 W
WThe Abbott-Firestone curve or bearing area curve (BAC) describes the surface texture of an object. The curve can be found from a profile trace by drawing lines parallel to the datum and measuring the fraction of the line which lies within the profile.
 W
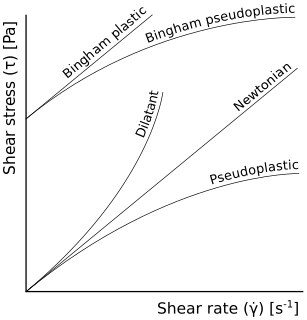
WApparent viscosity is the shear stress applied to a fluid divided by the shear rate. For a Newtonian fluid, the apparent viscosity is constant, and equal to the Newtonian viscosity of the fluid, but for non-Newtonian fluids, the apparent viscosity depends on the shear rate. Apparent viscosity has the SI derived unit Pa·s (Pascal-second, but the centipoise is frequently used in practice:.
 W
WIn materials science, asperity, defined as "unevenness of surface, roughness, ruggedness", has implications in physics and seismology. Smooth surfaces, even those polished to a mirror finish, are not truly smooth on a microscopic scale. They are rough, with sharp, rough or rugged projections, termed "asperities". Surface asperities exist across multiple scales, often in a self affine or fractal geometry. The fractal dimension of these structures has been correlated with the contact mechanics exhibited at an interface in terms of friction and contact stiffness.
 W
WA bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion, and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or to the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.
 W
WExtreme tribology refers to tribological situations under extreme operating conditions which can be related to high loads and/or temperatures, or severe environments. Also, they may be related to high transitory contact conditions, or to situations with near-impossible monitoring and maintenance opportunities. In general, extreme conditions can typically be categorized as involving abnormally high or excessive exposure to e.g. cold, heat, pressure, vacuum, voltage, corrosive chemicals, vibration, or dust. The extreme conditions should include any device or system requiring a lubricant operating under any of the following conditions:Beyond the original machinery design specifications. Beyond the original machinery ambient parameters. Application in an environmentally sensitive location. Beyond the original lubricant design specification.
 W
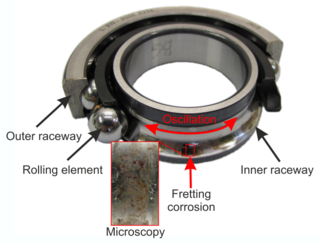
WFalse brinelling is a bearing damage caused by fretting, with or without corrosion, that causes imprints that look similar to brinelling, but are caused by a different mechanism. False brinelling may occur in bearings which act under small oscillations or vibrations.
 W
WFretting refers to wear and sometimes corrosion damage at the asperities of contact surfaces. This damage is induced under load and in the presence of repeated relative surface motion, as induced for example by vibration. The ASM Handbook on Fatigue and Fracture defines fretting as: "A special wear process that occurs at the contact area between two materials under load and subject to minute relative motion by vibration or some other force." Fretting tangibly degrades the surface layer quality producing increased surface roughness and micropits, which reduces the fatigue strength of the components.
 W
WFriction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into static friction ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and kinetic friction between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other.Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces.Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a solid material while it undergoes deformation.
 W
WGalling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material may appear gouged with balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface.
 W
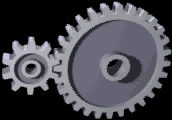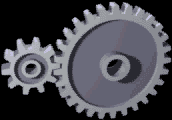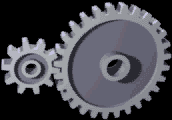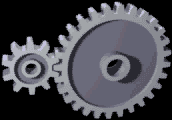
WA gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth, which mesh with another toothed part to transmit torque. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their gear ratio, and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape.
 W
WLubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology.
 W
WIn fluid dynamics, lubrication theory describes the flow of fluids in a geometry in which one dimension is significantly smaller than the others. An example is the flow above air hockey tables, where the thickness of the air layer beneath the puck is much smaller than the dimensions of the puck itself.
 W
WMotor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances that consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. Motor oil is used for lubrication of internal combustion engines. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts.
