHanaro Card is contactless smart card used in the public transportation system in Busan, South Korea. First used in 1997, the Hanaro Card is now also used for paying at parking lots and toll booths.
 W
WHNA Technology Investments Holdings Limited formerly known as Advanced Card Systems Holdings Limited is a Cayman Islands-incorporated offshore holding company. Its subsidiary, Advanced Card Systems Limited, was incorporated in British Hong Kong in 1995 by Denny Wong. In 2017, HNA Group, via HNA EcoTech Group and HNA EcoTech Group's subsidiary, acquired Advanced Card Systems Holdings as part of a reverse IPO.
 W
WInfineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 46,665 employees and is one of the ten largest semiconductor manufacturers worldwide. It is market leader in automotive and power semiconductors. In fiscal year 2020, the company achieved sales of €8.6 billion. Infineon bought Cypress in April 2020.
 W
WMore Card is a rechargeable smart card for paying transportation fares in public transport systems in India. Tipped as a nationwide interoperable transport card, the card aims to be a single point of transaction, applicable in state buses, Metro and even parking. The card was launched in 2012 in Delhi, initially acting as a common card for the Delhi Metro and its feeder buses.
 W
WIn cryptography, the OpenPGP card is an ISO/IEC 7816-4, -8 compatible smart card that is integrated with many OpenPGP functions. Using this smart card, various cryptographic tasks can be performed. It allows secure storage of secret key material; all versions of the protocol state, "Private keys and passwords cannot be read from the card with any command or function." However, new key pairs may be loaded onto the card at any time, overwriting the existing ones.
 W
WThe RioCard is a smartcard system used in the transport system of Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. The card is contactless and uses MIFARE technology. It is a form of electronic payment produced and distributed by the Fetranspor company, in cooperation with Itaú bank. Its installation was seen as strengthening Brazil's connection with the Open Standard for Public Transport (OSPT) Alliance.
 W
WSerbian identity card is the national identification card used in Serbia. Though the ID card is a primary photo ID, Serbian passport and national Drivers license are used as valid photo IDs for various purposes. It is issued to all Serbian citizens residing in the country above 10 years of age, while it's compulsory for those over the age of 16.
 W
WA SIM card also known as subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), is an integrated circuit running a card operating system (COS) that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.
 W
WSubtepass is the electronic smartcard used for trips on the Buenos Aires Metro. In addition to the regular Subtepass, there are special discounted and free versions available, based on category. Secondary and tertiary school students may purchase a discounted Abono Estudiantil . Teachers that are employed by the city school system may purchase a discounted Abono Maestro. Students in primary school may ride the metro to and from school for free with a Pase Escolar Primario, provided they are wearing their white smock uniform. In addition, retirees, pensioners, and certain classes of retired military personnel are eligible for a free Pase Jubilados y Pensionados. There are also free passes for visually impaired and disabled persons.
 W
WT-money is a rechargeable series of smart cards and other "smart" devices used for paying transportation fares in and around Seoul and other areas of South Korea. T-money can also be used in lieu of cash or credit cards in some convenience stores and other businesses. The T-money System has been implemented and is being operated by T-money Co., Ltd of which 34.4% owned by Seoul Special City Government, 31.85% owned by LG CNS, and 15.73% owned by Credit Card Union.
 W
WThe Técély Card is a smartcard in Lyon, France launched in 2005. Unlike other smartcards, where a topup amount is required at the start and is deducted each time you make a trip, the TCL card has a €5 fee, and the option to put on either a weekly or monthly pass on top of this. This must be renewed every week or month to ensure you can keep using the card. The card has a five-year expiry date from the date of when you first purchase it.
 W
WA SIM card also known as subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), is an integrated circuit running a card operating system (COS) that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.
 W
WA U-Key is an implementation of the MIFARE RFID chip, encased in a plastic key style housing. It is used as a prepayment system on vending machines and for some self-service diving air compressors in Switzerland
 W
WThe VEM is a Smart card system used in bus, train and metro of the metropolitan area of Recife, Brazil.