 W
WAfter the United Kingdom, France, and Italy signed with Germany the Munich Agreement on 30 September 1938, which "provided 'cession to Germany of the Sudeten German territory' of Czechoslovakia, despite existence of the 1924 alliance agreement and 1925 military pact between France and the Czechoslovak Republic, for which it is also known also as the Munich Betrayal," almost a year later, the Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany on 23 August 1939. In addition to stipulations of non-aggression, the treaty included a secret protocol that divided territories of Romania, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, and Finland into German and Soviet Union "spheres of influence", anticipating potential "territorial and political rearrangements" of these countries. In October and November 1940, German-Soviet talks about the potential of joining the Axis took place in Berlin, nothing came from the talks since Hitler's Ideological goal was Lebensraum in the East.
 W
WOperation Bagration was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian Strategic Offensive Operation, a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front of World War II, just over 2 weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west, causing the Germans to have to fight on two major fronts at the same time. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of 34 divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. It was the biggest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while 300,000 other German soldiers were cut off in the Courland Pocket.
 W
WThe Continuation War, also known as Second Soviet-Finnish war, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany, against the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1941 to 1944, as a part of World War II. In Soviet historiography, the war was called the Finnish Front of the Great Patriotic War. Germany regarded its operations in the region as part of its overall war efforts on the Eastern Front and provided Finland with critical material support and military assistance, including economic aid.
 W
WThe Deportation of the Balkars was the expulsion by the Soviet government of the entire Balkar population of the North Caucasus to Central Asia on March 8, 1944, during World War II. The expulsion was ordered by NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria after approval by Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin. All the 37,713 Balkars of the Caucasus were deported from their homeland in one day. The crime was a part of a Soviet forced settlement program and population transfer that affected several million members of non-Russian Soviet ethnic minorities between the 1930s and the 1950s. Officially the deportation was a response to the Balkars' supposed collaboration with occupying German forces. Later, in 1989, the Soviet government declared the deportation illegal.
 W
WThe Deportation of the Chechens and Ingush, also known as Aardakh, Operation Lentil was the Soviet forced transfer of the whole of the Vainakh populations of the North Caucasus to Central Asia on February 23, 1944, during World War II. The expulsion was ordered by NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria after approval by Soviet Leader Joseph Stalin, as a part of a Soviet forced settlement program and population transfer that affected several million members of non-Russian Soviet ethnic minorities between the 1930s and the 1950s.
 W
WThe deportation of the Crimean Tatars or the Sürgünlik ("exile") was the ethnic cleansing and cultural genocide of at least 191,044 Crimean Tatars in 18–20 May 1944 carried out by the Soviet government, ordered by Lavrentiy Beria, head of the Soviet state security and secret police, acting on behalf of Joseph Stalin. Within three days, the NKVD used cattle trains to deport mostly women, children, the elderly, even Communists and members of the Red Army, to mostly the Uzbek SSR, several thousand kilometres away. They were one of the several ethnicities who were encompassed by Stalin's policy of population transfer in the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe Deportation of the Meskhetian Turks was the forced transfer by the Soviet government of the entire Meskhetian Turk population from the Meskheti region of the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic to Central Asia on 14 November 1944. During the deportation, between 92,307 and 94,955 Meskhetian Turks were forcibly removed from 212 villages. They were packed into cattle wagons and mostly sent to the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic. Members of other ethnic groups were also deported during the operation, including Kurds and Hemshils, bringing the total to approximately 115,000 evicted people. They were placed in special settlements where they were assigned to forced labor. The deportation and harsh conditions in exile caused between 12,589 and 14,895 deaths, at a minimum.
 W
WOperation Frantic was a series of seven shuttle bombing operations during World War II conducted by American aircraft based in Great Britain and southern Italy which then landed at three Soviet airfields in Ukraine. The aircraft in Ukraine then flew bombing missions en route to their bases in Italy and Great Britain. The operation ran between June and September, 1944.
 W
WThis is a sub-article to Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive and Battle of Narva.
