 W
WThe Adorant from the Geißenklösterle cave is a 35,000-to-40,000-year-old section of mammoth ivory with a depiction of a human figure, found in the Geißenklösterle cave in the Swabian Jura near Blaubeuren, Germany.
 W
WChengtoushan was a Neolithic settlement located on the northwestern edge of Dongting Lake in Li County, Hunan, China.
 W
WElginhaugh Roman Fort was a Roman fort of the 1st century AD, located in Midlothian, Scotland.
 W
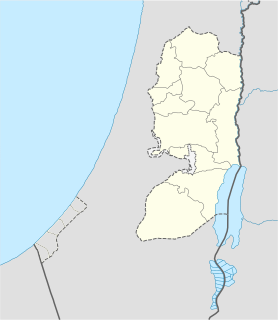
WGilgal I is an archaeological site in the Jordan Valley, West Bank, dated to the early Neolithic period. The site is located 8 mi (13 km) north of ancient Jericho. The features and artifacts unearthed at Gilgal I shed important light on agriculture in the Levant. The by far oldest domesticated figs found anywhere in the world were recovered from an incinerated house at the site, and have been described as coming from cultivated, as opposed to wild, fig trees.
 W
WThe ivory pomegranate is a thumb-sized semitic ornamental artifact acquired by the Israel Museum. It is not actually made of ivory, but of hippopotamus bone and bears an inscription; Holy (Sacred) to the Priest of the House of God (YHWH).
 W
WPiddington Roman Villa is the remains of a large Roman villa at Piddington, Northamptonshire, about 6 miles (9.7 km) south-east of Northampton, a county in the East Midlands of England.
 W
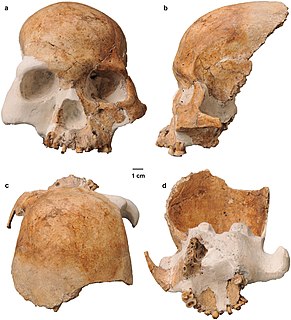
WThe Red Deer Cave people are a prehistoric archaic human population. Fossils dated to between about 17,830 to c. 11,500 years ago, were found in Red Deer Cave and Longlin Cave, Yunnan Province, in Southwest China.
 W
WThe Reh Inscription was discovered in 1979 near the Reh archaeological site along Yamuna River about 350 kilometres (220 mi) east of Mathura in India. It is a Prakrit inscription in Brahmi script near the bottom of a Shiva linga. The inscription is dated to between the 2nd century BCE and 2nd century CE based on the script style.
 W
WThe Thetford Hoard is a hoard of Romano-British metalwork found by Arthur and Greta Brooks at Gallows Hill, near Thetford in Norfolk, England, in November 1979, and now in the British Museum. Dating from the mid- to late-4th century AD, this hoard is a collection of thirty-three silver spoons and three silver strainers, twenty-two gold finger rings, four gold bracelets, four necklace pendants, five gold chain necklaces and two pairs of necklace-clasps, a gold amulet designed as a pendant, an unmounted engraved gem, four beads, and a gold belt-buckle decorated with a dancing satyr. A small cylindrical lidded box made from shale also belonged to the hoard.
 W
WXinzhai is an early Bronze Age archaeological site that was found 1979 in Henan, China. It is located about 20 kilometres (12 mi) southeast of Xinmi, Zhengzhou.