 W
WThe Soviet Union's 1979 nuclear test series was a group of 31 nuclear tests conducted in 1979. These tests followed the 1978 Soviet nuclear tests series and preceded the 1980 Soviet nuclear tests series.
 W
WAeroflot Flight 1691 crashed near Moscow Vnukovo Airport on 17 March 1979 killing 58 of the 119 people on board. The Tupolev Tu-104B operating the flight was overloaded and the crew received a false fire alarm.
 W
WAeroflot Flight 5484 was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Odessa to Kazan with a stopover in Kyiv that experienced loss of control followed by breaking up in the air on 29 August 1979 over the Tambov Oblast, killing all 63 people on board. It remains the deadliest Tu-124 crash and regular passenger services with the Tu-124 were permanently suspended after the accident, but the Tu-124 was still used by the Soviet military after the accident.
 W
WBeetle in the Anthill is a 1979 sci-fi novel by Boris and Arkady Strugatsky set in the Noon Universe.
 W
WThe Bodyguard is a 1979 Soviet action film released by Tadjikfilm. It is one of the best known of the Red Westerns and directed by the veteran feature and documentary maker, Ali Khamraev.
 W
WOn 11 August 1979, a mid-air collision occurred over the Ukrainian SSR, near the city of Dniprodzerzhynsk. The aircraft involved were both Tupolev Tu-134As on scheduled domestic passenger flights, operated by Aeroflot. All 178 people aboard both aircraft died in the accident. The Soviet aviation board investigating the accident concluded that the crash was caused by "mistakes and violations" made by air traffic controllers.
 W
WThe 1979 Soviet economic reform, or "Improving planning and reinforcing the effects of the economic mechanism on raising the effectiveness in production and improving the quality of work", was an economic reform initiated by Alexei Kosygin, the Chairman of the Council of Ministers. During Leonid Brezhnev's rule of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) the Soviet economy began to stagnate; this period is referred to by historians as the Era of Stagnation. Even after several reform attempts by Kosygin and his protégés, the economic situation in the country continued to deteriorate. In contrast to his earlier reform initiative, the 26th Congress decided that his government would implement the reform during the Eleventh five-year plan from 1981–1985. This never happened, and even Brezhnev complained that implementation of the reform had been slow. This unfinished reform is seen by some as the last major pre-perestroika reform initiative put forward by the Soviet government.
 W
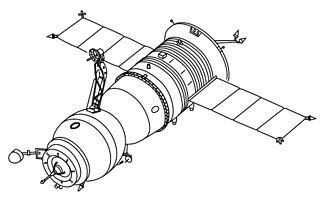
WKosmos 1074 was a Soviet unmanned long-duration test flight of the Soyuz-T spacecraft launched on January 31, 1979 and de-orbited on April 1, 1979.
 W
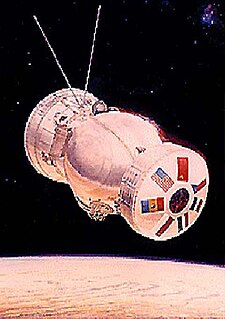
WBion 5, or also Kosmos 1129 was a Bion satellite. It was a biomedical research mission involving scientists from nine countries, launched on 29 September 1979, at 15:30:00 UTC. Among the experiments was the first attempt to breed mammals in space, which proved unsuccessful. The mission ended after 18.5 days, on 14 October 1979, at 02:24 UTC. The mission had the cooperation of the Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, France, Hungary, Poland, Romania, the United States and the Soviet Union.
 W
WThe Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed is a 1979 Soviet five-part television miniseries directed by Stanislav Govorukhin. The series achieved the status of a cult film in the USSR, and along with Seventeen Moments of Spring became a part of popular culture with several generations of Russian-speaking TV viewers. The series stars singer-songwriter Vladimir Vysotsky in one of his final screen appearances. Soviet screen and stage legends Sergey Yursky, Armen Dzhigarkhanyan, Zinovy Gerdt, Yevgeniy Yevstigneyev, and Leonid Kuravlev also appear in the film.
 W
WProgress 5, was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1979 to resupply the Salyut 6 space station. Served as a receptacle for contaminated fuel from the damaged Salyut 6 propulsion system.
 W
WProgress 6 was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft. It which was launched in May 1979 to resupply the Salyut 6 space station.
 W
WProgress 7 was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in June 1979 to resupply the Salyut 6 space station.
 W
WSiberiade is a 1979 epic Soviet film in four parts, spanning much of the 20th century. It was directed by Andrei Konchalovsky, working for the Mosfilm studio.
 W
WThe Soviet–Afghan War was a conflict wherein insurgent groups known collectively as the Mujahideen, as well as smaller Maoist groups, fought a nine-year guerrilla war against the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan and the Soviet Army throughout the 1980s, mostly in the Afghan countryside. The Mujahideen were variously backed primarily by the United States, Pakistan, Iran, Saudi Arabia, China, and the United Kingdom; the conflict was a Cold War-era proxy war. Between 562,000 and 2,000,000 Afghans were killed and millions more fled the country as refugees, mostly to Pakistan and Iran. Between 6.5%–11.5% of Afghanistan's population is estimated to have perished in the conflict. The war caused grave destruction in Afghanistan, and it has also been cited by scholars as a contributing factor to the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, in hindsight leaving a mixed legacy to people in both territories.
 W
WSoyuz 33 was an April, 1979, Soviet crewed space flight to the Salyut 6 space station. It was the ninth mission to the orbiting facility, but an engine failure forced the mission to be aborted, and the crew had to return to Earth before docking with the station. It was the first failure of a Soyuz engine during orbital operations.
 W
WOperation Storm-333, also known as the Tajbeg Palace Assault, was a covert operation that took place on 27 December 1979, in which Soviet special forces stormed the heavily fortified Tajbeg Palace in Afghanistan and assassinated People's Democratic Party General Secretary Hafizullah Amin. It marked the beginning of what would become the 10-year Soviet-Afghan War.
 W
WThe Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of talks and agreements: SALT I and SALT II.