 W
WThe Battle of Korsun–Cherkasy, or the battle of the Korsun–Cherkasy pocket, was a World War II battle fought from 24 January to 16 February 1944 in the course of the Soviet Dnieper–Carpathian offensive in Ukraine following the Korsun–Shevchenkovsky offensive. In the battle, the 1st and 2nd Ukrainian Fronts, commanded, respectively, by Nikolai Vatutin and Ivan Konev, encircled German forces of Army Group South in a pocket near the Dnieper River. During weeks of fighting, the two Red Army Fronts tried to eradicate the pocket. The encircled German units attempted a breakout in coordination with a relief attempt by other German forces, resulting in heavy casualties, estimates of which vary.
 W
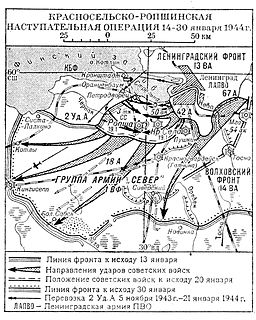
WThe Krasnoye Selo–Ropsha offensive, also known as Operation January Thunder and Neva-2, was a campaign between the Soviet Leningrad Front and the German 18th Army fought for the western approaches of Leningrad in 14–30 January 1944.
 W
WThe Soviet Union occupied most of the territory of the Baltic states in its 1944 Baltic Offensive during World War II. The Red Army regained control over the three Baltic capitals and encircled retreating Wehrmacht and Latvian forces in the Courland Pocket where they held out until the final German surrender at the end of the war. The German forces were deported and the leaders of Latvian collaborating forces were executed as traitors. After the war, the Baltic territories were reorganized into constituent republics of the USSR until they declared independence in 1990 amid the collapse of the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe occupation of the Baltic states involved the June 1940 invasion of the Red Army, and the subsequent military occupation of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania by the Soviet Union, under the leadership of Stalin and auspices of the August 1939 Nazi-Soviet Pact that had been signed immediately before the outbreak of World War II. The three countries were then annexed into the Soviet Union as constituent "republics" in August 1940, though United States and most other Western countries never recognised this incorporation, considering it illegal. On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany attacked the Soviet Union and within weeks occupied the Baltic territories. In July 1941, the Third Reich incorporated the Baltic territory into its Reichskommissariat Ostland. As a result of the Red Army's Baltic Offensive of 1944, the Soviet Union recaptured most of the Baltic states and trapped the remaining German forces in the Courland pocket until their formal surrender in May 1945.
 W
WOperation Tanne Ost was a German operation during World War II to capture the island Suursaari in the Gulf of Finland before it could fall into Soviet hands. Suursaari was especially important because it worked as a lock in the Finnish Gulf guarding the minefields keeping the Soviet Baltic Fleet in Kronstadt.
 W
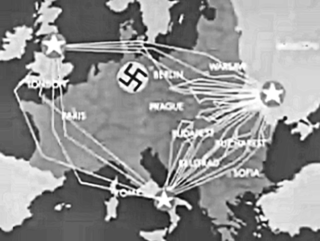
WThe Percentages Agreement was a secret informal agreement between British prime minister Winston Churchill and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin during the Fourth Moscow Conference in October 1944. It gave the percentage division of control over Eastern European countries, dividing them into spheres of influence. Franklin Roosevelt was consulted tentatively and conceded to the agreement. The content of the agreement was first made public by Churchill in 1953 in the final volume of his memoir. The US ambassador Averell Harriman, who was supposed to represent Roosevelt in these meetings, was excluded from this discussion.
 W
WRainbow, is a 1944 Soviet war film directed by Mark Donskoy and written by Wanda Wasilewska based on her novel, Tęcza. The film depicts life in a German-occupied village in Ukraine from the viewpoint of the terrorized villagers.
 W
WFinnmark was a former county in the northern part of Norway.
 W
WThe Soviet occupation of Romania refers to the period from 1944 to August 1958, during which the Soviet Union maintained a significant military presence in Romania. The fate of the territories held by Romania after 1918 that were incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1940 is treated separately in the article on Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina.
 W
WThe Tartu offensive operation, also known as the Battle of Tartu and the Battle of Emajõgi was a campaign fought over southeastern Estonia in 1944. It took place on the Eastern Front during World War II between the Soviet 3rd Baltic Front and parts of the German Army Group North.
 W
WThe Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years. The novel tells the story of a Russian youth, Alexander Grigoryev, as he grows up through Czarist Russia to the October Revolution to World War II. At the center of the story is Grigoriev's search for the lost Arctic expedition of Captain Ivan Tatarinov and the discovery of Severnaya Zemlya.