 W
WNormal contact stiffness is a physical quantity related to the generalized force displacement behavior of rough surfaces in contact with a rigid body or a second similar rough surface.. Rough surfaces can be seen as consisting of large numbers asperities. As two solid bodies of the same material approach one another, asperities interact with one another and they transition from conditions of non-contact to homogeneous bulk type behaviour. The varying values of stiffness and true contact area that is exhibited at an interface during this transition is dependent on conditions of applied pressure and is of notable importance for the study of systems involving the physical interactions of multiple bodies including granular matter, electrode contacts, and thermal contacts, where the interface-localized structures govern overall system performance.
 W
WThe Journal of Engineering Tribology, Part J of the Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE), is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes research on engineering science associated with tribology and its applications. The journal was first published in 1994 and is published by SAGE Publications on behalf of IMechE.
 W
WA rheometer is a laboratory device used to measure the way in which a liquid, suspension or slurry flows in response to applied forces. It is used for those fluids which cannot be defined by a single value of viscosity and therefore require more parameters to be set and measured than is the case for a viscometer. It measures the rheology of the fluid.
 W
WA rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements between two bearing rings called races. The relative motion of the races causes the rolling elements to roll with very little rolling resistance and with little sliding.
 W
WIn rheology, shear thinning is the non-Newtonian behavior of fluids whose viscosity decreases under shear strain. It is sometimes considered synonymous for pseudoplastic behaviour, and is usually defined as excluding time-dependent effects, such as thixotropy.
 W
WSplash lubrication is a rudimentary form of lubrication found in early engines. Such engines could be external combustion engines, or internal combustion engines.
 W
WSurface roughness often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface texture. It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, the surface is rough; if they are small, the surface is smooth. In surface metrology, roughness is typically considered to be the high-frequency, short-wavelength component of a measured surface. However, in practice it is often necessary to know both the amplitude and frequency to ensure that a surface is fit for a purpose.
 W
WSynthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially made. Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil, but can also be synthesized from other raw materials. The base material, however, is still overwhelmingly crude oil that is distilled and then modified physically and chemically. The actual synthesis process and composition of additives is generally a commercial trade secret and will vary among producers.
 W
WThixotropy is a time-dependent shear thinning property. Certain gels or fluids that are thick or viscous under static conditions will flow over time when shaken, agitated, shear-stressed, or otherwise stressed. They then take a fixed time to return to a more viscous state. Some non-Newtonian pseudoplastic fluids show a time-dependent change in viscosity; the longer the fluid undergoes shear stress, the lower its viscosity. A thixotropic fluid is a fluid which takes a finite time to attain equilibrium viscosity when introduced to a steep change in shear rate. Some thixotropic fluids return to a gel state almost instantly, such as ketchup, and are called pseudoplastic fluids. Others such as yogurt take much longer and can become nearly solid. Many gels and colloids are thixotropic materials, exhibiting a stable form at rest but becoming fluid when agitated. Thixotropy arises because particles or structured solutes require time to organize. An overview of thixotropy has been provided by Mewis and Wagner.
 W
WTribocorrosion is a material degradation process due to the combined effect of corrosion and wear. The name tribocorrosion expresses the underlying disciplines of tribology and corrosion. Tribology is concerned with the study of friction, lubrication and wear and corrosion is concerned with the chemical and electrochemical interactions between a material, normally a metal, and its environment. As a field of research tribocorrosion is relatively new, but tribocorrosion phenomena have been around ever since machines and installations are being used.
 W
WThe triboelectric effect is a type of contact electrification on which certain materials become electrically charged after they are separated from a different material with which they were in contact. Rubbing the two materials each with the other increases the contact between their surfaces, and hence the triboelectric effect. Rubbing glass with fur for example, or a plastic comb through the hair, can build up triboelectricity. Most everyday static electricity is triboelectric. The polarity and strength of the charges produced differ according to the materials, surface roughness, temperature, strain, and other properties.
 W
WTribo-Fatigue is a subdiscipline of mechanics, which studies wear-fatigue damage (WFD) in and the fracture of tribo-fatigue systems. The field was founded at the junction of tribology, and mechanics of fatigue damage and fracture in materials and structural elements.
 W
WA tribometer is an instrument that measures tribological quantities, such as coefficient of friction, friction force, and wear volume, between two surfaces in contact. It was invented by the 18th century Dutch scientist Musschenbroek
 W
WWear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical or chemical. The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology.