 W
WA 1951 USAF resolution test chart is a microscopic optical resolution test device originally defined by the U.S. Air Force MIL-STD-150A standard of 1951. The design provides numerous small target shapes exhibiting a stepped assortment of precise spatial frequency specimens. It is widely used in optical engineering laboratory work to analyze and validate imaging systems such as microscopes, cameras and image scanners.
 W
WANNINE-6plus is a water soluble voltage sensitive dye. This compound was developed at the Max Planck Institute for Biochemistry in Germany. It is used to optically measure the changes in transmembrane voltage of excitable cells, including neurons, skeletal and cardiac myocytes.
 W
WIn August 1988 Apple Computer introduced the Apple Scanner. It was their first A4 flatbed scanner. It was capable of a 4-bit image with 16 levels of grey in a maximum resolution of 300 dpi. The scanner could complete a full scan in 20.4 seconds. It shipped with a SCSI connection with an unused serial port.
 W
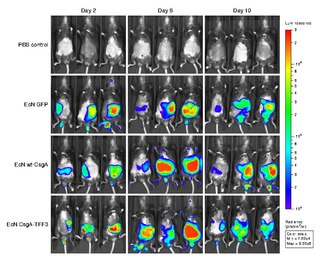
WBioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a technology developed over the past decade that allows for the noninvasive study of ongoing biological processes. Recently, bioluminescence tomography (BLT) has become possible and several systems have become commercially available. In 2011, PerkinElmer acquired one of the most popular lines of optical imaging systems with bioluminescence from Caliper Life Sciences.
 W
WDiffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging is the use of specific MRI sequences as well as software that generates images from the resulting data that uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. It allows the mapping of the diffusion process of molecules, mainly water, in biological tissues, in vivo and non-invasively. Molecular diffusion in tissues is not free, but reflects interactions with many obstacles, such as macromolecules, fibers, and membranes. Water molecule diffusion patterns can therefore reveal microscopic details about tissue architecture, either normal or in a diseased state. A special kind of DWI, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), has been used extensively to map white matter tractography in the brain.
 W
WDigital Variance Angiography (DVA) is a novel image processing method based on kinetic imaging, which allows the visualization of motion on image sequences generated by penetrating radiations. DVA is a specific form of kinetic imaging: it requires angiographic image series, which are created by X-ray or fluoroscopic imaging and by the administration of contrast media during various medical procedures. The resulting single DVA image visualizes the path of contrast agent with relatively low background noise.
 W
WFörster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance.
 W
WFourier ptychography is a computational imaging technique based on optical microscopy that consists in the synthesis of a wider numerical aperture from a set of full-field images acquired at various coherent illumination angles, resulting in increased resolution compared to a conventional microscope.
 W
WFree-Form Select is a technique in printmaking, graphic design and image processing.
 W
WHyperspectral imaging, like other spectral imaging, collects and processes information from across the electromagnetic spectrum. The goal of hyperspectral imaging is to obtain the spectrum for each pixel in the image of a scene, with the purpose of finding objects, identifying materials, or detecting processes. There are three general branches of spectral imagers. There are push broom scanners and the related whisk broom scanners, which read images over time, band sequential scanners, which acquire images of an area at different wavelengths, and snapshot hyperspectral imaging, which uses a staring array to generate an image in an instant.
 W
WKinetic imaging is an imaging technology developed by Szabolcs Osváth and Krisztián Szigeti in the Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology at Semmelweis University. The technology allows the visualization of motion; it is based on an altered data acquisition and image processing algorithm combined with imaging techniques that use penetrating radiation. Kinetic imaging has the potential for use in a wide variety of areas including medicine, engineering, and surveillance. For example, physiological movements, such as the circulation of blood or motion of organs can be visualized using kinetic imaging. Because of the reduced noise and the motion-based image contrast, kinetic imaging can be used to reduce X-ray dose and/or amount of required contrast agent in medical imaging. In fact, clinical trials are underway in the fields of vascular surgery and interventional radiology. Non-medical applications include non-destructive testing of products and port security scanning for stowaway pests.
 W
WA METATOY is a sheet, formed by a two-dimensional array of small, telescopic optical components, that switches the path of transmitted light rays. METATOY is an acronym for "metamaterial for rays", representing a number of analogies with metamaterials; METATOYs even satisfy a few definitions of metamaterials, but are certainly not metamaterials in the usual sense. When seen from a distance, the view through each individual telescopic optical component acts as one pixel of the view through the METATOY as a whole. In the simplest case, the individual optical components are all identical; the METATOY then behaves like a homogeneous, but pixellated, window that can have very unusual optical properties.
 W
WA multispectral image is one that captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected via the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range, i.e. infrared and ultra-violet. Spectral imaging can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis.4
 W
WNanoSIMS is an analytical instrument manufactured by CAMECA which operates on the principle of secondary ion mass spectrometry. The NanoSIMS is used to acquire nanoscale resolution measurements of the elemental and isotopic composition of a sample. The NanoSIMS is able to create nanoscale maps of elemental or isotopic distribution, parallel acquisition of up to seven masses, isotopic identification, high mass resolution, subparts-per-million sensitivity with spatial resolution down to 50 nm.
