 W
WAntifeedants are organic compounds produced by plants to inhibit attack by insects and grazing animals. These chemical compounds are typically classified as secondary metabolites in that they are not essential for the metabolism of the plant, but instead confer longevity. Antifeedants exhibit a wide range of activities and chemical structures as biopesticides. Examples include rosin, which inhibits attack on trees, and many alkaloids, which are highly toxic to specific insect species.
 W
WAcylsugars are a group of plant-derived protective secondary metabolites that lack nitrogen. They typically consist of aliphatic acyl groups of low to medium chain lengths esterified to the hydroxyl groups of glucose or sucrose. Presence of such acyl groups gives these compounds hydrophobic properties. This group of compounds has been extensively studied in tomato and related species, in which these compounds are produced and secreted in sporadic amounts from trichomes on the plant leaf and stem surface. Production of copious quantities of these acylsugars give a sticky feel to the plant tissue. In particular, this flower has shown to distract herbivorous insect pests against thrips damage. It is believed that acylsugars provide physical and/or chemical defense to the plant.
 W
WAtropine is a medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings.
 W
WCocaine, also known as coke, is a strong stimulant most frequently used as a recreational drug. It is commonly snorted, inhaled as smoke, or dissolved and injected into a vein. Mental effects may include an intense feeling of happiness, sexual arousal, loss of contact with reality, or agitation. Physical symptoms may include a fast heart rate, sweating, and large pupils. High doses can result in very high blood pressure or body temperature. Effects begin within seconds to minutes of use and last between five and ninety minutes. Cocaine has a small number of accepted medical uses, such as numbing and decreasing bleeding during nasal surgery.
 W
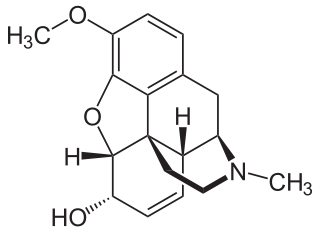
WCodeine is an opiate used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours.
 W
WMorphine is a pain medication of the opiate family that is found naturally in a number of plants and animals, including humans. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to decrease the feeling of pain. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction and during labor. Morphine can be administered by mouth, by injection into a muscle, by injection under the skin, intravenously, injection into the space around the spinal cord, or rectally. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine also exist.
 W
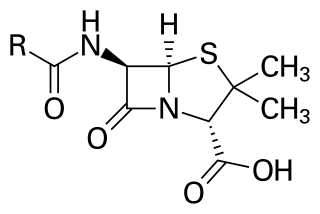
WPenicillin is a group of antibiotics, derived originally from common moulds known as Penicillium moulds; which includes penicillin G, penicillin V, procaine penicillin, and benzathine penicillin. Penicillin antibiotics were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.
 W
WScytonemin is a secondary metabolite and an extracellular matrix (sheath) pigment synthesized by many strains of cyanobacteria, including Nostoc, Scytonema, Calothrix, Lyngbya, Rivularia, Chlorogloeopsis, Hyella etc. Scytonemin-synthesizing cyanobacteria often inhabit highly insolated terrestrial, freshwater and coastal environments such as deserts, semideserts, rocks, cliffs, marine intertidal flats, hot springs, etc.
 W
WTetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovered in these fish and found in several other animals, it is actually produced by certain infecting or symbiotic bacteria like Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, and Vibrio as well as other species found in animals.