 W
WDemining or mine clearance is the process of removing land mines from an area. In military operations, the object is to rapidly clear a path through a minefield, and this is often done with devices such as mine plows and blast waves. By contrast, the goal of humanitarian demining is to remove all of the landmines to a given depth and make the land safe for human use. Specially trained dogs are also used to narrow down the search and verify that an area is cleared. Mechanical devices such as flails and excavators are sometimes used to clear mines.
 W
WBomb disposal is an explosives engineering profession using the process by which hazardous explosive devices are rendered safe. Bomb disposal is an all-encompassing term to describe the separate, but interrelated functions in the military fields of explosive ordnance disposal (EOD) and improvised explosive device disposal (IEDD), and the public safety roles of public safety bomb disposal (PSBD) and the bomb squad.
 W
WThe Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) is an international treaty that prohibits all use, transfer, production, and stockpiling of cluster bombs, a type of explosive weapon which scatters submunitions ("bomblets") over an area. Additionally, the Convention establishes a framework to support victim assistance, clearance of contaminated sites, risk reduction education, and stockpile destruction. The convention was adopted on 30 May 2008 in Dublin, and was opened for signature on 3 December 2008 in Oslo. It entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states. As of July 2021, a total of 123 States have joined the Convention – 110 States Parties and 13 Signatories.
 W
WDiana, Princess of Wales, was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of Charles, Prince of Wales—the heir apparent to the British throne—and mother of Prince William and Prince Harry. Diana's activism and glamour made her an international icon and earned her enduring popularity as well as unprecedented public scrutiny, exacerbated by her tumultuous private life.
 W
WJohn Vernon Head was a New Zealand peace activist. After a 40-year teaching career, he founded the New Zealand Campaign Against Landmines (CALM) in 1993. He boosted New Zealand's awareness of the scale of worldwide landmine problems and his efforts were the catalyst for the Anti-Personnel Mines Prohibition Act 1988, which became New Zealand law early in 1999.
 W
WThe Mine Kafon Drone is a drone for demining, led by Afghanistan-born Massoud Hassani. The drone is designed to map an area for land mines, detect the mines, and then detonate them remotely. It has been field-tested with the Dutch Ministry of Defence. The use of a drone is safer and less expensive than typical methods for mine removal, which endanger trained mine disposal experts and dogs. The Mine Kafon Foundation, established by Hassani in 2013, is based in Eindhoven, Netherlands.
 W
WMinesweeping is the practice of the removal of explosive naval mines, usually by a specially designed ship called a minesweeper using various measures to either capture or detonate the mines, but sometimes also with an aircraft made for that purpose. Minesweeping has been practiced since the advent of naval mining in 1855 in the Crimean War. The first minesweepers date to that war and consisted of British rowboats trailing grapnels to snag the mines.
 W
WMKE TAMGEÇ is a mine destruction system produced by MKEK, consisting of chain explosives attached to the back of a rocket.
 W
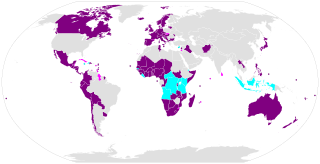
WThe Convention on the Prohibition of the Use, Stockpiling, Production and Transfer of Anti-Personnel Mines and on their Destruction, known informally as the Ottawa Treaty, the Anti-Personnel Mine Ban Convention, or often simply the Mine Ban Treaty, aims at eliminating anti-personnel landmines (AP-mines) around the world. To date, there are 164 state parties to the treaty. One state has signed but not ratified the treaty, while 32 UN states, including China, Russia, and the United States have not; making a total of 33 United Nations states not party.
 W
WThis is a list of states that have signed and ratified or acceded to the Ottawa Treaty. The treaty, which outlaws anti-personnel mines, was opened for signature on December 3, 1997. Canada, Ireland, and Mauritius became the first states to ratify the treaty that same day. The treaty came into force and closed for signature on March 1, 1999 with the ratification by 40 states. Since then, states that did not sign the treaty can now only accede to it. Currently, 164 states have ratified or acceded to the treaty, and one state had signed the treaty but not ratified it.
 W
WKenneth R. Rutherford is co-founder of the Landmine Survivors Network and a researcher in the field of political science.
 W
WCornelio Sommaruga is a Swiss humanitarian, lawyer and diplomat who is best known for being President of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) from 1987 to 1999. Today, he chairs the Geneva International Centre for Humanitarian Demining (GICHD) in Geneva. He is also active on a number of boards, such as the International Union Against Cancer. Currently he is Chair of the Board of Directors of the Foundation For the Future, an organization dedicated to promoting human rights in the Middle East and North Africa, and the honorary President of Initiatives of Change International, a global organization dedicated to "building trust across the world's divides" of culture, nationality, belief, and background.
 W
WSuperman: Deadly Legacy is a special-edition "humanitarian comic book" featuring Superman that promotes “landmine awareness" among children, particularly from countries where there are active landmines after war. The Superman comic book was published by DC Comics, the United States government, and United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF) in 1996. In Superman: Deadly Legacy, Superman – a well-known superhero in the United States and Europe – acts as a teacher educating children about the dangers of landmines. The target countries for disseminating copies of the comic book include Bosnia, the Former Yugoslavia, and Kosovo.
 W
WThe United Nations Mine Action Service (UNMAS) is a service located within the United Nations Department of Peacekeeping Operations that specializes in coordinating and implementing activities to limit the threat posed by mines, explosive remnants of war and improvised explosive devices.
 W
WJody Williams is an American political activist known for her work in banning anti-personnel landmines, her defense of human rights, and her efforts to promote new understandings of security in today's world. She was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1997 for her work toward the banning and clearing of anti-personnel mines.
 W
WZero Landmine is an Extended play (EP) created to promote awareness of the problem of landmines and to promote a ban on landmines. Japanese recording artist Ryuichi Sakamoto led a collection of musicians to form a group called NML, and they released the single Zero Landmine on April 25, 2001.