 W
WNeutron imaging is the process of making an image with neutrons. The resulting image is based on the neutron attenuation properties of the imaged object. The resulting images have much in common with industrial X-ray images, but since the image is based on neutron attenuating properties instead of X-ray attenuation properties, some things easily visible with neutron imaging may be very challenging or impossible to see with X-ray imaging techniques.
 W
Wpara-Nitroblebbistatin is a non-phototoxic, photostable myosin inhibitor with low fluorescence. Its myosin inhibitory properties are very similar to those of blebbistatin.
 W
WNoesis is software for viewing, converting, and reverse engineering data. Common data types supported by the software include images, 3D models, medical imaging (DICOM), and animation.
 W
WOsiriX is an image processing application for Mac dedicated to DICOM images produced by equipment. OsiriX is complementary to existing viewers, in particular to nuclear medicine viewers. It can also read many other file formats: TIFF, JPEG, PDF, AVI, MPEG and QuickTime. It is fully compliant with the DICOM standard for image communication and image file formats. OsiriX is able to receive images transferred by DICOM communication protocol from any PACS or medical imaging modality.
 W
WThe term panomorph derives from the Greek words pan meaning all, horama meaning view, and morph meaning form. A panomorph lens is a particular type of wide-angle lens specifically designed to improve the optical performances in predefined zones of interest or in the whole image compared to traditional fisheye lenses. Some examples of improved optical parameters include the number of pixels, the MTF or the relative illumination.
 W
WPhase-contrast X-ray imaging (PCI) or phase-sensitive X-ray imaging is a general term for different technical methods that use information concerning changes in the phase of an X-ray beam that passes through an object in order to create its images. Standard X-ray imaging techniques like radiography or computed tomography (CT) rely on a decrease of the X-ray beam's intensity (attenuation) when traversing the sample, which can be measured directly with the assistance of an X-ray detector. In PCI however, the beam's phase shift caused by the sample is not measured directly, but is transformed into variations in intensity, which then can be recorded by the detector.
 W
WPhotoacoustic microscopy is an imaging method based on the photoacoustic effect and is a subset of photoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustic microscopy takes advantage of the local temperature rise that occurs as a result of light absorption in tissue. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser beam, tissues undergo thermoelastic expansion, resulting in the release of a wide-band acoustic wave that can be detected using a high-frequency ultrasound transducer. Since ultrasonic scattering in tissue is weaker than optical scattering, photoacoustic microscopy is capable of achieving high-resolution images at greater depths than conventional microscopy methods. Furthermore, photoacoustic microscopy is especially useful in the field of biomedical imaging due to its scalability. By adjusting the optical and acoustic foci, lateral resolution may be optimized for the desired imaging depth.
 W
WPrior Scientific Instruments Ltd was established in London in 1919 as a manufacturer of optical microscopes. It is the last traditional microscope manufacturer of makers such as Vickers, W.Watson and Son, Baker, Charles Perry, Cooke, Troughton & Simms and many others who have ceased to produce microscopes.
 W
WRaking light, the illumination of objects from a light source at an oblique angle or almost parallel to the surface, provides information on the surface topography and relief of the artefact thus lit. It is widely used in the examination of works of art.
Schlieren imaging is a method to visualize density variations in transparent media.
 W
WSpatio-spectral scanning is one of four techniques for hyperspectral imaging, the other three being spatial scanning, spectral scanning and non-scanning, or snapshot hyperspectral imaging.
 W
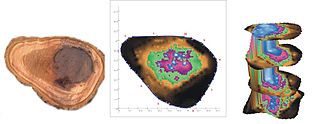
WAcoustic or stress wave tomography is a non-destructive measurement method for the visualization of the structural integrity of a solid object. It is being used to test the preservation of wood or concrete, for example. The term acoustic tomography refers to the perceptible sounds that are caused by the mechanical impulses used for measuring. The term stress wave tomography describes the measurement method more accurately.
 W
WThermal acoustic imaging (TAI) is an inspection process developed in about 2005 to detect internal and external cracking in hollow core turbofan engine fan blades by Pratt and Whitney (P&W). The TAI is accomplished in an enclosed air-conditioned room within P&W's overhaul and repair facility in East Hartford, Connecticut. This process is used to inspect the PW4000 112-inch diameter fan blades, and is proprietary to P&W. Sound energy is utilized to generate an excitation of the fan blade’s internal and external structure. The sound energy excitation will cause relative movement between each side of a contacting discontinuity that will cause frictional heating. The frictional heat generated by the movement of each side of the discontinuity is detected on the surface of the fan blade by a thermal sensor.
 W
WVoxel-based morphometry is a computational approach to neuroanatomy that measures differences in local concentrations of brain tissue, through a voxel-wise comparison of multiple brain images.