 W
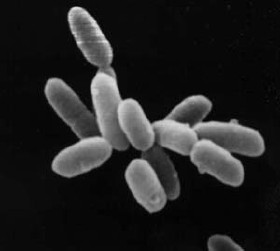
WArchaea constitute a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this classification is obsolete.
 W
WArchaeal Richmond Mine acidophilic nanoorganisms (ARMAN) were first discovered in an extremely acidic mine located in northern California by Brett Baker in Jill Banfield's laboratory at the University of California Berkeley. These novel groups of archaea named ARMAN-1, ARMAN-2, and ARMAN-3 were missed by previous PCR-based surveys of the mine community because the ARMANs have several mismatches with commonly used PCR primers for 16S rRNA genes. Baker et al. detected them in a later study using shotgun sequencing of the community. The three groups were originally thought to represent three unique lineages deeply branched within the Euryarchaeota, a subgroup of the Archaea. However, based on a more complete archaeal genomic tree, they were assigned to a new superphylum named DPANN. The ARMAN groups now comprise deeply divergent phyla named Micrarchaeota and Parvarchaeota. Their 16S rRNA genes differ by as much as 17% between the three groups. Prior to their discovery, all of the Archaea shown to be associated with Iron Mountain belonged to the order Thermoplasmatales.
 W
WArchaeal transcription is the process in which a segment of archeaeal DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of RNA using the sole Pol II-like RNA polymerase (RNAP). The process occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination; and the end result is a strand of RNA that is complementary to a single strand of DNA. A number of transcription factors govern this process with homologs in both bacteria and eukaryotes, with the core machinery more similar to eukaryotic transcription.
 W
WAsgard or Asgardarchaeota is a proposed superphylum consisting of a group of archaea that includes Lokiarchaeota, Thorarchaeota, Odinarchaeota, and Heimdallarchaeota. A representative of the group was cultivated. The Asgard superphylum represents the closest prokaryotic relatives of eukaryotes, which possibly emerged from an ancestral lineage of Asgardarchaeota after assimilating bacteria through the process of symbiogenesis.
 W
WDPANN is a superphylum of Archaea first proposed in 2013. Many members show novel signs of horizontal gene transfer from other domains of life. They are known as nanoarchaea or ultra-small archaea due to their smaller size (nanometric) compared to other archaea.
 W
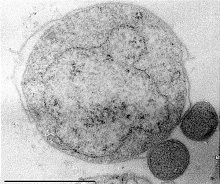
WNanoarchaeum equitans is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains of this microbe were also found on the Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, and in the Obsidian Pool in Yellowstone National Park. Since it grows in temperatures approaching boiling, at about 80 degrees Celsius, it is considered to be a thermophile. It grows best in environments with a pH of 6, and a salinity concentration of 2%. Nanoarchaeum appears to be an obligate symbiont on the archaeon Ignicoccus; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive. Nanoarchaeum equitans cannot synthesize lipids but obtains them from its host. Its cells are only 400 nm in diameter, making it one of the smallest known cellular organisms, and the smallest known archaeon.
 W
WProteoarchaeota are a proposed archaeal kingdom thought to be closely related to the Eukaryotes.
 W
WTACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota, Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic thermophiles to mesophiles and psychrophiles and with different types of metabolism, predominantly anaerobic and chemosynthetic. TACK is a clade that is close to the branch that gave rise to the eukaryotes. The name Filarchaeota has been proposed.