 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WThe Johnson boiler is a water-tube boiler used for ship propulsion.
 W
WA launch-type, gunboat or horizontal multitubular boiler is a form of small steam boiler. It consists of a cylindrical horizontal shell with a cylindrical furnace and fire-tubes within this.
 W
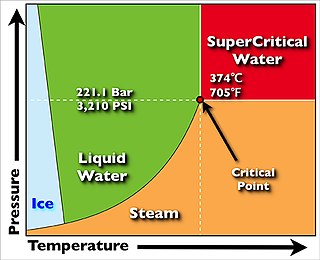
WA supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure, frequently used in the production of electric power.
 W
WSpiral water-tube boilers are a family of vertical water-tube boilers. Their steam generating tubes are narrow spiral tubes, arranged in circular fashion around a central vertical water drum.
 W
WA high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.
 W
WSpiral water-tube boilers are a family of vertical water-tube boilers. Their steam generating tubes are narrow spiral tubes, arranged in circular fashion around a central vertical water drum.
 W
WA shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships.
 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WThe Fairbairn-Beeley boiler was a design of fire-tube stationary boiler developed in the late 19th century. It takes its name from its two developers, Sir William Fairbairn and Thomas Beeley
 W
WW & J Galloway and Sons was a British manufacturer of steam engines and boilers based in Manchester, England. The firm was established in 1835 as a partnership of two brothers, William and John Galloway. The partnership expanded to encompass their sons and in 1889 it was restructured as a limited liability company. It ceased trading in 1932.
 W
WA launch-type, gunboat or horizontal multitubular boiler is a form of small steam boiler. It consists of a cylindrical horizontal shell with a cylindrical furnace and fire-tubes within this.
 W
WA haycock boiler is an early form of steam locomotive boiler with a prominently raised firebox of "Gothic arch", "haystack", or "coppernob" shape. The term haystack is most commonly used, but is avoided here as it is confusingly used for three quite different forms of boiler. This particularly large outer firebox served as the steam dome and was often highly decorated with polished brass. These were popular for early railway locomotives, from 1840 to the 1850s.
 W
WA shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships.
 W
WSpiral water-tube boilers are a family of vertical water-tube boilers. Their steam generating tubes are narrow spiral tubes, arranged in circular fashion around a central vertical water drum.
 W
WThe Johnson boiler is a water-tube boiler used for ship propulsion.
 W
WA shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships.
 W
WA launch-type, gunboat or horizontal multitubular boiler is a form of small steam boiler. It consists of a cylindrical horizontal shell with a cylindrical furnace and fire-tubes within this.
 W
WA launch-type, gunboat or horizontal multitubular boiler is a form of small steam boiler. It consists of a cylindrical horizontal shell with a cylindrical furnace and fire-tubes within this.
 W
WSpiral water-tube boilers are a family of vertical water-tube boilers. Their steam generating tubes are narrow spiral tubes, arranged in circular fashion around a central vertical water drum.
 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
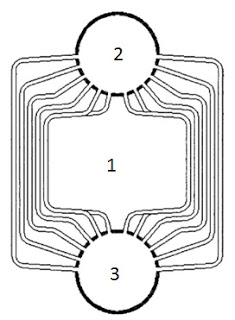
WAn O-type boiler is a form of water-tube boiler. It is named, like the D-type and A-type boilers, from the approximate shape of its tubes.
 W
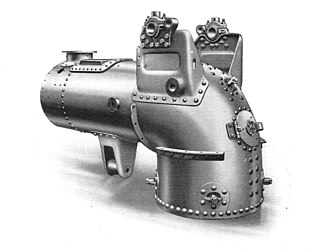
WA package boiler is a factory-made boiler. Package boilers are available in a range of standard designs. Package boilers are used for heating and act as a steam generator for small power purposes such as self-powered industrial plants. They cannot be used for large-scale power plants such as co-generation plants due to their size and lack of efficiency. Advantages of package boilers are that they can be brought in as a whole assembly, perfect for tight spaces, and easily installed. They require steam pipes, water pipes, fuel supply, electrical connections and can be made ready almost immediately. Because of their compact design, these boilers are cheaper to operate due to their automatic burner management system as well as maintenance cost.
 W
WA pistol boiler is a design of steam boiler used in light steam tractors and overtype steam wagons. It is noted for the unusual shape of the firebox, a circular design intended to be self-supporting without the use of firebox stays.
 W
WA shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships.
 W
WA "Scotch" marine boiler is a design of steam boiler best known for its use on ships.
 W
WThe Sentinel boiler was a design of vertical boiler, fitted to the numerous steam waggons built by the Sentinel Waggon Works.
 W
WSpiral water-tube boilers are a family of vertical water-tube boilers. Their steam generating tubes are narrow spiral tubes, arranged in circular fashion around a central vertical water drum.
 W
WThe Stirling boiler is an early form of water-tube boiler, used to generate steam in large land-based stationary plants. Although widely used around 1900, it has now fallen from favour and is rarely seen.
 W
WA thimble tube boiler is a form of steam boiler, usually provided as an auxiliary boiler or heat-recovery boiler. They are vertical in orientation and would be considered a form of water-tube boiler.
 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WA transverse boiler is a boiler used to generate steam to power a vehicle. Unlike other boilers, its external drum is mounted transversely across the vehicle.
 W
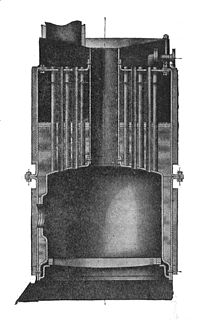
WA cross-tube boiler was the most common form of small vertical boiler. They were widely used, in the age of steam, as a small donkey boiler, for the independent power of winches, steam cranes etc.
 W
WA vertical fire-tube boiler or vertical multitubular boiler is a vertical boiler where the heating surface is composed of multiple small fire-tubes, arranged vertically.
 W
WA vertical fire-tube boiler or vertical multitubular boiler is a vertical boiler where the heating surface is composed of multiple small fire-tubes, arranged vertically.
 W
WThree-drum boilers are a class of water-tube boiler used to generate steam, typically to power ships. They are compact and of high evaporative power, factors that encourage this use. Other boiler designs may be more efficient, although bulkier, and so the three-drum pattern was rare as a land-based stationary boiler.
 W
WYarrow boilers are an important class of high-pressure water-tube boilers. They were developed by Yarrow & Co. (London), Shipbuilders and Engineers and were widely used on ships, particularly warships.