 W
WA power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The primary function of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.
 W
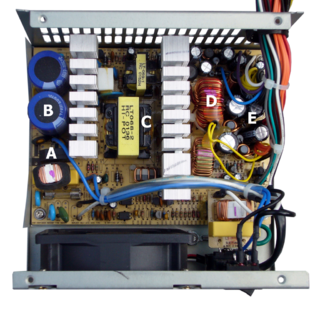
WA power supply unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power supplies. Some power supplies have a manual switch for selecting input voltage, while others automatically adapt to the mains voltage.
 W
W80 Plus is a voluntary certification program launched in 2004, intended to promote efficient energy use in computer power supply units (PSUs).
 W
WAn AC adapter, AC/DC adapter, or AC/DC converter is a type of external power supply, often enclosed in a case similar to an AC plug. Other common names include plug pack, plug-in adapter, adapter block, domestic mains adapter, line power adapter, wall wart, power brick, wall charger, and power adapter. Adapters for battery-powered equipment may be described as chargers or rechargers. AC adapters are used with electrical devices that require power but do not contain internal components to derive the required voltage and power from mains power. The internal circuitry of an external power supply is very similar to the design that would be used for a built-in or internal supply.
 W
WA battery eliminator is a device powered by an electrical source other than a battery, which then converts the source to a suitable DC voltage that may be used by a second device designed to be powered by batteries. A battery eliminator eliminates the need to replace batteries but may remove the advantage of portability. A battery eliminator is also effective in replacing obsolete battery designs.
 W
WA capacitive power supply, also called a capacitive dropper, is a type of power supply that uses the capacitive reactance of a capacitor to reduce the mains voltage to a lower voltage. There are several important limitations: First, the high withstanding voltage required of the capacitor, along with the high-capacitance required for a given output current, mean that this type of supply is only practical for low-power applications. The second is that due to the absence of electrical isolation between input and output, anything connected to the power supply must be reliably insulated so that it is not possible for a person to come into electrical contact with it.
 W
WIn the theory of electrical networks, a dependent source is a voltage source or a current source whose value depends on a voltage or current elsewhere in the network.
 W
WA joule thief is a minimalist self-oscillating voltage booster that is small, low-cost, and easy to build, typically used for driving small loads. This circuit is also known by other names such as blocking oscillator, joule ringer, vampire torch. It can use nearly all of the energy in a single-cell electric battery, even far below the voltage where other circuits consider the battery fully discharged ; hence the name, which suggests the notion that the circuit is stealing energy or "joules" from the source – the term is a pun on "jewel thief". The circuit is a variant of the blocking oscillator that forms an unregulated voltage boost converter. The output voltage is increased at the expense of higher current draw on the input, but the integrated (average) current of the output is lowered and brightness of a luminescence decreased.
 W
WPower over Ethernet, or PoE, describes any of several standards or ad hoc systems that pass electric power along with data on twisted-pair Ethernet cabling. This allows a single cable to provide both data connection and electric power to devices such as wireless access points (WAPs), Internet Protocol (IP) cameras, and voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) phones.
 W
WPoweredUSB, also known as Retail USB, USB PlusPower, and USB +Power, is an addition to the Universal Serial Bus standard that allows for higher-power devices to obtain power through their USB host instead of requiring an independent power supply or external AC adapter. It is mostly used in point-of-sale equipment, such as receipt printers and barcode readers.
 W
WA switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently.
 W
WA Tesla coil is an electrical resonant transformer circuit designed by inventor Nikola Tesla in 1891. It is used to produce high-voltage, low-current, high frequency alternating-current electricity. Tesla experimented with a number of different configurations consisting of two, or sometimes three, coupled resonant electric circuits.